Battery Swapping Market Research, 2032
The global battery swapping market size was valued at $120.3 million in 2022, and battery swapping industry is projected to reach $642.7 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18.3% from 2023 to 2032. The battery swapping market has grown rapidly, driven by the increase in demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and the lack of adequate public charging infrastructure. Battery swapping offers a quick and convenient solution to reduce EV charging time, allowing drivers to exchange depleted batteries for fully charged ones without waiting for traditional charging. This is particularly valuable in regions where increasing the number of public charging stations is costly and time-consuming.

Introduction
Electric vehicle battery swapping is a location where a discharged battery or battery pack in an electric vehicle may be immediately swapped for a fully charged one, eliminating the time spent waiting for a battery of the vehicle to charge. Battery swapping stations provide a faster solution to address range anxiety because each battery swap takes less than 10 minutes and requires much less space to install when compared to charging stations. Furthermore, battery-as-a-service (BaaS) is another solution gaining traction in the battery swapping industry due to its impact on the reduction of the high upfront cost of electric vehicles by separating battery ownership. Furthermore, battery swapping reduces vehicle downtime and acquisition costs because the customer just pays for the energy.
Report Key Highlighters:
- The report provides competitive dynamics by evaluating business segments, product portfolios, target market revenue, geographical presence, and key strategic developments by prominent manufacturers.
- The battery swapping market is fragmented in nature among prominent companies such as Gogoro, Aulton New Energy Automotive Technology Co., Ltd., Numocity, Esmito Solutions Pvt Ltd., NIO Power, BattSwap Future, Kwang Yang Motor Co., Ltd., Ample, Inc., Sun Mobility Private Limited, and Shenzhen Immotor Technology Co., Ltd.
- The study contains qualitative information such as the market dynamics (drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities), key regulation analysis, pricing analysis, and Porter’s Five Force Analysis across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, LAMEA regions.
- Latest trends in global battery swapping market such as undergoing R&D activities, public policies, and government initiatives are analyzed across 16 countries in 4 different regions.
- More than 2,500 battery swapping-related product literatures, industry releases, annual reports, and other such documents of key industry participants along with authentic industry journals and government websites have been reviewed for generating high-value industry insights for global battery swapping market.
Market Dynamics
The rise in demand for electric vehicles coupled with a lack of adequate public charging facilities creates a favorable environment for the growth of the battery swapping market. The need for accessible charging infrastructure becomes increasingly apparent as more consumers embrace electric vehicles as a sustainable and cost-effective mode of transportation. However, the installation and expansion of public charging stations may be a time-consuming and costly process.In this scenario, battery swapping offers a compelling solution by circumventing the need for extensive charging infrastructure. Instead of relying on traditional charging stations, electric vehicle owners may simply visit battery swapping stations to exchange their depleted batteries for fully charged ones.
This eliminates the need to wait for lengthy charging sessions and provides a quick and convenient alternative. Furthermore, the reduced time for electric vehicle charging provided by battery swapping technology is expected to drive market growth. However, the growth of the battery swapping market faces certain obstacles. One of the challenges is the differentiation in battery technology and design. Electric vehicles utilize various types of batteries, including lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and solid-state batteries, each with different specifications and requirements. This diversity poses challenges for standardization and compatibility in battery swapping stations. As a result, the market growth is anticipated to be hindered by the need for adaptable infrastructure that may accommodate a wide range of battery technologies.
Another factor that hampers the market growth is the high initial set-up and operating costs associated with battery swapping stations. Establishing a robust network of swapping stations requires significant investments in infrastructure, including the construction of stations, battery inventory, and maintenance systems. In addition, the operational costs, such as battery inspection, charging, and storage, may be substantial. These cost factors present a barrier to market entry and expansion, particularly for smaller players in the industry.
Furthermore, the rapid emergence of shared e-mobility and the introduction of innovative & advanced battery swapping models and services by market players are some of the factors that are expected to offer lucrative battery swapping market opportunities during the forecast period.
Increase in demand for electric vehicles, coupled with lack of adequate public charging facilities
The increase in popularity of electric vehicles may be attributed to their superior efficiency and environmentally friendly characteristics. Moreover, consumer demand for enhanced vehicle efficiency and reduced fuel costs has driven continuous technological advancements in the electric vehicle industry.
In addition, the rise in costs of gasoline and strict government regulations on carbon dioxide emissions have further accelerated the adoption of electric vehicles, particularly in developed regions such as North America and Europe. However, electric vehicles have a limited driving range per charge and require charging twice a day based on usage, which typically takes 6 to 10 hours to fully charge the battery. In contrast, battery swapping eliminates the need for extended downtime by providing a nearly instantaneous battery replacement, in contrast to the 6-10 hours required for traditional charging methods. Moreover, the inadequate availability of public charging infrastructure and the absence of standardized charging facilities have contributed to the demand for battery swapping stations. Consequently, these factors collectively stimulate the growth of the battery swapping market.
Reduced time for electric vehicle charging
Charging time is a critical factor for the optimal functioning of electric vehicles, particularly in long-haul applications. Currently, most electric vehicles utilize a slow charging system to replenish their batteries, which typically takes up to eight hours for a full charge. Moreover, electric two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and four-wheelers generally have onboard chargers that provide a charging rate of 2.5-3 kW per hour. Consequently, it takes at least an hour to charge a two-wheeler with a battery energy density of up to 3 kWh, and five to six hours to charge a four-wheeler or larger vehicle with batteries of 12 kWh or more.
Battery-swapping technology assumes a crucial role in addressing these challenges. It significantly reduces the waiting time for charging by enabling the quick exchange of batteries within three minutes. Electric vehicle owners may simply visit a swapping station and have their depleted battery replaced with a fully charged one. This implementation of battery swapping effectively reduces the charging time for electric vehicles, which in turn stimulates the battery swapping market growth.
Segmentation Analysis
The battery swapping market forecast is segmented on the basis of station type, service type, capacity type, vehicle type, and region. On the basis of station type, it is bifurcated into manual, and automatic. On the basis of service type, it is bifurcated into a subscription model and pay-per-use model. On the basis of capacity type, it is bifurcated into less than 30 kWh, and more than 30 kWh. On the basis of vehicle type, it is categorized into two-wheeler, three-wheeler, and four-wheeler. On the basis of region, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
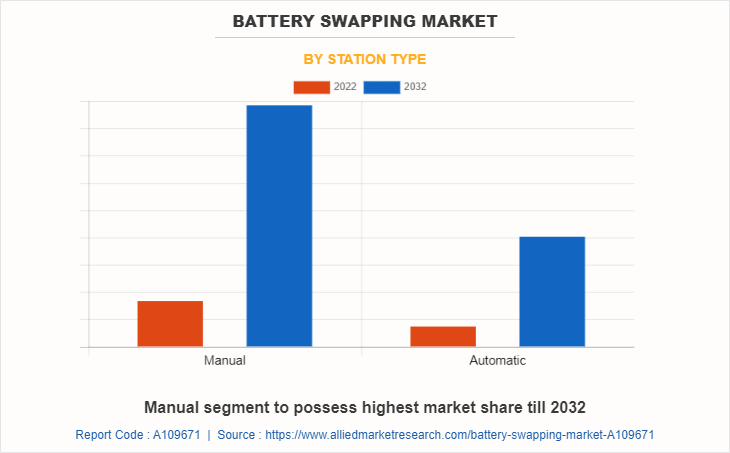
By Station Type
On the basis of station type, the manual segment emerged as the global leader by acquiring more than two-thirds battery market share in 2022 and is anticipated to continue this trend during the forecast period. The increase in adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) drives the demand for convenient charging solutions. However, the market has shifted toward fast-changing technologies, and automation is emerging as a trend, expected to restrain the development of the manual battery swapping market. The growth of manual battery swapping stations depends on infrastructure expansion and offers opportunities in commercial fleets and niche markets.
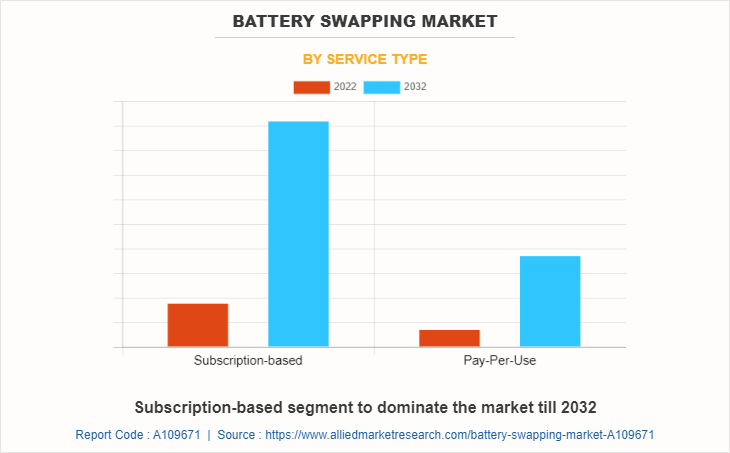
By Service Type
On the basis of service type, the subscription-based segment emerged as the global leader by acquiring more than two-thirds of battery swapping market share in 2022 and is anticipated to continue this trend during the forecast period. The battery-swapping subscription model is primarily driven, owing to its benefits offered over the pay-per-use model, such as battery leasing, low cost per swapping, and affordability. In addition, the market has witnessed a surge in the adoption of subscription models as subscribers do not have to worry about maintenance, roadside assistance, and service expense of the battery.
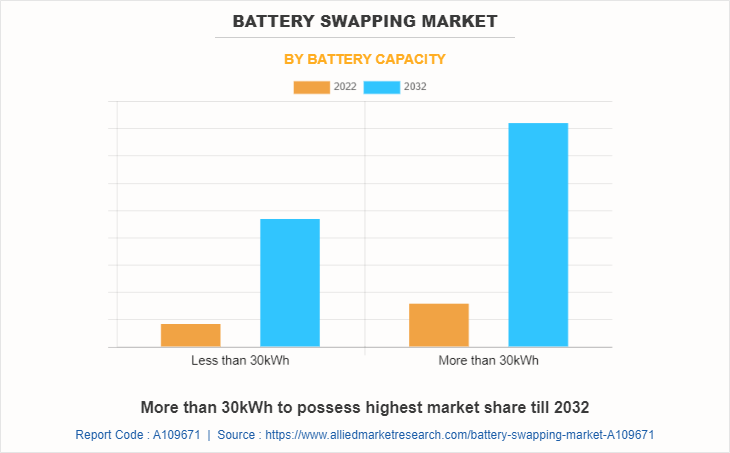
By Capacity
On the basis of battery capacity, the more than 30 kWh segment emerged as the largest market share in 2022, which accounts for nearly two-thirds of the battery swapping market share. The increase in demand for electric vehicles (EVs), and the growth in need for vehicles with longer driving ranges, which may be fulfilled by higher-capacity batteries, had a positive impact on the market. The expansion of high-performance EVs and the adoption of electric propulsion in commercial and heavy-duty applications further drives the demand for larger battery capacity.
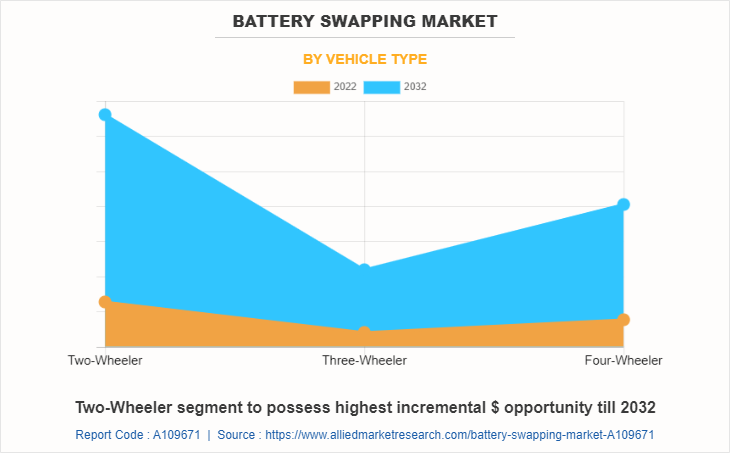
By Vehicle Type
On the basis of vehicle type, the two-wheeler segment emerged as the largest market share in 2022 accounting for more than half of the battery swapping market share, and is anticipated to continue this trend during the forecast period. Two wheelers battery swapping technique has gained immense traction in the global electric vehicle charging infrastructure due to the under-developing EV charging infrastructure across the globe. Governments across the globe and private companies are investing in developing battery swapping infrastructure, which leads to the growth of the market.
By Region
On the basis of region, Asia-Pacific is the major consumer of batteries among other regions. It accounted for more than half of the global battery swapping market share in 2022. Governments of many Asian countries have plans to end production and sales of gasoline and diesel vehicles in the coming years. This move is expected to increase the market for electric vehicles in the region, benefiting the growth of the battery swapping market during the forecast period.
Competitive Landscape
Key players operating in the global battery swapping market are Gogoro, Aulton New Energy Automotive Technology Co., Ltd., Numocity, Esmito Solutions Pvt Ltd., NIO Power, BattSwap Future, Kwang Yang Motor Co., Ltd., Ample, Inc., Sun Mobility Private Limited, and Shenzhen Immotor Technology Co., Ltd.
“Pilot Projects”
Better Place (Israel): Better Place, a prominent player in the battery swapping market, conducted pilot projects in Israel. They established a network of battery swapping stations and provided compatible electric vehicles for testing. The project aimed to demonstrate the viability of battery swapping and its potential to address the range anxiety associated with EVs. However, despite early success, Better Place faced financial difficulties and eventually discontinued its operations.
NIO (China): NIO, a Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer, launched pilot projects for battery swapping in various cities in China. They established battery swapping stations, known as NIO Power Swap, which allowed users to exchange depleted batteries for fully charged ones within a few minutes. These pilot projects aimed to evaluate the efficiency, reliability, and user experience of the NIO Power Swap system.Gogoro (Taiwan): Gogoro, a Taiwanese electric scooter manufacturer, implemented an extensive battery-swapping network in Taiwan.
The project involved setting up Gogoro Energy Network, a network of battery swapping stations, to cater to the growth in number of electric scooters on the island. Gogoro's battery-swapping system gained popularity due to its convenience and ease of use.
Renault (France): Renault, a leading automotive manufacturer, conducted a pilot project in France known as "EVSOS." The project aimed to study the potential of battery swapping as a viable solution for electric vehicle charging. Renault collaborated with several partners, including energy companies and municipalities, to establish battery-swapping stations and assess the technical and economic feasibility of the concept.
SWAP Stations (U.S.): SWAP Stations, a startup based in California, initiated a pilot project to test battery swapping for electric bicycles. They set up swapping stations in partnership with bike-sharing programs to provide a quick and convenient charging option for electric bicycles. The pilot project aimed to evaluate the demand, usability, and scalability of battery swapping for e-bikes.
Historical Trends of Battery Swapping
Early Attempts (2000s): The concept of battery swapping dates to the early 2000s. Better Place, an Israeli company founded in 2007, was one of the first major companies to attempt implementing battery swapping as a business model. The company aimed to set up a network of battery swapping stations for electric vehicles (EVs), where drivers could exchange depleted batteries for fully charged ones. However, despite initial enthusiasm, Better Place went bankrupt in 2013 due to high infrastructure costs, limited EV adoption, and challenges in standardizing battery designs across different automakers.
Initial Struggles (2010-2015): After the failure of Better Place, battery swapping technology faced skepticism, and many manufacturers chose to focus on expanding traditional charging infrastructure. High costs of setting up swapping stations, lack of standardized battery designs, and the increase in availability of fast chargers further slowed the growth of battery swapping. During this time, Tesla experimented with battery swapping, however, eventually abandoned the project in favor of Supercharger networks.
Revival in China (2017-present): Battery swapping saw a resurgence in China, led by companies such as NIO and Gogoro. In 2017, NIO launched its battery swapping stations, primarily for its electric SUVs. China's push for electrification, government support, and the rising popularity of EVs helped battery swapping gain momentum in the country. By 2020, NIO had completed over one million battery swaps at its stations.
Gogoro, a Taiwan-based company, also successfully implemented battery swapping for electric scooters, expanding rapidly in urban areas. This model was highly effective in regions where two-wheelers dominate the transportation landscape, further boosting battery swapping as a viable solution for fast charging.
Battery Swapping for Two-Wheelers and Commercial Vehicles: In addition to China, battery swapping started gaining traction in India, particularly for electric two-wheelers and commercial vehicles such as rickshaws and delivery fleets. In 2020, Sun Mobility in India introduced battery swapping networks designed to support the growing demand for electric rickshaws, buses, and commercial fleets.
Recent Growth and Innovation (2020-Present): Battery swapping is now increasingly recognized as a solution to address the limitations of traditional charging infrastructure. It offers rapid energy replenishment, which is essential for fleet operators and shared mobility services. The advent of the Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) model, pioneered by companies such as NIO, further lowered the cost of EV ownership, making it more attractive for consumers. This period also saw increased efforts toward standardizing batteries, making it easier for different manufacturers to adopt battery swapping.
Global Expansion and Government Support: Governments, especially in China and India, have introduced policies promoting battery swapping to accelerate EV adoption. These policies, combined with technological advancements and partnerships, have led to a global push toward expanding battery swapping infrastructure, especially for two-wheelers and commercial fleets.
Government Incentives for Promoting Battery Swapping
China: China is the largest market for battery swapping, and the government plays a pivotal role in promoting this technology. The Chinese government offers subsidies and incentives to EV manufacturers and infrastructure developers that include battery-swapping technologies. These policies are part of a broader effort to reduce carbon emissions and enhance urban mobility through electric vehicles.
For instance, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has included battery swapping as a core part of its New Energy Vehicle (NEV) promotion, offering incentives to EV manufacturers that produce cars with swappable batteries.
India: India’s FAME II (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme encourages the adoption of electric vehicles and emphasizes battery swapping, particularly for two- and three-wheelers. The Indian government supports pilot projects and infrastructure development for battery swapping, reducing import duties on EV components to make battery-swapping tech more affordable.
Europe: European countries are gradually adopting battery-swapping technology, particularly in commercial vehicle sectors. Governments provide grants and tax exemptions to support EV infrastructure, including battery swapping stations. Some cities in Europe offer free or reduced-cost parking and other benefits for EVs to encourage their use, indirectly supporting battery-swapping growth.
U.S.: The U.S. government supports battery swapping primarily through tax incentives and grants for electric mobility under the Department of Energy (DoE). Several initiatives aimed at increasing EV adoption also provide federal tax credits and infrastructure grants for innovations such as battery swapping.
Impact of Russia-Ukraine War on Global Battery Swapping Market
- First, disruptions in the supply chain could lead to shortages or increased prices of batteries for swapping services. This is expected to affect the availability and cost of batteries in regions across the globe.
- Secondly, if the conflict persists, companies are expected to consider shifting their battery production facilities away from the affected regions, potentially impacting the global supply of batteries.
- Thirdly, market uncertainty caused by geopolitical tensions could influence investor sentiment, potentially affecting funding and expansion plans of battery swapping companies worldwide.
North America is expected to prioritize supporting local battery production. This could lead to the implementation of trade policies and incentives aimed at boosting domestic manufacturing and reducing dependence on foreign suppliers. Battery-swapping companies in North America are expected to benefit from increased government support and investment in the local industry, potentially driving growth and innovation in the market.
Europe is anticipated to focus on bolstering domestic battery production capabilities. The European Union has been actively promoting the development of a sustainable battery industry through initiatives such as the European Battery Alliance. The conflict could further emphasize the need for self-sufficiency in battery supply chains, leading to increased investments in European battery manufacturing.
Asia-Pacific is a major hub for battery production and electric vehicle manufacturing. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea have been actively investing in battery technologies and infrastructure while the conflict causes disruptions in the supply chain. These countries are anticipated to work towards securing alternative supply routes or diversifying their sources of raw materials. Battery swapping companies in the Asia-Pacific are expected to experience some short-term disruptions but could benefit from the overall focus on advancing battery technology in Asia-Pacific.
The LAMEA region is expected to face increased import challenges due to disruptions in supply chains caused by the conflict. Reliance on battery imports could result in delays and increased costs for battery swapping services in the region.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the battery swapping market analysis from 2022 to 2032 to identify the prevailing battery swapping market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the battery swapping market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global battery swapping market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Battery Swapping Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 642.7 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 18.3% |
| Forecast period | 2022 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 259 |
| By Station Type |
|
| By Service Type |
|
| By Battery Capacity |
|
| By Vehicle Type |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Gogoro, NIO, Shenzhen Immotor Technology Limited, Aulton New Energy Automotive Technology Co., Ltd., Numocity, Sun Mobility Private Limited, Esmito Solutions Pvt Ltd, BattSwap Future, KWANG YANG MOTOR CO., LTD., Ample, Inc. |
Analyst Review
According to the insights of CXOs of leading companies, the battery swapping market is projected to witness a moderate growth rate, owing to an increase in demand for electric vehicles coupled with a lack of adequate public charging facilities. Companies in this industry have adopted various innovative techniques to provide customers with advanced and innovative feature offerings.
For instance, according to Ola Electric Co-Founder Ankit Jain, the battery swapping market has a significant potential to grow in the future as a mode for charging small vehicles, creating favorable economics for consumers and for the power sector. In addition, according to P R Kumar, CEO of BSES Yamuna Power Limited (BYPL), setting up battery swapping stations eliminates the wait time for charging, thus removing a major impediment preventing the adoption of electric vehicles. In addition, he said, such measures provide a much-needed trigger to increase the adoption of electric vehicles and help in reducing pollution.
Moreover, the battery swapping market is driven by reduced time for electric vehicle charging, resulting in a rise in demand for electric vehicle battery swapping. In addition, the introduction of innovative & advanced battery swapping models and services by market players also fosters the growth of the market. However, differentiation in battery technology & design and high initial set-up & operating cost of battery swapping stations hinder the market growth.
Among the analyzed regions, Asia-Pacific accounted for the highest revenue in the global market in 2022. However, LAMEA is expected to grow at a higher rate, predicting lucrative opportunities for the key players operating in the battery swapping market.
Increase in demand for electric vehicles coupled with a lack of adequate public charging facilities and reduced time for electric vehicle charging are the key factors boosting the Battery swapping market growth.
Automotive application is projected to increase the demand for Battery swapping Market
Rapid emergence of shared e-mobility is the Main Driver of Battery swapping Market.
The market value of Battery swapping in 2032 is expected to be $642.7 million
The battery swapping market forecast is segmented on the basis of station type, service type, capacity type, vehicle type, and region. On the basis of station type, it is bifurcated into manual, and automatic. On the basis of service type, it is bifurcated into a subscription model and pay-per-use model. On the basis of capacity type, it is bifurcated into less than 30 kWh, and more than 30 kWh. On the basis of vehicle type, it is categorized into two-wheeler, three-wheeler, and four-wheeler. On the basis of region, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Gogoro, Aulton New Energy Automotive Technology Co., Ltd., Numocity, Esmito Solutions Pvt Ltd., NIO Power, BattSwap Future, Kwang Yang Motor Co., Ltd., Ample, Inc., Sun Mobility Private Limited, and Shenzhen Immotor Technology Co., Ltd.
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



