Biomass Heating Plant Market Research, 2033
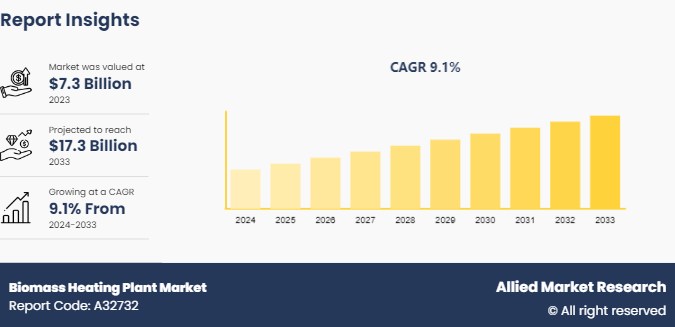
The global biomass heating plant market size was valued at $7.3 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $17.3 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2024 to 2033.
Market Introduction and Definition
A biomass-fired heating plant is a facility that generates heat energy by burning biomass materials. Biomass refers to organic materials derived from living or recently living organisms, such as wood, agricultural residues, and organic waste. These materials are renewable and can be sourced sustainably, making biomass a key component of the renewable energy landscape. Biomass-fired heating plants convert the chemical energy stored in these organic materials into thermal energy through combustion processes, which can then be used for various applications including heating, electricity generation, and industrial processes.
One of the primary applications of biomass-fired heating plants is district heating. District heating systems distribute heat generated in a centralized location to residential, commercial, and industrial buildings through a network of insulated pipes. Biomass-fired plants are increasingly being used in these systems as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based heating. By utilizing locally sourced biomass, these plants can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on imported fuels, while also supporting local economies and creating jobs in the biomass supply chain.
In the industrial sector, biomass-fired heating plants play a crucial role in providing process heat. Industries such as food processing, paper and pulp, and chemical manufacturing require significant amounts of thermal energy for their operations. Biomass can be used to generate steam or hot water that is then used in various stages of production. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint of these industries but also provides a reliable and often cost-effective source of energy.
Key Takeaways
- The biomass heating plant industry covers 20 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value for the projected period.
- The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of the global biomass heating plant market overview and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions to achieve their growth objectives in biomass heating plant market report.
- Over 3, 700 product literature, annual reports, industry statements, and other comparable materials from major industry participants were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the biomass heating plant market overview.
- The biomass heating plant market share is highly fragmented, with several players including Enviva, Drax Global, RWE, ANDRITZ, ENERGEX PELLET FUEL, INC., German Pellets GmbH, Viridis Energy Inc, Fram Fuels, Bioenergy International, and Verdo. Also tracked key strategies such as acquisitions, product launches, mergers, and expansion of the players operating in the biomass heating plant market growth.
Market Segmentation
The biomass heating plant market is segmented into fuel type, application, technology and region. On the basis of fuel type, the market is divided into solid biomass, liquid biomass, and gaseous biomass. On the basis of end-use, the market is classified into residential, commercial, and industrial. By technology, the market is divided into direct combustion, gasification, anaerobic digestion, and others. Region-wise, the market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Key Market Dynamics
Increase in demand for renewable energy sources in biomass heating plants is expected to drive the growth of biomass heating plant market during the forecast period. Biomass heating plants, a crucial component of renewable energy infrastructure, offer numerous environmental benefits that make them a viable alternative to fossil fuel-based energy systems. By utilizing organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and dedicated energy crops, biomass heating plants help mitigate climate change, reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources, and contribute to sustainable energy development. This essay delves into the environmental advantages of biomass heating plants, focusing on their role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing dependence on fossil fuels.
One of the most significant environmental benefits of biomass heating plants is their ability to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide (CO2) that has been sequestered for millions of years, biomass emits CO2 that is part of the current carbon cycle. This means that the CO2 released during biomass combustion is roughly equal to the CO2 absorbed by plants during their growth, making biomass a carbon-neutral energy source under sustainable management practices. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, in 2022, biomass played a significant role in the U.S. energy landscape, comprising nearly 5% of total primary energy consumption. It serves as a versatile energy source, utilized for heating, generating electricity, and even as a transportation fuel. Globally, biomass remains crucial, particularly in developing nations where it fulfills essential needs such as cooking and household heating.
The high initial investment cost for biomass heating plants is expected to hamper the growth of biomass heating plant market during the forecast period. The establishment of biomass heating plants entails substantial initial investments, presenting a significant barrier to entry for potential investors and stakeholders. These high setup costs encompass various expenses related to equipment procurement, site preparation, technological infrastructure, and regulatory compliance. While biomass heating plants offer long-term economic and environmental benefits, the upfront financial outlay required can deter investors and limit the widespread adoption of this renewable energy technology. Central to the high initial investment in biomass heating plants are the costs associated with acquiring and installing specialized equipment and infrastructure. Biomass combustion systems, boilers, turbines, and associated machinery must be selected and installed to ensure efficient energy conversion and compliance with regulatory standards. These components often require customization to accommodate specific biomass feedstocks and operational requirements, adding to their procurement costs.
Moreover, increase in use of biomass plants to convert waste materials is expected to offer lucrative opportunities in the biomass heating plant market forecast. Agricultural residues, such as crop residues and agricultural by-products, represent abundant biomass sources that can be efficiently converted into energy. These residues are typically generated during agricultural operations and are often underutilized or disposed of through burning or landfilling. By integrating biomass plants into agricultural regions, these residues can be collected, processed, and used to generate heat and electricity, reducing the environmental impact of agricultural waste disposal. In October 2023, U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Secretary Tom Vilsack emphasized advances in collaborating with farmers and American businesses to enhance domestic fertilizer production. The USDA also announced $52.6 million in awards through the Fertilizer Production Expansion Program. These funds will support 17 new projects aimed at increasing domestic fertilizer manufacturing, promoting innovative technologies in fertilizer production, and reducing costs for the U.S. farmers. Additionally, efforts were highlighted to facilitate double cropping practices, aimed at improving agricultural productivity across the country.
The municipal solid waste (MSW) presents another significant opportunity for biomass-fired plants. MSW consists of various organic materials, including food waste, paper, and yard trimmings, which can be converted into biomass feedstock. Instead of landfilling MSW, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and leachate contamination, biomass plants can utilize advanced conversion technologies like anaerobic digestion or thermochemical processes to extract energy from these materials. This approach not only diverts waste from landfills but also reduces methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas produced during organic waste decomposition.
Regional Market Outlook
Region-wise, the biomass heating plant market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. In North America, biomass-fired heating plants are prominent in regions with abundant forestry and agricultural residues. Countries such as the U.S. and Canada have seen significant investments in biomass energy, driven by policies supporting renewable energy sources. Biomass plants here often serve both industrial and residential heating needs, contributing to regional energy diversity and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Europe leads globally in biomass energy adoption, with numerous countries actively promoting biomass-fired heating plants as part of their renewable energy strategies. Countries such as Sweden, Finland, and Austria have extensive biomass utilization networks, utilizing wood biomass and agricultural residues extensively. These plants are integral to achieving renewable energy targets set by the European Union, supporting local economies through sustainable forestry practices and biomass supply chains.
In the Asia-Pacific region, biomass-fired heating plants are emerging as viable alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. Countries such as China, Japan, and India are increasingly investing in biomass energy infrastructure to diversify their energy mix and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. Biomass plants in these regions utilize diverse feedstocks, including rice husks, bamboo, and agricultural residues, contributing to rural development and improving energy access in remote areas.
Industry Trends
- In July 2022, the European Union implemented a ban on importing Russian woody biomass used for energy generation, in response to the war in Ukraine. To compensate for the loss of Russian supply, the EU has turned to imports of wood pellets from the U.S. and Eastern Europe. Notably, Enviva has ramped up its shipments to the EU since the onset of the conflict and has secured a 10-year contract with an undisclosed European customer to supply 800, 000 metric tons of pellets annually by 2027.
- In October 2022, Novi Pazar inaugurated a new biomass heating plant to replace its old fuel oil facility. The new plant, reported by Sandžakpress, will heat a total area of 240, 000 square meters, a significant increase from the 100, 000 square meters covered by the previous facility. The heating plant features a biomass boiler with an eight-megawatt capacity, supported by two auxiliary boilers with capacities of 4.5 MW and 7 MW, which will operate on natural gas. The project included the expansion of the heating network by 1, 800 meters and the modernization of 700 meters of existing pipes. The main contractor for the project was the Austrian company Urbas, with Iskop gradnja serving as the subcontractor.
- In October 2023, Göteborg Energi announced plans to construct a new biomass-fired steam boiler, which will be integrated with the Rya heat and power plant in Sweden. The project represents an investment of $230.8 million (SEK 2.53 billion) . The boiler generates 156 megawatts of heat and 39 megawatts of electricity for the local energy system. The facility, expected to be operational during the 2025/2026 heating season, and also features a visually striking presence at the entrance to the Port of Gothenburg.
Key Regulations of Biomass Heating Plant Market
On February 21, 2011, the EPA established Clean Air Act emissions standards for large and small boilers and incinerators that burn solid waste and sewage sludge. These standards cover more than 200, 000 boilers and incinerators that emit harmful air pollution, including mercury, cadmium, and particle pollution
Greenhouse Gas Permitting - The EPA enacted Clean Air Act Permitting for Greenhouse Gas Emissions on January 2, 2011. This process requires permitting for greenhouse gas production but exempts smaller facilities. Woody biomass is commonly used for facility heating in three forms: whole logs or firewood, wood chips, and wood pellets. Systems are available from 6, 000 British thermal units (Btu) /hr to over 100 million Btu/hr
State Regulations - In 2009, the State of Massachusetts issued the Biomass Boiler & Furnace Emissions and Safety Regulations in the Northeast States. Although this document provides a review of existing regulations in that region, it can be a useful reference for other parts of the country
Key Sources Referred
- The International Trade Administration
- Algae Biomass Organization
- U.S. Department of Commerce
- Biomass Power Association
- Department of Energy
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory
- International Energy Agency
- California Biomass Energy Alliance
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the biomass heating plant market analysis from 2024 to 2033 to identify the prevailing biomass heating plant market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the biomass heating plant market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global biomass heating plant market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Biomass Heating Plant Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2033 | USD 17.3 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.1% |
| Forecast period | 2024 - 2033 |
| Report Pages | 300 |
| By Fuel Type |
|
| By End-Use |
|
| By Technology |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Siemens AG, Aalborg Energie Technik a/s, Energy Saving Trust, Valmet, HoSt Energy Systems, Thermax Limited, Hurst Boiler & Welding Co, Inc, Doosan Enerbility, Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc, Treco Ltd |
The global biomass heating plant market was valued at $7.3 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $17.3 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2024 to 2033.
Key market players in the biomassfired heating plant market include Enviva, Drax Global, RWE, ANDRITZ, ENERGEX PELLET FUEL, INC., German Pellets GmbH, Viridis Energy Inc, Fram Fuels, Bioenergy International, and Verdo.
Asia-Pacific is the largest market for biomass heating plant market.
Industrial application is the leading application of biomass heating plant market.
Increase in demand for renewable energy sources in biomass heating plants are the upcoming trends of biomass heating plant market in the globe.
Loading Table Of Content...



