E-Waste Management Market Insights: 2032
The global e-waste management market size was valued at USD 57.8 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach USD 244.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.7% from 2023 to 2032.
The key factor that is driving the growth of e-waste management market is the reduced lifespan of electronic devices and lack of precious metal sources. This is attributed to rapid technological development and ongoing product innovation. Manufacturers are introducing new products with additional features that are not very durable after 2- or 3-years products are becoming outdated thus forcing businesses to set-up e-waste collection centers and forming a large network for collecting e-waste.

Furthermore, lack of rare and precious metal resources such as silver, gold, platinum, and others are driving manufacturers to use e-waste management approaches to recycle, repair and reuse electronic devices. However, the high recycling cost factor is hampering the growth of the e-waste management market. Lack of e-waste collection facilities and expensive processing techniques are creating obstruction for electronic device manufacturers to apply e-waste management approach.
Moreover, initiatives taken by electronic manufacturers are providing a lucrative opportunity for e-waste management market growth. Various cell phone manufacturers are launching different initiatives to collect old phones from users who want technology upgradation. In addition, governments are also taking decisions by requesting manufacturers to develop internal e-waste management programs or to take assistance from third party e-waste management organizations to outsource e-waste initiatives.
E-waste refers to a waste from an electrical product that is no longer required. Electrical and electronic equipment, including all the parts, consumables, and spares that have been rejected from the manufacturing, refurbishing, and maintenance processes and entirely or partially thrown away as garbage by the customer, is referred to as e-waste. Electronic equipment waste contains metal, and the most harmful chemical compounds are far more hazardous than conventional trash. These characteristics of electronic trash have prompted the development of e-waste management techniques.
The report focuses on growth prospects, restraints, and trends of the e-waste management market analysis. The study provides Porter’s five forces analysis to understand the impact of various factors, such as bargaining power of suppliers, competitive intensity of competitors, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and bargaining power of buyers, on the market.
Segment Review:
The e-waste management market is segmented on the basis of material, source type, application, and region. In terms of material, the market is divided into metal, plastic, glass and others. By source type, the market is divided into household appliances, industrial electronics, and consumer electronics. Based on application, it is bifurcated into trashed and recycled. On the basis of region, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
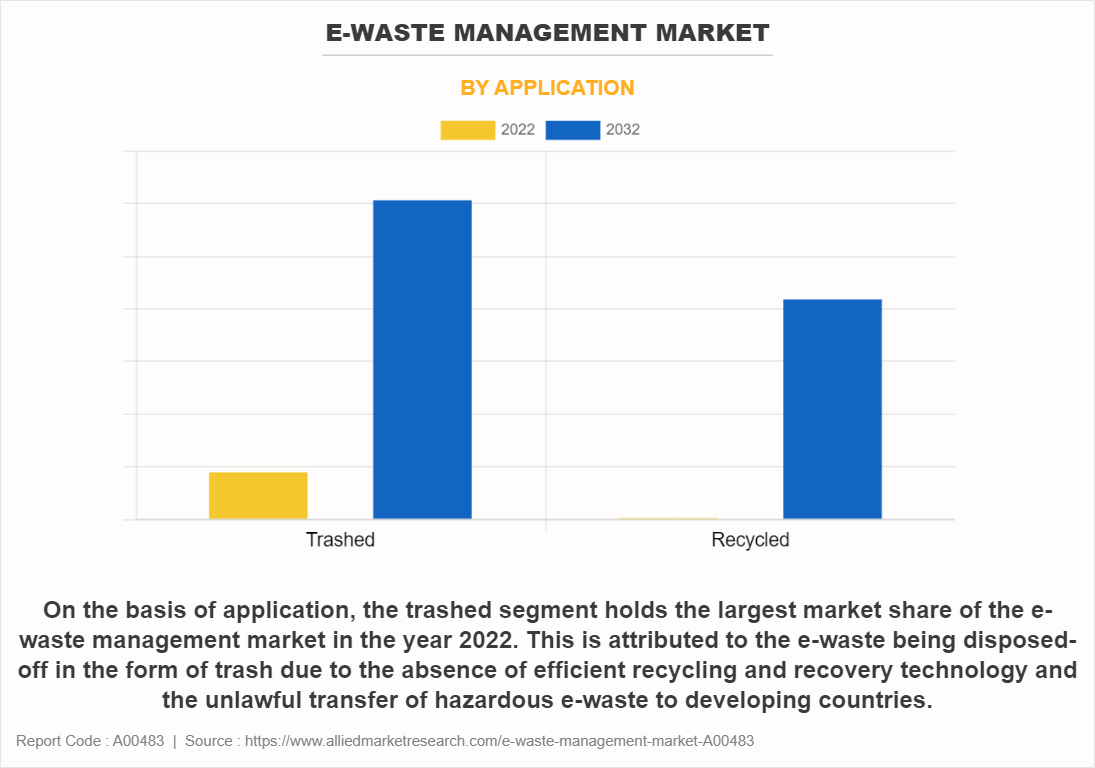
On the basis of application, the trashed segment holds the largest market share of the e-waste management market in the year 2022. This is attributed to the e-waste being disposed-off in the form of trash due to the absence of efficient recycling and recovery technology and the unlawful transfer of hazardous e-waste to developing countries.

On the basis of region, Asia-Pacific dominated the e-waste management market in the year 2022. This is due to the new product development, price reductions and increasing per capita income.
The report analyzes the profiles of key players operating in the e-waste management market such as Eniro-Hub Holdings Ltd., TES, Capital Environment Holdings Limited, Tetronics Technologies Limited, ERI, WM Intellectual Property Holdings L.L.C., Sembcorp Industries (Temasek Holdings), Veolia, MRI Technolgies, and Umicore. These players have adopted various strategies to increase their market penetration and strengthen their position in the market.
Market landscape and Trendss:
The expansion of the e-waste management market is driven by various trends. Recently the European union passed the universal charger policy. According to the policy, phones and electronic devices will have to use USB-c by 2024. Laptops will follow the same approach after two years of applicability. Furthermore, all in one battery recycling approach is witnessing a growth. Recently, ERI, Call2Recycle, and Cell Block FCS partnered on a unique recycling container, One Drum. Different kinds of batteries can be recycled together using a One Drum battery recycling container. Recycling facilities can add a mixture of mineral-based fire protection material made from recycled glass to the container. Moreover, companies such as Best Buy help in removing unwanted and dead electronics by providing transport facilities to the people location, who want their electronics to be recycled or disposed off.
Top Impacting Factors:
Reduction in Life Span of Electronic Devices
Growing advancements in technology and regular innovations in the product are resulting in the increasing sale of electronic products. In addition, an increase in purchasing power and a rise in disposable income is also resulting in the growth of the e-waste management market. Furthermore, consumers are increasingly replacing their outdated items with new ones when new products with improved features and extra services are introduced. As a result, these gadgets have a 3–4 years of lifespan. In addition, the amount of e-waste being produced is increasing at an incredible rate, which is motivating industry participants to grow their companies and establish larger networks for the collection and processing of e-waste.
Moreover, an increasing production of electronic products is taking place every year. For instance, Statista, stated that electronics production across India was estimated to be valued at over 6.4 trillion Indian rupees in 2022. In recent years, the continued sale of electronic goods, particularly in developing nations, is creating a profitable climate for the management of e-waste. Furthermore, the companies in the electronic business are introducing new items on a daily basis due to the rapid developments in technology and ongoing product innovations, which causes the lifespan of all white goods to decrease. Therefore, all these factors are likely to drive the growth of the e-waste management industry for the forecast period.
Scarcity of Sources of Precious Metals
Rise in demand and scarcity of precious and rare metal resources is resulting in rapid increase in prices of these metals. Such metals are required to be recovered from e-waste for reuse in another production cycle. For instance, a research paper named extraction of precious metals from e-waste, by A.V. Kavitha, a lecturer of computer science in the Government College of Guntur, stated that from one million of e-waste generated from mobile phones is nearly equivalent to about 250kg of silver, 24kg of gold and 9 tons of copper that can be recovered. This can provide an advantage to the manufacturers to produce electronic devices at lower cost, thus gaining cost advantages over competitors. Special and valuable metals including silver, gold, palladium, platinum, indium, and gallium are found in e-waste.
The manufacturing of consumer electronics including IT and communication gadgets makes extensive use of these rare elements. These metals are rare; hence the cost of their goods is high, hence this factor is raising demand for recycling, refurbishing, and reusing metal-based electronics. Thus, these issues would certainly force the manufacturers of electronic devices to look for raw materials available from recycled e-waste. This would also benefit the nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and certainly help to reduce the danger of global warming. Therefore, all these factors are likely to propel e-waste management industry growth for the forecast period.
Government Policies and Regulations for an Effective E-waste Management
Certain laws are being implemented by the government to manage e-waste. For instance, China, one of the largest generators of e-waste in the world, has implemented a regulation to manage and treat electronic waste. The name of the regulation is China WEEE (waste electronic and electrical products) Regulation. This regulation ensures mandatory recycling of e-waste, implementing extending producer responsibility (EPR) and establishing a fund to subsidize e-waste recycling. Furthermore, in India, the e-waste management rules 2016 mandated collection targets and transferred responsibilities to the producers of e-waste. Therefore, these kinds of initiatives will escalate the e-waste management market size growth for the forecast period.
Increase in Recycling Cost Incurred Due to Inadequacy of Infrastructure
The recycling of e-waste has been hindered by the lack of e-waste collecting locations and expensive processing methods. Many old products are either tossed in the trash or stored in storerooms and warehouses due to the lack of such a system. Therefore, a system for the regular collection of e-waste needs to be established to improve the situation. The recycling operations are hampered by an inadequate number of waste pickup zones. In addition, consumers are unaware of these collection zones, which forces them to dispose of waste in a harmful manner like burning the waste, thus resulting in pollution and health risks.
However, as tight regulatory frameworks are being established in developing nations, the landscape is shifting. Furthermore, to control e-waste, the producers are gathering abandoned electronic items, planning garbage collection events and creating a vast network of collection zones, all these operations are demanding heavy investments. Moreover, less awareness among the people about e-waste recycling programs is also slowing down the growth of e-waste management market. In addition, to implement recycling programs, different resources are required such as trucks and employees that add up to the cost, making recycling a costly method for e-waste management. Therefore, all these factors are likely to hamper the growth of e-waste management market share for the forecast period.
E-waste Initiatives by Electronic Manufacturers Across the Globe
Various manufacturers are taking strong initiatives to efficiently manage electronic waste. For instance, South Korean consumer durables giant LG created a pan-India network of 40 recyclers and collected and recycled almost 100 kilo metric tons of e-waste during the year 2017-2020. In addition, Dell Technologies have followed a decade long program to recover plastic from old computer systems to develop new parts. Moreover, the company has set up e-waste drop-off points in 23 locations.
Furthermore, smartphone manufacturer Xiaomi launched a product take back and recycling program, through which Mi account is credited with a Rs 100 discount coupon for every old product collected. In addition, the company collaborated with Karo Sambhav platform, a technology platform to assist businesses to implement circular economy seamlessly, to set up over 1,150 e-waste collection points for old phones, batteries, accessories at all Xiaomi Mi Homes and Mi Authorized Service Centers in over 500 cities. In addition, the company has collected more than 400 tones of e-waste in the past recent years. Therefore, all these factors will propel e-waste management industry growth for the forecast period.
Key Industry Developments:
Recent Partnerships
In April 2022, Call2Recycle Inc. partnered with Cell Block FCS and ERI and launched One Drum, the first mixed consumer battery collection product in the market. One Drum solution allows customers to place and transport large volumes of consumer single-use and rechargeable batteries in one convenient container eliminating the need to sort by chemistry or individually bag or tape battery terminals.
In December 2020, MG Motor India partnered with TES for recycling batteries of its electric vehicle, ZS EV. The partnership ensures environmentally-sustainable and secure recycling of ZS EV batteries.
Recent Acqusition
In January 2020, Sembcorp Industries, through its wholly-owned subsidiary SembWaste, acquired Veolia ES Singapore (VESS) and public cleaning business of Veolia ES Singapore Industrial. The acquisition is expected to enhance e-waste management capabilities of the Sembcorp Industries.
Recent Investment
TES announced investment in Green Li-ion, a start-up technology innovator based in Singapore focused on creating sustainable models for battery recycling. This investment is aimed at extending Green Li-ion’s proprietary battery recycling technology to TES’s suite of battery recycling solutions.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders
This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the e-waste management market forecast from 2022 to 2032 to identify the prevailing market opportunities.
Market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities of e-waste management market outlook.
Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders to make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
In-depth analysis of the e-waste management market segmentation assists in determining the prevailing market opportunity.
Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global e-waste managementmarket.
Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the e-waste management market players.
The report includes an analysis of the regional as well as global e-waste management market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
E-Waste Management Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 244.6 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 15.7% |
| Forecast period | 2022 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 376 |
| By Application |
|
| By Material |
|
| By Source Type |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | SembCorp Industries, WM Intellectual Property Holdings, LLC, TES Amm, Tetronics Technologies Limited, MRI Technologies, Electronic Recyclers International, Umicore, Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd., Veolia, Capital Environment Holdings Limited |
Analyst Review
As per the insights of the top-level CXOs, the adoption of e-waste management has had a profound impact on the ICT sector revolutionizing various aspects of the industry. E-waste management helps in preventing harmful substances present in electronic devices, such as lead, mercury and cadmium from contaminating soil and water. Furthermore, the proper system of e-waste management ensures that ICT companies comply with rules and regulations governing the disposal of e-waste. Moreover, ICT companies are using e-waste management techniques to promote environmental sustainability by properly managing their e-waste. In addition, in the ICT sector, data security is paramount. E-waste management ensures that data is securely wiped and destroyed from devices before recycling and disposal. This prevents sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands, safeguarding both individuals and organizations from data breaches.
The CXOs further added that market players are adopting strategies like partnership for enhancing their services in the market and improving customer satisfaction. For instance, in March 2021, Veolia announced partnership with Groupe Renault and Solvay. This partnership aims to provide solutions to recycle the metals in electric vehicle batteries in a closed loop. In addition, in September 2020, the Massachusetts Biotechnology Council (MassBio) partnered with Veolia North America, Boston. Under the partnership agreement, Veolia serves as a preferred partner of MassBio for all streams of waste management. Furthermore, some companies adopted collaboration strategy, for instance, in October 2020, Umicore AG & Co. KG announced collaboration with AZUR SPACE. This collaboration aims to develop a tailor-made solution enabling the collection of high concentrates of germanium from very low concentration waste streams. Therefore, such strategies are expected to boost the growth of the e-waste management market in the upcoming years.
The key players profiled in the e-waste management in ICT market analysis are A Eniro-Hub Holdings Ltd., TES, Capital Environment Holdings Limited, Tetronics Technologies Limited, ERI, WM Intellectual Property Holdings L.L.C., Sembcorp Industries (Temasek Holdings), Veolia, MRI Technolgies, and Umicore. These players have adopted various strategies to increase their market penetration and strengthen their position in the e-waste management industry.
The global e-waste management market size was valued at USD 57.8 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach USD 244.6 billion by 2032
The global E-Waste Management market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 15.7% from 2023 to 2032 to reach USD $244.6 billion by 2032
A Eniro-Hub Holdings Ltd., TES, Capital Environment Holdings Limited, Tetronics Technologies Limited, ERI, WM Intellectual Property Holdings L.L.C., Sembcorp Industries (Temasek Holdings), Veolia, MRI Technolgies, and Umicore are the top companies to hold the market share in E-Waste Management.
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market for E-Waste Management.
Growing electronic consumption, rapid technology upgrades, and environmental concerns are key factors driving the E-Waste Management market.
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



