Building-to-Grid Technology Market Overview
The global building-to-grid technology market size was valued at USD 54.9 billion in 2024, and is projected to reach USD 147.8 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% from 2025 to 2034. Growth in distributed energy resources (DERs) is driving the adoption of building-to-grid technology, enabling buildings to generate, store, and supply power back to the grid. Rooftop solar, residential wind, and battery storage are transforming buildings into active energy participants, enhancing grid efficiency and sustainability.
Key Market Trend & Insights
- Smart metering platform dominated the market, with a CAGR of 10.7% during the forecast period.
- Software segment was the most lucrative, growing at a CAGR of 10.8%.
- Commercial end-use segment led the building-to-grid technology market in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific accounted for over one-third of the market share in 2024.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 147.8 billion
- 2024 Market Size: USD 54.9 billion
- Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) (2025-2034): 10.5%

Introduction
Building-to-grid technology represents a transformative approach to how buildings interact with the electrical grid. Traditionally, buildings have been passive consumers of electricity. With the advent of B2G systems, buildings are now evolving into active energy participants able to generate, store, manage, and even return power to the grid. This dynamic and bidirectional interaction plays a pivotal role in enabling smart grids, optimizing energy usage, reducing peak demand, and enhancing overall grid resilience. B2G is a subset of the broader concept of Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings (GEBs), which incorporates demand flexibility and smart energy management to align building energy consumption with grid needs.
Commercial real estate, including office buildings, malls, and data centers, has emerged as a leading adopter of B2G technologies. These facilities often have predictable energy usage patterns and large energy footprints, making them ideal for demand response programs and grid-supportive functions. For example, office buildings can pre-cool spaces before peak grid hours and reduce HVAC operations during those times. Shopping malls can shift escalator and lighting loads, while data centers are often equipped with large backup power supplies and advanced BMS participate in energy arbitrage and frequency regulation markets. With the help of smart energy platforms, facility managers can schedule operations to align with lower tariffs or provide ancillary services to the grid.
Key Takeaways
- The building-to-grid technology market study covers 20 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value for the projected period.
- The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of global building-to-grid technology market share and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions in order to achieve their most ambitious growth objectives.
- Over 3,700 product literature, annual reports, industry statements, and other comparable materials from major industry participants were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the market.
- The key players in the building-to-grid technology market are Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, ABB Ltd., General Electric, Honeywell International Inc., Landis+Gyr Group AG, Enphase Energy, S&C Electric Company, Itron Inc, and Oracle. They have adopted strategies such as acquisition, product launch, merger, and expansion to gain an edge in the market.
Market Dynamics
Advancements in smart building technologies are expected to drive the growth of building-to-grid technology market. Smart building-to-grid systems, particularly in the areas of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and energy management systems (EMS) have significantly enhanced the feasibility and operational efficiency of Building-to-Grid (B2G) integration. These technologies serve as the foundation for intelligent interaction between buildings and the grid, facilitating real-time data exchange, autonomous decision-making, and optimized energy use. IoT plays a critical role by enabling seamless communication between a building’s various components and external grid systems. Through a network of connected sensors, meters, and control devices, buildings can monitor parameters such as occupancy, temperature, and energy consumption in real time. This granular visibility allows building operators and automated systems to respond dynamically to grid signals, shifting or shedding loads as required to maintain grid stability or take advantage of demand-response incentives. In May 2024, ABB Ltd. partnered with Powrmatic to provide electrical distribution solutions in the Canadian market. This partnership combines ABB's advanced electrical products with Powrmatic's extensive distribution network. The collaboration aims to enhance the availability and implementation of high-quality, reliable electrical solutions across Canada, catering to various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial applications, and supporting the growing demand for efficient electrical distribution systems.
However, high initial investment for building-to-grid technology is expected to restrain the growth of the building[1]to-grid technology market. The high initial investment remains a key barrier to adopting building-to-grid (B2G) technology. Implementing a B2G system involves significant costs for smart meters, energy management systems, IoT sensors, battery storage, and control software. For older buildings, retrofitting requires complex upgrades like new wiring, rooftop solar panels, and automation systems, along with customized interoperability solutions, making integration even costlier. To ease financial strain, Smart Metering-as-a-Service (SaaS) models are gaining traction. This model shifts capital expenses to operational costs, allowing utilities to avoid upfront payments of $100–$300 per meter. By outsourcing ownership and maintenance, providers handle updates and cybersecurity, reducing long-term risks and enabling more scalable, future-proof deployment of B2G technologies.
Segments Analysis
The building-to-grid technology market is segmented into platform, component, end-use, and region. On the basis of platform, the market is divided into smart sensing, smart metering, control technology, energy storage, and others. As per component, the building-to-grid technology market is categorized into hardware, software, and service. On the basis of end-use, the building-to-grid technology market is divided into commercial, industrial, and residential. Region-wise, the market is divided into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
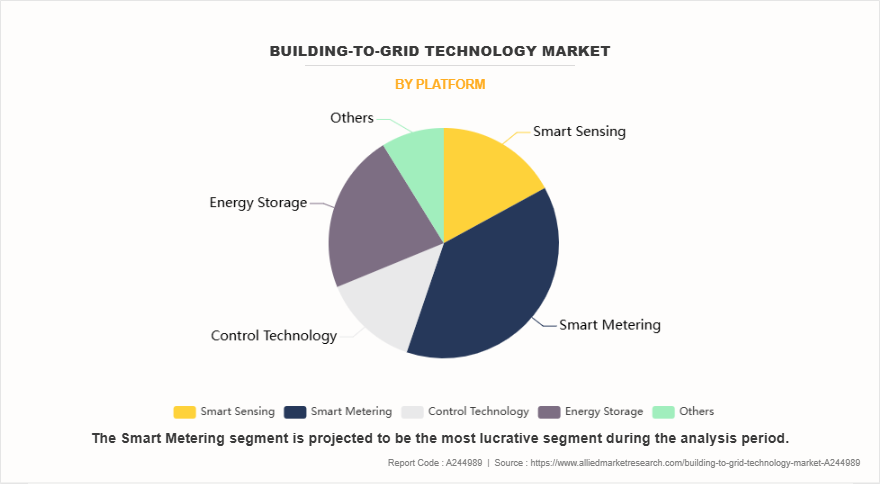
On the basis of platform, the smart metering segment dominated the market, accounting for more than one third of the market share in 2024. Building automation systems represent a transformative advancement in how buildings interact with the power grid, particularly when integrated with smart metering systems. In smart buildings equipped with renewable energy sources like solar panels or energy storage technology combined with smart metering allows these buildings not only to consume energy but also to supply excess energy back to the grid. Smart meters measure the bidirectional flow of electricity, which supports net metering and facilitates energy trading or compensation. In August 2024, the Union Cabinet approved the establishment of 12 industrial smart cities across 10 states, including Agra, Prayagraj, and Jodhpur. With an investment of ₹28,500 crore ($3,434 million), these cities aim to generate around 1 million direct and up to 3 million indirect jobs, emphasizing clean and sustainable industrial development.
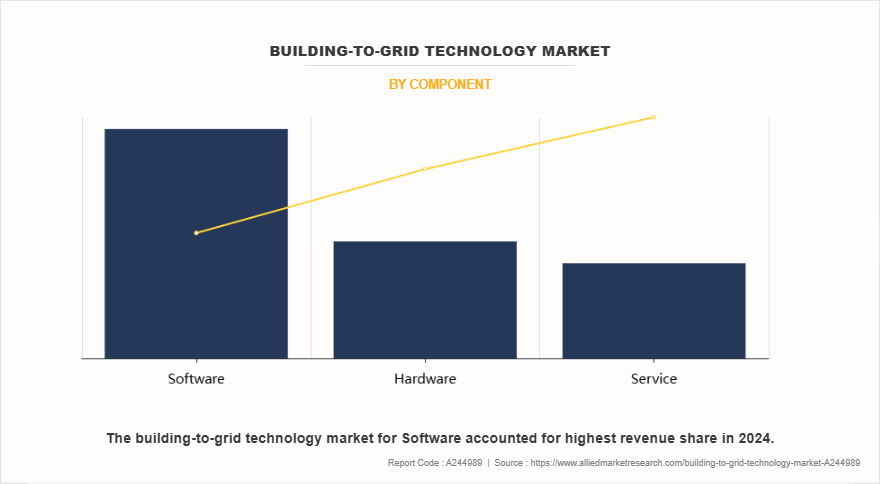
On the basis of the component, the software segment dominated the market in 2024. Software plays a central role in enabling demand response programs and predictive energy optimization through B2G. Cloud-based platforms and energy management systems (EMS) are developed with AI and machine learning algorithms that continuously monitor weather conditions, occupancy rates, and grid signals. This allows the building's systems, HVAC, lighting, smart grid integration, EV charging, and storage units, to adjust their operations proactively. Advanced analytics and visualization dashboards also provide facility managers with actionable insights to reduce energy costs and carbon footprints. In June 2023, Siemens launched the Xcelerator platform, an open digital business platform that integrates IoT-enabled hardware, software, and digital services, aiming to accelerate digital transformation in buildings.
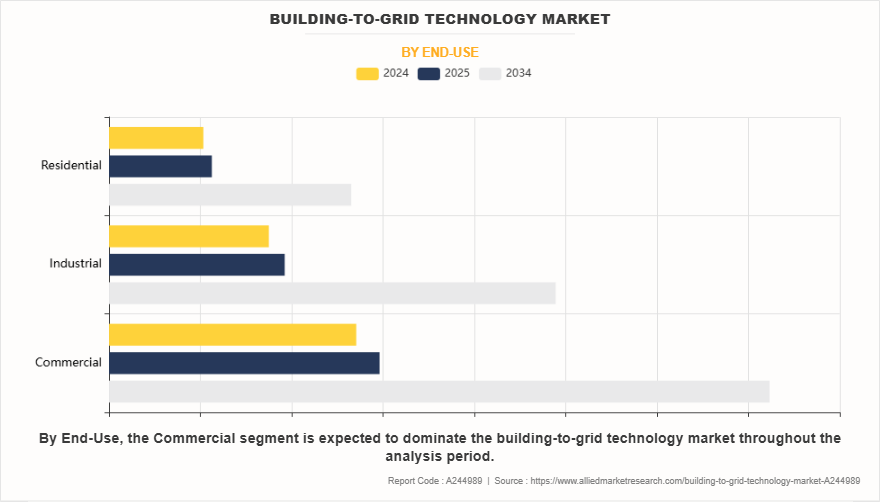
On the basis of end-use, the commercial segment dominated the market in 2024. The implementation of B2G technology in commercial sectors like retail, hospitality, and office complexes offers numerous benefits. By leveraging dynamic pricing models and demand response programs, businesses can significantly lower their energy costs while also contributing to environmental goals. Moreover, B2G-enabled buildings often utilize on-site renewable energy sources such as solar panels, which can feed excess power back into the grid, creating a decentralized and more resilient energy infrastructure. This not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also aligns with corporate sustainability goals and evolving regulatory standards.
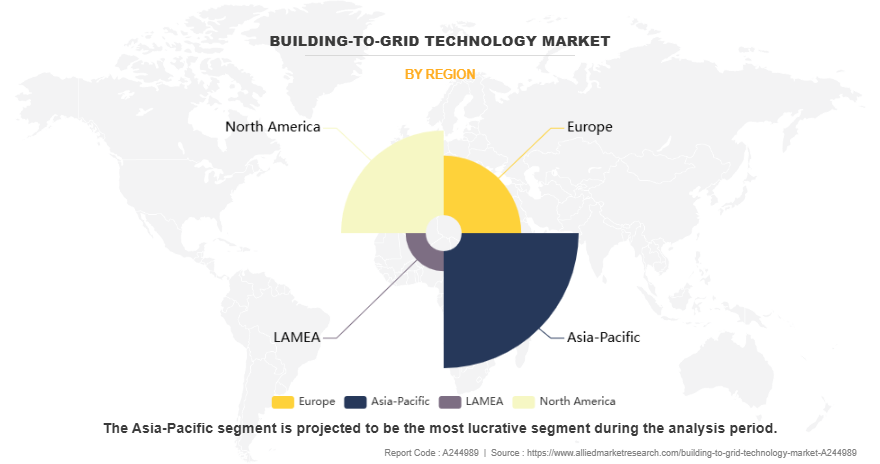
Region-wise, Asia-Pacific dominated the building-to-grid technology market in 2024 accounting for more than one third of the market share. China, as the largest energy consumer in the region, has also made significant strides in B2G adoption. While the primary focus has been on large-scale renewable integration, pilot programs in cities like Shanghai and Shenzhen are exploring how B2G systems can support grid flexibility and reduce strain during peak periods. These efforts are bolstered by China’s ambitious carbon neutrality targets, pushing for deeper synergy between buildings and the power grid. Countries like Japan and South Korea are at the forefront of adopting B2G systems. Japan’s Smart Community initiatives have integrated B2G concepts into smart city projects, enabling residential and commercial buildings to balance demand through distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar panels and battery storage. In February 2025, the Australian government has designated multiple REZs across New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, and Queensland. These zones aim to co-locate renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar and wind farms, with storage solutions and high-voltage transmission, facilitating efficient energy distribution and integration into the National Electricity Market (NEM).
Which are the Top Building-to-Grid Technology companies
The following are the leading companies in the market. These players have adopted various strategies to increase their market penetration and strengthen their position in the building-to-grid industry.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- ABB Ltd.
- General Electric
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Landis+Gyr Group AG
- Enphase Energy
- S&C Electric Company
- Itron Inc
- Oracle
What are the Recent Developments in the Building-to-Grid Technology Market
In March 2024, Schneider Electric partnered with Mainspring Energy to deliver a hybrid energy technology combining microgrid solutions with linear generators, enhancing energy resilience for commercial and industrial customers.
In May 2023, Siemens acquired the EV division of Mass-Tech Controls to enhance its capabilities in India's growing EV charging infrastructure market. This move supports Siemens' efforts to integrate EVs into the grid, promoting efficient energy distribution construction buildings.
In April 2025, China's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) announced pilot projects in nine cities, including Beijing and Shanghai, to integrate electric vehicles (EVs) with the power grid. These projects utilize V2G technology, allowing EVs to store and return electricity to the grid, aiding in demand management and grid stability. The initiative aims to address concerns about the rapid adoption of EVs potentially overwhelming energy systems. Power grid companies are responsible for setting up these pilots, while provincial governments will develop the necessary charging infrastructure.
In August 2024, UK-based AI company Infogrid acquired Buildings IOT, enhancing its ability to implement autonomous building efficiency measures. This acquisition supports the development of smart buildings capable of dynamic interaction with the grid.
In April 2022, CPower introduced the Building Management System as a Service (BMS-aaS) in New York City. This service allows commercial property owners to optimize energy consumption, reduce carbon emissions, and provide demand flexibility to the grid without significant upfront investment.
Trump’s Tarriff Impact on Building-to-Grid Technology Industry
Trump’s reimplementation of tariffs is targeting Chinese clean tech imports, including solar panels, batteries, and smart grid components has begun to show measurable impacts on the U.S. building-to-grid (B2G) technology sector. This increase has affected project feasibility across both commercial and municipal deployments. Data from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) indicates that B2G project starts in Q1 2025 fell by 12% compared to the same quarter in 2024. Notably, this contraction comes despite rising demand for building electrification and distributed energy resources (DERs), which are central to net-zero building strategies. Large-scale developments in states like California, New York, and Illinois have slowed or downsized their smart infrastructure plans due to cost overruns tied to imported control systems and battery storage modules.
Moreover, U.S.-based B2G firms are experiencing a competitiveness squeeze. Many rely on lithium-ion batteries, inverters, and advanced control systems from China or Southeast Asia, where technological capabilities and economies of scale offer lower costs. With these tariffs in place, domestic alternatives are still ramping up production and lack the price parity and proven scalability. As a result, a survey conducted by the Building Grid Alliance in April 2025 found that 64% of U.S. B2G companies expect to delay expansion plans or restructure their product offerings if the tariffs remain through 2026.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the building-to-grid technology market analysis from 2024 to 2034 to identify the prevailing building-to-grid technology market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the building-to-grid technology market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global building-to-grid market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and building-to-grid market forecast.
Building-to-Grid Technology Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2034 | USD 147.8 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 10.5% |
| Forecast period | 2024 - 2034 |
| Report Pages | 373 |
| By Component |
|
| By Platform |
|
| By End-Use |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Landis+Gyr Group AG, Enphase Energy, Itron Inc., Schneider Electric, General Electric, Siemens AG, ABB Ltd., Oracle, S&C Electric Company, Honeywell International Inc. |
Analyst Review
According to the opinions of various CXOs of leading companies, an increase in grid decentralization trends is expected to drive the growth of the building-to-grid technology market. In a decentralized grid, energy flows are no longer one-directional. Buildings equipped with generation and storage capabilities can interact bi-directionally with the grid—consuming electricity during periods of low supply and feeding energy back when there is a surplus. B2G technology serves as the crucial interface enabling this interaction, optimizing energy use at the building level while supporting grid reliability and flexibility. This localized approach reduces the strain on transmission infrastructure, minimizes energy losses, and allows for more responsive energy management. In January 2025, Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) aggregate decentralized energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage using advanced software to optimize energy production and distribution. This approach enhances grid stability and efficiency by balancing supply and demand in real-time.
However, data privacy and cybersecurity risks are expected to hamper the growth of the building-to-grid technology market. Data privacy and cybersecurity risks pose a major barrier to the widespread adoption of Building-to-Grid (B2G) technology. As buildings integrate with the grid via smart meters, sensors, and cloud-based platforms, they generate and transmit sensitive data such as energy use patterns and occupancy schedules. Without robust security, this data is vulnerable to breaches, leading to privacy violations, loss of public trust, and potential regulatory penalties. Continuous two-way communication between buildings and utilities increases the risk of cyberattacks, which could manipulate data, disrupt operations, or even destabilize the grid—particularly in high-risk areas like hospitals or data centers.
The major prominent players operating in the building-to-grid technology market include Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, ABB Ltd., General Electric, Honeywell International Inc., Landis+Gyr Group AG, Enphase Energy, S&C Electric Company, Itron Inc, and Oracle.
The global building-to-grid technology market was valued at $54.9 billion in 2024, and is projected to reach $147.8 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% from 2025 to 2034.
Asia-Pacific is the largest region for building-to-grid technology market.
Commercial is the leading end-use of building-to-grid technology market.
Expansion in smart cities are the upcoming trends of building-to-grid technology market.
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



