Narrowband IoT Enterprise Application Market Research, 2032
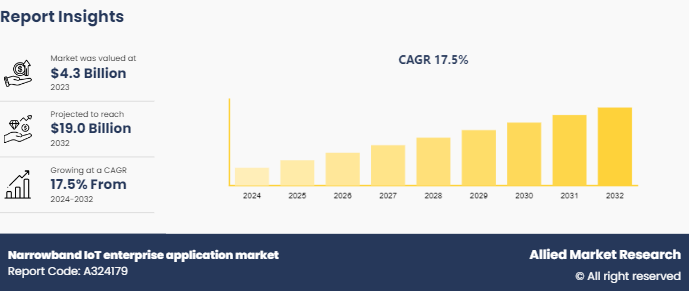
The global narrowband iot enterprise application market was valued at $4.3 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $19.0 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.5% from 2024 to 2032. This market includes the implementation of NB-IoT solutions across diverse sectors to improve operational efficiency, enable real-time monitoring and control, and drive innovation through scalable and secure IoT networks.
Market Introduction and Definition
The narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) enterprise application market includes the use and deployment of NB-IoT technology within various industries to enhance connectivity and data management for low-power, wide-area network solutions. NB-IoT is designed to support a broad range of applications, including smart city infrastructure, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, and agriculture, by providing reliable, low-cost, and energy-efficient communication for devices that require infrequent data transmission over large areas.
Key Takeaways
The narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) enterprise application market study covers 20 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value for the projected period.
More than 1, 500 product literatures, industry releases, annual reports, and other such documents of major narrowband IoT enterprise application industry participants along with authentic industry journals, trade associations' releases, and government websites have been reviewed for generating high-value industry insights.
The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of global markets and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions in order to achieve their most ambitious growth objectives.
Key Market Dynamics
One of the primary drivers of the narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) enterprise application market is rise in demand for efficient, low-power, and wide-area connectivity solutions. NB-IoT's ability to handle a large number of connected devices with very low energy consumption with minimal energy consumption makes it particularly attractive for applications in smart cities, industrial automation, and agriculture. As enterprises seek to optimize operations and enhance operational efficiency, the cost-effective and scalable nature of NB-IoT technology aligns well with their needs for reliable, long-range connectivity. In addition, technological advancements in NB-IoT technology and its integration with existing systems are fueling market growth. Innovations such as improved network coverage, enhanced security features, and the integration of NB-IoT with other IoT technologies and platforms are making it increasingly viable for a wide range of applications. This technological progress supports the development of new solutions and services, expanding the potential use cases for NB-IoT in enterprise applications.
However, the limitation of NB-IoT is its lower bandwidth and data transfer rates as compared to other IoT technologies like LTE and 5G. While NB-IoT is well-suited for applications requiring small, infrequent data transmissions, it may not be ideal for use cases that demand high data throughput or real-time data processing. This limitation can restrict its adoption in applications that require more robust data handling capabilities. Although NB-IoT offers cost-effective solutions in terms of device and network operation, the initial infrastructure and deployment costs can be significant. Setting up NB-IoT networks, particularly in areas with limited existing infrastructure, can require substantial investment. This cost can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises or in regions with lower budgets for technology upgrades.
Moreover, there is significant growth potential for NB-IoT in emerging markets, where rapid urbanization and industrialization are creating a demand for efficient connectivity solutions. These regions are investing in smart infrastructure and digital transformation, presenting opportunities for NB-IoT providers to expand their offerings and capture new market segments. The adoption of NB-IoT in these markets can drive further innovation and growth. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental management is creating opportunities for NB-IoT applications that support smart agriculture, energy management, and resource optimization. As businesses and governments prioritize sustainable practices, NB-IoT technology can play a crucial role in enabling smart solutions that reduce waste, improve efficiency, and contribute to environmental goals.
LTE-M Vs NB-IoT
Low Throughput Bluetooth Mesh (LTB_M) and Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) are both technologies designed to enable connectivity for the Internet of Things (IoT) , but they serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways. LTB_M is a low-power wireless communication protocol optimized for short-range, low-throughput applications, typically used in Bluetooth mesh networks for scenarios like smart lighting or building automation. It focuses on providing reliable communication in environments with many devices within close proximity. In contrast, NB-IoT is a cellular-based technology designed for wide-area, low-power, low-bandwidth applications, suitable for devices spread across large geographic areas such as smart meters or industrial sensors. NB-IoT operates over existing cellular networks, offering better range and deeper indoor coverage compared to LTB_M, but with a focus on lower data rates and longer-range connectivity.
Feature | LTE-M | NB-IoT |
Uplink and downlink speeds | Low (Kbit/s) . LTE Cat NB2 offers max 159 Kbit/s uplink and 127 Kbit/s downlink. | High (Mbits/s) . LTE Cat M2 offers max 7 Mbit/s uplink and 4 Mbit/s downlink. |
Coverage/Penetration | Great coverage and penetration. | Great coverage and penetration. |
Global availability | Good availability. Requires new infrastructure. Cheaper to roll-out than LTE. | Great availability where LTE already exists. Built on existing LTE technology. |
Roaming capability | Technically possible, but basically non-existent in reality. Check regions of interest. | Good roaming availability. Check regions of interest. |
Module costs | Typically, cheaper than LTE-M. | Typically, more expensive than NB-IoT. |
Power saving features | PSM and eDRX support. | PSM and eDRX support. |
Mobility | No handover when moving, only suitable for static devices. | Suitable for static and mobile devices. |
Freedom to leave | Typically, there is no SMS support. Not good for freedom to leave and eUICC (eSIM) . | Supports freedom to leave and eUICC (eSIM) . |
Market Segmentation
The narrowband IoT enterprise application market is segmented on the basis of enterprise size, application, industry vertical, and region. On the basis of application, it is divided into smart metering, smart asset tracking, security solutions, smart parking management, and others. By enterprise size, it is segmented into large enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises. By industry vertical, it is fragmented into BFSI, manufacturing, IT and telecom, healthcare, retail, energy and utilities, and others. Region-wise, the market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Regional/Country Market Outlook
In the UK and the U.S. narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) enterprise application markets, there is a strong focus on leveraging NB-IoT technology to enhance connectivity and operational efficiency across diverse sectors. In the UK, the market is driven by advancements in smart city projects, such as intelligent infrastructure and environmental monitoring, supported by major telecom operators like Vodafone and BT Group. The U.S. market emphasizes large-scale industrial IoT applications and smart agriculture, with significant contributions from telecom giants like AT&T and Verizon. Both markets are characterized by a growing adoption of NB-IoT for its cost-effective, low-power connectivity solutions, aimed at improving urban management, industrial operations, and resource optimization, while also facing challenges related to network deployment and regulatory compliance.
In July 2020, China Mobile, the world’s largest mobile operator in terms of subscribers, planned to deploy 118, 000 NB-IoT base stations across the country during 2020. China Mobile stopped adding new IoT connections to its 2G network as the telco accelerates the deployment of NB-IoT infrastructure across the country, according to the report.
In February 2019, Australian service provider, Telstra partnered with Ericsson, to deliver Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity to global enterprises by integrating Ericsson’s Connectivity Management services from Ericsson’s IoT Accelerator solution into Telstra’s IoT solution and world-class mobile network.
In February 2019, Singtel and China Mobile International Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of China Mobile, the leading telecommunications services provider in China, signed a Master Services Agreement to collaborate on accelerating enterprise adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) in the Asia-Pacific region. Both parties enabled each other’s enterprise customers to seamlessly deploy their IoT devices installed in cars, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment across China and Singapore. The partners will also cooperate on using Singtel’s network to roll-out China Mobile International’s range of Narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) products and devices in Singapore.
Industry Trends:
The integration of narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) into smart city projects is rapidly expanding as municipalities seek to enhance urban management and promote sustainable development. NB-IoT's ability to support a vast number of connected devices with low power consumption and wide-area coverage makes it ideal for smart city applications, such as smart lighting, waste management, and environmental monitoring. By leveraging NB-IoT, cities can achieve real-time data collection and analysis, leading to more efficient resource management, reduced operational costs, and improved quality of life for residents. This trend is driven by the growing demand for scalable and cost-effective solutions to address urban challenges, optimize infrastructure, and advance sustainability goals, positioning NB-IoT as a key enabler in the evolution of smart urban environments.
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is increasingly being adopted to revolutionize crop and livestock management through enhanced data collection and analysis. NB-IoT’s low power consumption, wide coverage, and ability to handle large volumes of data make it well-suited for monitoring environmental conditions, soil moisture, and livestock health over vast agricultural areas. By deploying NB-IoT sensors and devices, farmers can gain real-time insights into their operations, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that optimize resource use, improve yield, and reduce waste. This trend reflects the growing demand for advanced, cost-effective solutions that boost agricultural productivity and sustainability by providing accurate, actionable information to manage farming practices more effectively. For instance, in April 2023, John Deere introduced the John Deere G5 display family, and the JDLinkTM M modem. These enhancements make John Deere’s precision farming technology quicker, more sophisticated, and more cost-effective for all farmers and contractors.
Competitive Landscape
The major players operating in the narrowband IoT enterprise application market include Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Qualcomm Incorporated, Nokia Corporation, Intel Corporation, Vodafone Group Plc, China Mobile Limited, Deutsche Telekom AG, AT&T Inc., Cisco Systems, Inc., ZTE Corporation, Sony Corporation, Sierra Wireless, Inc., Semtech Corporation, and Telstra Group Limited.
Recent Key Strategies and Developments
In March 2024, Semtech Corporation, a high-performance semiconductor, IoT systems, and connectivity service provider, announced the integration of Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) support into its HL series LPWA modules, specifically the HL7810 and HL7812. This significant advancement showcases a major leap forward in enabling uninterrupted global connectivity even amidst the most challenging conditions.
In May 2020, Telstra started its work on the Internet of Things (IoT) with the launch of new location products for enterprise customers. 'Location of Things, ' which was also made available to small businesses and consumers, helped customers keep track of their valuables, such as business assets like hardware and vehicles. This announcement followed Telstra’s deployment of Cat-M1 and Narrowband IoT technology on its mobile network over the previous 12 months, and the June T22 strategy update, which highlighted Telstra’s plan to deliver the next generation of connected experiences for customers.
In September 2020, China Telecom Global (CTG) , a subsidiary of China Telecommunications Corporation, one of the largest providers of integrated telecommunications services and 1NCE, an international, fully-fledged Tier-1 IoT network carrier, announced the commercial launch of a NB-IoT roaming product for China. Following the initial announcement of the cooperation with CTG in February this year, the 1NCE IoT Lifetime Flat with NB-IoT/4G coverage can now be ordered at 1nce.com.
Key Sources Referred
1. Onomondo ApS
2. appinventiv.com
3. semtech.com
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the narrowband iot enterprise application market analysis from 2024 to 2032 to identify the prevailing narrowband iot enterprise application market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the narrowband iot enterprise application market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global narrowband iot enterprise application market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Narrowband IoT enterprise application market, by Enterprise Size Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 19.0 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 17.5% |
| Forecast period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 221 |
| By Enterprise Size |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Industry Vertical |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Sony Corporation, Intel Corporation, AT&T Inc., Deutsche Telekom AG, ZTE Corporation, Nokia Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Sierra Wireless, Inc., Vodafone Group Plc, Qualcomm Incorporated, China Mobile Limited |
The global narrowband IoT enterprise application market was valued at $4.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $19.0 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.5% from 2024 to 2032.
The rise in demand for efficient connectivity solutions and the rise in adoption of smart city initiatives are the upcoming trends of Narrowband IoT enterprise applications around the globe.
Increased focus on sustainability is the leading application of Narrowband IoT enterprise application.
North America is the largest regional market for Narrowband IoT enterprise applications.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Qualcomm Incorporated, Nokia Corporation, Intel Corporation, Vodafone Group Plc, China Mobile Limited, Deutsche Telekom AG, AT&T Inc., Cisco Systems, Inc., ZTE Corporation, Sony Corporation, Sierra Wireless, Inc., Semtech Corporation, and Telstra Group Limited. are the top companies to hold the market share in Narrowband IoT enterprise application.
Loading Table Of Content...



