Military Trainer Aircraft Market Research, 2033
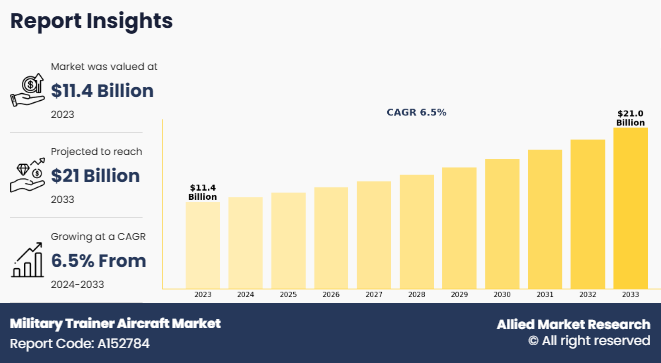
The global military trainer aircraft market size was valued at $11.4 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $21 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways
- On the basis of type, the fixed wing segment held the largest share in the military trainer aircraft market in 2023.
- By training type, the basic and intermediate pilot training segment was the major shareholder in 2023.
- By seat type, the twin segment dominated the market, in terms of share, in 2023.
- On the basis of application, the unarmed segment dominated the market, in terms of share, in 2023.
- Region wise, North America held the largest market share in 2023.
Military trainer aircraft are specialized aircraft designed to train pilots and crew members in various aspects of flight operations, combat tactics, and mission-specific procedures before transitioning to frontline combat aircraft. These aircraft serve as an essential component of military aviation training programs, helping pilots develop fundamental and advanced flying skills in a controlled environment. Trainer aircraft are typically classified into basic, advanced, and lead-in fighter trainers, each serving a distinct role in the pilot training pipeline.
Basic trainers are used to teach fundamental flight skills, while advanced trainers focus on aerobatics, navigation, and combat tactics. Lead-in fighter trainers bridge the gap between training and operational aircraft, equipping pilots with experience in handling high-performance jets. Trainer aircraft often incorporate modern avionics, simulated combat systems, and dual-seat configurations for instructor oversight. As air forces modernize, the demand for technologically advanced trainer aircraft continues to grow, ensuring pilots are well-prepared for operational missions.
For instance, in January 2025, Textron Inc. collaborated with Kanematsu Group to modernize pilot training for the Japan Air Self-Defense Force (JASDF) by integrating Beechcraft T-6 Texan II Training System (ITS). The Japan Air Self-Defense Force (JASDF) is modernizing its training program with an integrated solution featuring T-6 Texan II trainer aircraft, a comprehensive Ground Based Training System, training for instructor pilots and aircraft maintainers and long-term logistic and sustainment support.
For instance, in August 2024, Lockheed Martin Corporation signed an agreement with Martin-Baker Australia to deliver ejection seat training. As Defence's partner for delivering the AIR5428 Phase 1 Pilot Training System, Lockheed Martin Australia conducted a rigorous selection and evaluation tender process for ejection seat survival training services for the PC-21 trainer aircraft.
Increase in defense budgets and spending globally are significantly driving the demand for the military trainer aircraft market demand. As nations prioritize pilot training and air force modernization. Many countries are investing in advanced trainer aircraft to ensure their pilots are well-prepared for operating next-generation fighter jets and multi-role aircraft. The growing need for pilot proficiency, coupled with technological advancements in training systems, is further boosting the market. Geopolitical tensions and modernization programs are prompting defense forces to enhance training capabilities, fueling demand for advanced military trainers. Furthermore, Ongoing efforts towards enhancing pilot skills and flight readiness among air forces globally have driven the demand for military trainer aircraft industry.
However, high procurement costs are restraining the growth of the military trainer aircraft market forecast. As budget constraints force defense agencies to reconsider large-scale acquisitions. The development and integration of advanced avionics, simulation systems, and high-performance capabilities increase overall costs, making procurement challenging for smaller and developing nations. maintenance and operational expenses further add to the financial burden, limiting adoption. Many governments are prioritizing cost-effective solutions, including extending the lifespan of existing fleets or relying on simulator-based training, impacting new military trainer aircraft demand. Moreover, long equipment lifecycles are major factors that hamper the growth of the military trainer aircraft market share.
On the contrary, the emergence of multi-role trainer aircraft, combined with ongoing operational fleet upgrades, presents a lucrative opportunity for the military trainer aircraft industry. Modern air forces are seeking versatile trainers that can transition from pilot instruction to light combat and support roles, maximizing cost-effectiveness. These advanced trainers, equipped with next-generation avionics and combat capabilities, enhance pilot readiness while complementing frontline fleets. As countries upgrade their operational aircraft, demand for compatible trainer platforms rises, driving market growth and technological advancements in military aviation training.
Segment Review
The global Military trainer aircraft market is segmented on the basis of type, training type, seat type, application, and region. On the basis of type, the market is bifurcated into fixed wing, and rotary wing. By training type, the market is divided into combat training, basic and intermediate pilot training, and advanced pilot training. On the basis of seat type, the market is bifurcated into single, and twin. By application, the market is divided into armed, and unarmed. Region wise, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa.
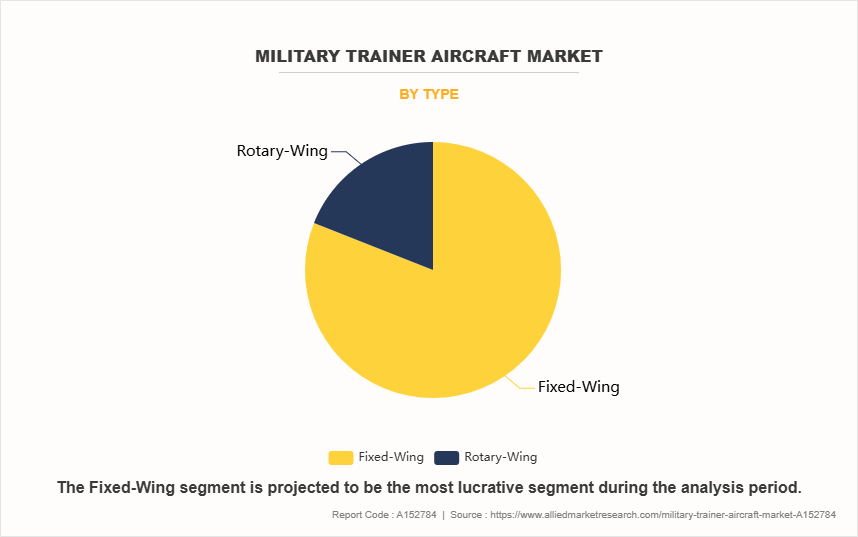
By Type
On the basis of type, the fixed wing segment attained the highest market share in 2023. This is due to its extensive use in pilot training programs worldwide. Fixed-wing trainers are essential for developing fundamental and advanced flying skills, preparing pilots for combat and transport aircraft operations. Their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to simulate real-world flight conditions make them the preferred choice for air forces. The growing demand for lead-in fighter trainers (LIFT) and advanced jet trainers (AJT) has further fueled segment growth. Technological advancements, including modern avionics and integrated training systems, have strengthened the dominance of fixed-wing trainers in military aviation.

By Training Type
On the basis of training type, the basic and intermediate pilot training segment acquired the highest market share in 2023. This is due to the essential role it plays in determining future military pilots. Every air force requires a structured training pipeline, starting with basic and intermediate training before advancing to complex combat aircraft. These trainers are widely used to teach fundamental flight skills, navigation, and aerobatics, making them a critical investment for defense forces. The increasing demand for new pilot training programs, coupled with the affordability and widespread adoption of basic trainer aircraft, has contributed to this segment's dominance in the market.
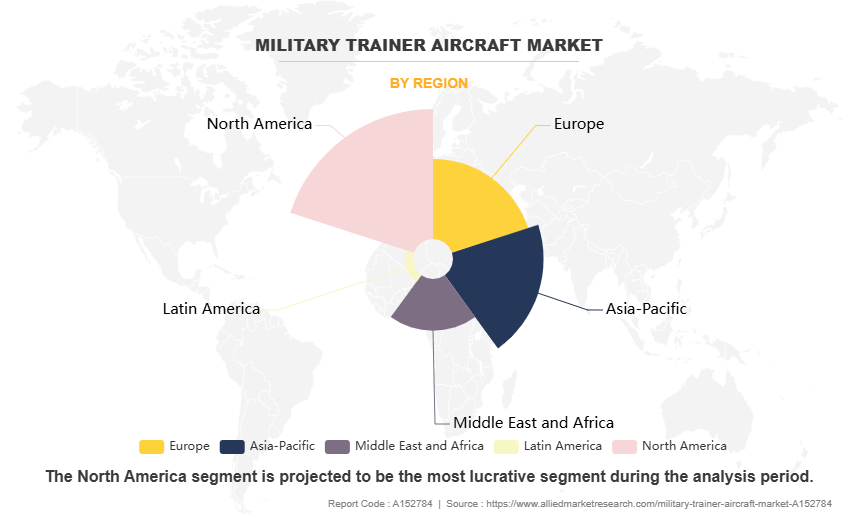
By Region
Region wise, North America attained the highest market share in 2023 and emerged as the leading region in the Military trainer aircraft market. This is due to strong defense spending, advanced aviation infrastructure, and the presence of leading aircraft manufacturers such as Boeing and Lockheed Martin. The U.S. Air Force and Navy maintain extensive pilot training programs, continuously upgrading their trainer fleets with advanced fixed-wing and rotary-wing platforms. The U.S. governments focus on next-generation training solutions, including simulation-based training and lead-in fighter trainers (LIFT), has driven market growth. The region's established defense industry and frequent aircraft modernization programs further contribute to North Americas dominant market position.
However, Asia-Pacific is projected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. This due to rising defense budgets, increasing geopolitical tensions, and large-scale military modernization programs. Countries like India, China, and South Korea are heavily investing in advanced trainer aircraft to strengthen their air forces and enhance pilot training capabilities. Domestic aircraft production, such as India‐™s HAL Tejas and South Koreas KAI T-50, is accelerating regional market expansion. Growing collaborations with Western defense firms and increasing demand for multi-role trainer aircraft further fuel market growth, positioning Asia-Pacific as the fastest-growing region in military aviation training.
The report focuses on growth prospects, restraints, and trends of the military trainer aircraft market analysis. The study provides Porters five forces analysis to understand the impact of numerous factors, such as bargaining power of suppliers, competitive intensity of competitors, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and bargaining power of buyers, on the military trainer aircraft market.
Competitive Analysis
The report analyzes the profiles of key players operating in the Military trainer aircraft market such as Airbus SE, Bae Systems plc, Leonardo SpA, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Saab AB, Textron Inc., The Boeing Company, Embraer SA, and Korea Aerospace Industries, Ltd. These players have adopted various strategies to increase their market penetration and strengthen their position in the Military trainer aircraft market.
Increase in Defense Budgets and Spending Globally
Rise in global defense budgets enable military aviation modernization across air forces, including upgrades of aging trainer aircraft fleets. Many countries such as the U.S., Germany, France, Spain, and others have increased their military expenditure allocations in recent years in response to geopolitical tensions, security priorities and the need to retire Soviet-era equipment. Higher budgets facilitate new trainer aircraft procurement programs even as research and development funding flows towards augmented simulation systems and next-gen technologies. For example, the U.S. and India have rolled out new jet trainer contracts amidst rising regional instability.
Moreover, the U.S. President, Joe Biden enacted the 2023 fiscal year National Defense Authorization Act, granting the Department of Defense $816.7 billion in funding. Moreover, European Union member states are increasing military budgets substantially, with spending reached to approximately $295 billion in 2023 as the alliance mobilizes support for Ukraine against Russia's invasion. In addition, the Russian government stated its intention to significantly hike defense allocation by 68% for 2024.
The growth is expected to continue in the coming years as well, providing opportunities for defense contractors. Air forces need to continually train pilots to operate new aircraft being inducted. With multi-role fighters, helicopters, transports, and surveillance planes being acquired, compatible trainers are essential for the transition. Companies such as Northrop Grumman Corporation and Lockheed Martin Corporation are developing new jets integrated with simulation and networked battle management software to prepare pilots thoroughly. The investments make it possible for militaries to purchase such platforms. Thus, increased defense budgets further support the military training requirement, which in turn drives the military trainer aircraft market growth.
Ongoing Efforts Towards Enhancing Pilot Skills and Flight Readiness Among Air Forces Globally
Air forces around the world are placing a significant focus on enhancing the skills and flight readiness of their pilot corps. The increasing complexity of modern aerial warfare platforms and operations has necessitated very high training standards. This focus is driving strong demand for advanced military trainer aircraft equipped with sophisticated capabilities.
Moreover, major market players are partnering to provide advanced military trainer aircraft and its services. For instance, in June 2023, Airbus SE and Leonardo SpA signed an agreement to promote integrated training systems and explore future solutions for air dominance capabilities. These companies are expected to jointly pursue opportunities to provide advanced training leveraging Leonardo's M-346 aircraft, which has over 100,000 global flight hours. In addition, they will investigate deeper industrial cooperation on emerging military pilot training needs. This collaboration aims to offer synergistic platforms and programs within broader European and international partnerships. According to both companies, there is a sizable market for training services, with a projected demand of over $13 billion over the next 20 years and over 400 new advanced European trainers.
Furthermore, advancements in defense technology have led to the induction of 4th and 5th generation combat jets, integrated UAV operations, increased use of precision guided munitions, and other trends. For pilots to effectively employ these assets, training has become longer and more thorough. Simulation-based education, networked battle management software, and artificial intelligence-enabled training are key advancements.
Technological Advancements in Trainer Aircraft
Technological advancements in trainer aircraft are significantly increasing demand in the military trainer aircraft market. Modern trainer aircraft are now equipped with advanced avionics, digital cockpits, and simulation-based training systems, providing pilots with a more realistic and efficient learning experience. These innovations bridge the gap between basic training and the operational requirements of next-generation fighter jets. Features such as fly-by-wire systems, augmented reality (AR)-based training modules, and integrated mission simulators enhance pilot proficiency while reducing training costs. For instance, in November 2022, BAE Systems collaborated with Red 6, an augmented reality technology firm at the forefront of synthetic air combat training. Through this strategy Red 6 provides helmet-mounted displays with Red 6‐™s breakthrough ATARS technology to boost training experience.
In addition, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics are enabling more personalized and adaptive training programs, further improving pilot skill development. The integration of multi-role capabilities, allowing trainers to perform both training and light combat roles, is also contributing to increased adoption. As air forces worldwide modernize their fleets, technologically advanced trainer aircraft are becoming essential for preparing pilots to operate sophisticated military aircraft, driving sustained growth in the market.
High Procurement Costs
High cost of procuring new military trainer aircraft can act as a restraint, especially for developing countries with budget constraints. The HTT-40 trainer aircraft costs approximately $116.5 million. These advanced jets integrate complex subsystems and require long development cycles, which raises the cost. Particularly, contemporary trainers incorporate digital glass cockpits, simulated radar and weapons employment capabilities, and tactical battle management systems used in frontline fighters. This significantly raises engineering and production expenses incurred by manufacturers, limiting the adoption by developing economic air forces and smaller defense setups. Operating and maintenance costs are also significant given the complex twin-engine configurations and avionics that some platforms incorporate.
Some emerging regions are experiencing delays or reduced orders for trainer jet acquisitions as global defense spending is directed toward combat fleet upgrades and multirole aircraft. However, larger air forces still value frontline readiness facilitated through robust pilot curriculums. Domestic manufacturing also helps to reduce cost reduction. Overall, high capital costs, particularly for advanced trainer aircraft, remain a barrier to adoption; however, if budgets allow for sufficient fleet maintenance, their crucial role in capability development justifies their use.
Long Equipment Lifecycles
Military trainer aircraft often have very long service lives of around 40 years, sometimes even more before retirement. This extended lifespan acts as a restraint on the global trainer aircraft market, slowing the pace of replacement and upgrade programs which provide sales opportunities. Such lengthy lifecycles mean air forces can train countless batches of pilots on a single trainer fleet. These ongoing incremental improvements reduce the need for full-scale replacements, which would result in increased production sales. The T-38 Talon jet has served as the U.S. Air Force's advanced trainer since entering service in 1961. It continues fulfilling that role of advanced trainer, even as the Boeing-Saab T-7A Red Hawk is set to replace the aging T-38 fleet.
Strong dependability and performance are a result of the designs' deep experience and maturation. However, the longer lead times make it more difficult for the trainer aircraft value chain to quickly incorporate new advancements in aircraft technology. The prolonged operational lifespans of military training aircraft severely limit customers for modernization initiatives and integration of modern aviation developments. Overall, opportunities for industry are hindered and progress in the field is restricted due to the extended use of outdated trainer fleets.
Emergence of Multi-Role Trainers Alongside Operational Fleet Upgrades
Rise in adoption of multi-role trainer aircraft by air forces globally represents a major opportunity for the military trainer market. This trend is linked to the induction of advanced 4th and 5th generation combat jets and the imperative to optimize pilot training budgets. Moreover, contemporary trainer platforms are being designed not just to train pilots, but also to serve operational missions such as light attack, intelligence gathering and maritime patrol. This allows a single aircraft type to perform both training and active-duty roles. For instance, Korea's T-50 Golden Eagle functions as a supersonic trainer and light fighter.
The demand for multi-role trainers is surging as many countries face constraints on total fleet size due to budget limitations. By acquiring dual-use platforms, air forces can augment their operational capacity even with small procurement volumes. For instance, in October 2023, India-based Korea Aerospace Industries, Ltd (HAL) delivered the first twin-seat trainer variant of the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas jet to the Indian Air Force at a ceremony attended by Minister of State for Defense, Ajay Bhatt. HAL designed the lightweight multirole 4.5-generation trainer to meet both training needs and serve as an operational fighter if required. Air Chief Marshal, V.R. Chaudhari stated the IAF plans further orders totaling 97 Tejas aircraft, which would bring its fleet to 220 jets. The twin-seater configuration specifically supports pilot instruction, building skills on the Tejas platform to ease transitions to frontline variants. Its successful handover represents a capacity boost for Indian aircrew preparation.
This presents an opportunity for manufacturers to integrate sensors, weapons, and other subsystems on trainers to undertake combat missions. Overall, the demand for multi-mission trainers that reduce fleet expenses while increasing pilot experience creates major innovation and sales potential. It incentivizes investments in high-value trainer platforms with the latest aviation technologies and mission systems. This shift towards multi-role trainer aircraft is expected to reshape market dynamics throughout the forecast period.
Surge in Public-Private Partnerships
The growing adoption of public-private partnerships (PPPs) in the defense sector is creating notable opportunities within the military trainer aircraft market. Faced with budget constraints, many countries are exploring joint initiatives between government agencies and private industry to develop and manufacture trainer platforms.
For instance, in March 2023, India's defense ministry signed an agreement with Korea Aerospace Industries, Ltd (HAL) to procure 70 HTT-40 basic trainer aircraft for approximately $816 million (Rs 6,800 crore). In addition, the cabinet authorized contracting state-owned shipbuilder Larsen & Toubro (L&T) for three cadet training ships worth over approximately $372 million (Rs 3,100 crore). This deal also falls under the Buy Indian-IDDM category focused on domestically designed, developed, and made defense equipment. The trainer jet and naval ship agreements underscore sustained efforts to build indigenous capacity and reduce import dependence for key military hardware.
By leveraging private capital and defense contractor expertise in the framework of PPPs, air forces can field new aircraft with lower upfront public investment. The risk-sharing model results in innovations as companies compete to supply solutions tailored to customer requirements. Overall, public-private partnerships facilitate better alignment of defense customer objectives with industry offerings. For trainer aircraft manufacturers, it unlocks avenues for growth by enabling collaborative business models before untapped markets.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the Military trainer aircraft market analysis from 2023 to 2032 to identify the prevailing Military trainer aircraft market opportunities.
- Market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders to make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the Military trainer aircraft market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global Military trainer aircraft market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Military Trainer Aircraft Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2033 | USD 21 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.5% |
| Forecast period | 2023 - 2033 |
| Report Pages | 405 |
| By Type |
|
| By Training Type |
|
| By Seat Type |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | BAE Systems, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Airbus, Boeing, Leonardo S.p.A., Saab AB, Textron Inc., Northrop Grumman, Korea Aerospace Industries, Embraer |
Upcoming trends in the global military trainer aircraft market include the integration of advanced simulation technologies, AI-driven pilot training systems, multi-role trainer aircraft, increased adoption of stealth and supersonic trainer jets, and the development of cost-effective training solutions through public-private partnerships to meet evolving defense requirements.
Unarmed is the leading application of Military Trainer Aircraft Market
North America is the largest regional market for Military Trainer Aircraft
$21037 million is the estimated industry size of Military Trainer Aircraft
Airbus SE, Bae Systems plc, Leonardo SpA, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Saab AB, Textron Inc., The Boeing Company, Embraer SA, and Korea Aerospace Industries, Ltd.
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



