Table Of Contents
- Navigating How Virtual Care Transformed Healthcare to Telehealth
- Unlocking the Potential of Telehealth Applications
- From Dial-up to Digital: The Evolution of Telehealth
- Navigating how Pandemic Accelerated Virtual Healthcare
- Visionaries of Telehealth
- Technological Advancements in Telehealth
- Potential Future Capabilities

Roshan Deshmukh

Anuya Rupesh Waghmare
Telehealth: The New Face of Healthcare System

Telehealth, also known as telemedicine, is a technology-enabled approach to delivering healthcare services remotely, using telecommunications technology. It includes a wide range of digital solutions that facilitate virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and health-related education & support. It enables healthcare providers to interact with patients in real-time, regardless of their physical location, using video conferencing, messaging platforms, and other communication tools. This technology allows patients to connect with healthcare providers remotely, eliminating the need for in-person visits. At a basic level, telehealth platforms typically involve the following steps:
Firstly, patients initiate the process by scheduling appointments with healthcare providers using online portals or mobile applications. This streamlined approach allows for convenient booking and efficient coordination of care. Following appointment scheduling, patients and providers engage in virtual consultations. Through video conferencing or secure messaging platforms, individuals can communicate in real-time, enabling effective dialogue and information exchange. This virtual interaction bridges the gap between patients and healthcare professionals, ensuring timely access to medical expertise.
Subsequently, telehealth platforms support follow-up and monitoring mechanisms. Providers utilize these platforms to maintain ongoing care management, monitor health metrics, and manage medications for patients. This continuous monitoring and follow-up care contribute to improved patient outcomes and enhanced overall healthcare delivery. In essence, telehealth platforms revolutionize the healthcare landscape by streamlining appointment scheduling, enabling virtual consultations, facilitating medical assessments, and supporting follow-up and monitoring processes. Through these integrated steps, telehealth platforms enhance access to quality healthcare services and promote efficient remote care delivery.

Navigating How Virtual Care Transformed Healthcare to Telehealth
Telehealth technology is well-established and has experienced significant growth and adoption in recent years. While it has been in use for decades, recent advancements in technology, changes in healthcare delivery models, and the COVID-19 pandemic have accelerated its adoption and mainstream acceptance. It is considered an established technology, with ongoing innovation and refinement to improve usability, interoperability, and outcomes.
This technology has reached a high level of maturity and is experiencing widespread adoption across the healthcare industry. It has evolved from simple video conferencing tools to comprehensive platforms that support virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and patient engagement. Telehealth solutions are now integrated into healthcare systems and practices worldwide, with established protocols and standards for remote care delivery. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of telehealth, leading to its mainstream acceptance as an essential component of modern healthcare delivery.
Unlocking the Potential of Telehealth Applications
Core potential application for telehealth include:
- Primary care consultations play an important role in addressing common health concerns such as cold, flu, and minor injuries, providing patients with timely medical attention and guidance for managing this routine issue effectively.
- Specialty consultations offer patients access to expert’s specialists in diverse fields such as cardiology, dermatology, psychiatry and neurology, ensuring personalized and advanced care for complex medical conditions that require specialized expertise.
- Remote monitoring technology enables healthcare providers to track patients vital signs, manage chronic conditions, and oversee post-operative recovery from a distance, enhancing patients safety, convenience, and continuity of care.
- Mental health counseling and therapy sessions conducted remotely offer individuals access to professional support and guidance for managing emotional well-being and mental health concerns, providing a convenient and confidential platform for seeking help and improving overall mental wellness.
From Dial-up to Digital: The Evolution of Telehealth
Numerous innovators, researchers, and companies are driving advancements in telehealth technology. Established healthcare providers, tech giants, startups, and academic institutions are all contributing to the development and expansion of telehealth solutions. Companies such as Teladoc Health, Amwell, Doctor on Demand, and Babylon Health, are among the key players in telehealth, offering comprehensive platforms for virtual care delivery. Academic institutions and research organizations are conducting studies and trials to assess the efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of telehealth interventions across various specialties and patient populations. For instance, in 2021, CVS partnered with Teladoc to launch CVS Health's Aetna Virtual Primary Care. The partnership aimed that CVS Health use Teladoc's physician network to deliver virtual care services to patients remotely through video consultations, decreasing the patient's dependency on in-person consultations and visits.
Telehealth technology has evolved from basic telephone consultations to encompass a wide range of advanced capabilities. Initially relying on landline telephones, telehealth expanded with the internet to include email consultations and online patient portals. The advent of video conferencing revolutionized telehealth by enabling real-time, face-to-face interactions between patients and providers regardless of location. Mobile health technologies further enhanced telehealth by allowing patients to monitor their health using smartphones and wearable devices. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has improved diagnosis, treatment recommendations, and predictive analytics. Looking ahead, telehealth is eased to integrate virtual reality and augmented reality to enhance patient experiences and expand services. The ongoing evolution of telehealth technology continues to improve access to care, quality of services, and patients’ outcomes globally.
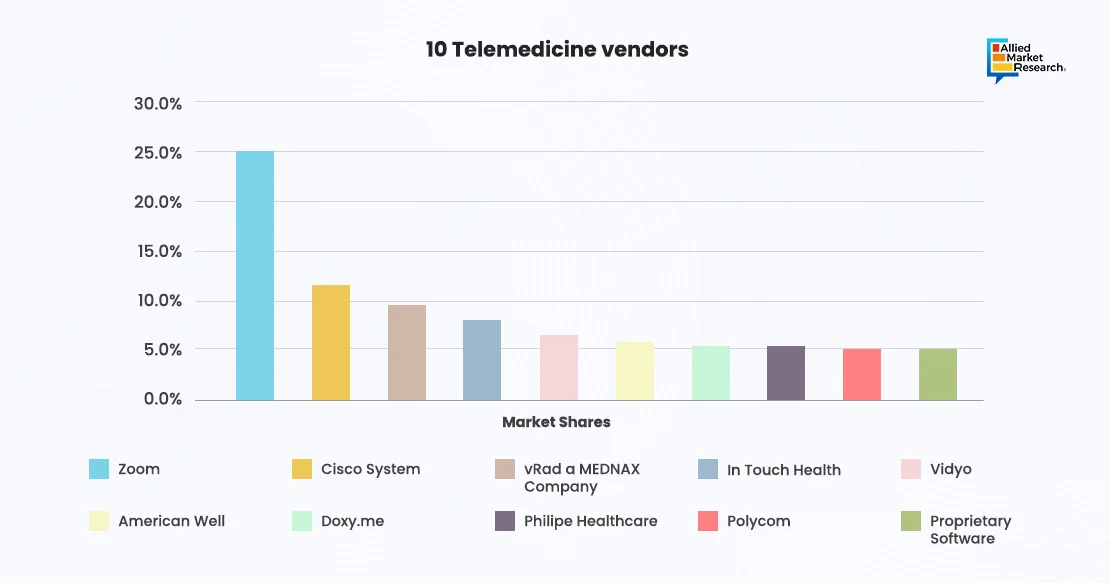
Despite its maturity and widespread adoption, telehealth still faces several technical limitations and challenges. These include issues related to data privacy and security, interoperability between different telehealth platforms and electronic health record (EHR) systems, reimbursement policies, and regulatory compliance. Connectivity issues, particularly in rural or underserved areas with limited internet access, pose challenges to delivering high-quality virtual care. Additionally, the digital divide may exacerbate disparities in access to telehealth services among vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, low-income individuals, and those with limited digital literacy skills. However, several cyber security measures such as regular risk assessment, end-to-end encryption and multi factor authentication can solve the security and privacy issues. Furthermore, different governments across the world are collaborating with the internet providers to bring connectivity to remote regions.
Telehealth technology integrates with a wide range of existing technologies to enhance its functionality and effectiveness. Integration with electronic health records (EHRs) enables seamless sharing of patient information and facilitates care coordination between healthcare providers. Wearable devices and remote monitoring sensors provide real-time health data that can be incorporated into virtual consultations to inform clinical decision-making and monitor patient progress. AI-driven analytics tools analyze large datasets generated by telehealth encounters to identify trends, predict outcomes, and personalize treatment plans. Additionally, telehealth platforms may integrate with patient engagement tools, secure messaging platforms, and telemedicine carts to provide a comprehensive virtual care experience.
Navigating how Pandemic Accelerated Virtual Healthcare
The adoption of telehealth is at an all-time high, with the technology being used across various contexts within the healthcare industry. Telemedicine platforms have experienced significant adoption, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, as they allow patients to access healthcare services remotely, minimizing the need for in-person visits and reducing the risk of virus transmission. Telemedicine is being used for a wide range of medical specialties, including primary care, mental health, dermatology, and chronic disease management. Additionally, wearable devices and health apps are increasingly popular among consumers for monitoring fitness and wellness metrics, tracking chronic conditions, and managing medication adherence. Electronic health records (EHRs) are standard in healthcare facilities for managing patient data and streamlining administrative tasks.
Several factors are driving interest and adoption momentum in telehealth. The COVID-19 pandemic has been a significant catalyst, accelerating the adoption of telemedicine and remote monitoring solutions as healthcare providers seek to maintain continuity of care while minimizing in-person contact. Advancements in technology, such as the proliferation of smartphones, wearable devices, and internet connectivity, have made health tech more accessible and user-friendly. Changing consumer expectations, particularly among younger generations accustomed to digital experiences, are driving the demand for convenient and personalized healthcare services. Additionally, regulatory changes and reimbursement policies that support telehealth and remote monitoring have incentivized healthcare providers to invest in digital health solutions.
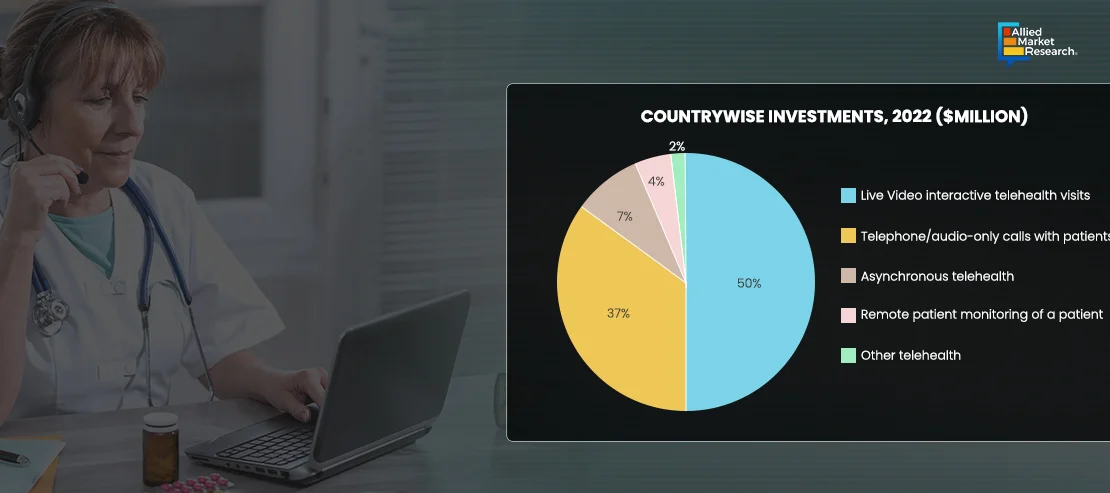
Despite the momentum, several factors are expected to hinder the adoption of telehealth. These include concerns about data privacy and security, particularly as healthcare data becomes increasingly digitized and vulnerable to cyber threats. Interoperability challenges between different health IT systems can hinder seamless data sharing and care coordination, leading to fragmented patient care. Regulatory barriers, such as varying telemedicine licensure requirements across states and countries, can create compliance challenges for healthcare providers and limit the scalability of telehealth solutions. Additionally, resistance to change among healthcare professionals, workflow disruptions, and upfront costs associated with implementing health tech solutions may slow adoption in some settings.
Visionaries of Telehealth
Healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and private practices, are early adopters of telemedicine, remote monitoring, and electronic health record systems to improve efficiency and modernize their operations to deliver more personalized, value-based care. Pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and academic medical centers are leveraging telehealth for drug discovery, clinical trials, and precision medicine initiatives. Employer-sponsored wellness programs and insurance companies are also early adopters of telehealth to promote employee wellness, reduce healthcare costs, and improve health outcomes. As adoption spreads, other industries and sectors, such as retail, technology, and government agencies, may increasingly leverage telehealth to improve population health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. For instance, in January 2024, Caregility launched a new intelligent telehealth edge device that supports multiple audio and video streams at bedside, enabling providers to deploy advanced hybrid care delivery models at scale. In a significant leap for inpatient care, Caregility introduced a new class of adaptive telehealth edge devices designed to seamlessly support hybrid care models that bring remote clinicians and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities into bedside workflows at the point of care. The groundbreaking APS200 Duo is the company’s first dual-camera, all-in-one system with onboard edge computing and a powerful dedicated graphics engine. The APS200 Duo includes a wide-angle camera for remote patient observation and a high definition 40x power zoom camera for virtual nursing programs and remote patient examinations.

Technological Advancements in Telehealth
The implementation of new technologies in telehealth is rapidly transforming the way healthcare is delivered, offering innovative solutions to improve access, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Some of the key technologies being integrated into telehealth platforms include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being used to analyze vast amounts of healthcare data, including patient records, medical images, and genomic information, to support clinical decision-making, personalize treatment plans, and predict patient outcomes. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also being deployed to enhance patient engagement and streamline administrative tasks.
Remote Monitoring Devices: Wearable devices and IoT (Internet of Things) sensors enable real-time monitoring of patients' vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, from the comfort of their homes. This continuous monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect early signs of deterioration, manage chronic conditions more effectively, and intervene proactively to prevent hospital readmissions.
Telemedicine Carts and Devices: Specialized telemedicine carts equipped with high-definition cameras, digital stethoscopes, and other medical peripherals enable remote consultations with specialists in various medical disciplines. These carts are particularly useful in emergency departments, intensive care units, and rural healthcare settings where access to specialist care may be limited.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is being explored to improve the security, integrity, and interoperability of health data exchanged during telehealth consultations. By creating a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger of patient records, blockchain can enhance data privacy and streamline data sharing between different healthcare providers and systems.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies are being used for medical training, patient education, and surgical planning in telehealth settings. Medical students and healthcare professionals can immerse themselves in virtual environments to practice complex procedures, while patients can use VR and AR applications to visualize their anatomy and better understand their medical conditions and treatment options.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms are being employed to transcribe and analyze audio recordings of telehealth consultations, converting spoken language into structured clinical notes and extracting relevant information for documentation and billing purposes. NLP can also assist with language translation services, enabling multilingual telehealth consultations.
Overall, the integration of these new technologies into telehealth platforms is revolutionizing healthcare delivery, expanding access to quality care, and empowering patients to take a more active role in managing their health. As technology continues to evolve, telehealth is expected to become an indispensable tool in the modern healthcare ecosystem, providing efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered care.
Potential Future Capabilities
The future of telehealth holds immense promise for transformative capabilities and applications. Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to enable more accurate and personalized medical diagnoses, treatment recommendations, and drug discovery processes. Wearable devices and biosensors may evolve to provide real-time monitoring of vital signs, early detection of diseases, and personalized health coaching. Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies can revolutionize medical training, patient education, and surgical simulations. Additionally, the integration of blockchain technology may enhance data security, interoperability, and transparency in healthcare transactions and medical records management.
Experts forecast continued growth and mainstream adoption of telehealth solutions, driven by factors such as demographic shifts, advances in technology, evolving healthcare delivery models, and changing patient expectations. Development roadmaps prioritize interoperability, usability, and data analytics capabilities to support seamless integration into existing healthcare workflows and systems. Telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and AI-driven diagnostic tools are expected to become standard components of healthcare delivery, expanding access to care, improving outcomes, and reducing costs.
To realize the full potential of telehealth, several technical, business, and social innovations or conditions need to occur. These include enhancing data privacy and security measures, fostering interoperability between disparate health IT systems, improving digital literacy among healthcare providers and patients, addressing regulatory barriers, and incentivizing collaboration and innovation across industry stakeholders. Additionally, the integration of health tech into value-based care models and payment structures can help align incentives and drive adoption.
Despite the promise of telehealth, several risks and concerns exist. These include data privacy and security risks, potential biases in AI algorithms, regulatory uncertainty, reimbursement challenges, and the digital divide, which may exacerbate healthcare disparities. Addressing these concerns requires robust data protection measures, transparent algorithmic validation processes, regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with patient safety, and efforts to bridge gaps in access to technology and digital literacy. Collaborative efforts among industry, government, and advocacy groups are essential to mitigate risks and ensure the responsible development and adoption of telehealth solutions.

