Table Of Contents
- Roadmap to Industrial 5.0
- Industry 5.0 Innovations Driving Human-Centric Manufacturing Excellence
- Future Industry 5.0 Applications
- Challenges and Opportunities
- Top Trends and Industry Leaders
- Future Trends in the Industry 5.0 Market: Anticipated Transformations
- Transformations in the Manufacturing Processes

Onkar Sumant

Shraboni Sen
Industry 5.0: The Evolution of Manufacturing in the Fourth Industrial Revolution

The convergence of physical production systems, digital technologies, human ingenuity, and creativity is what distinguishes Industry 5.0 from the previous industrial revolutions that focused on automation and optimization. In contrast to its predecessors, which were mostly about automation and optimization, it emphasizes collaboration between humans and machines to improve productivity, flexibility, and innovation in manufacturing processes. Using advanced technologies such as AI, robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR), Industry 5.0 aims to develop intelligent and adaptive production environments that empower workers while driving operational excellence.
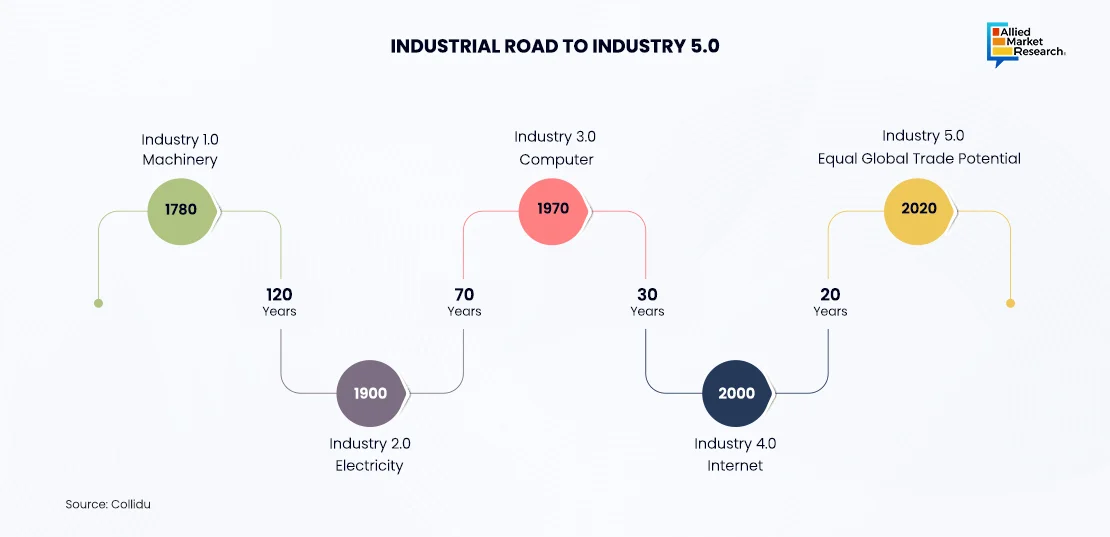
Roadmap to Industrial 5.0
Industry 5.0 works on the previous foundations of Industry 1.0 to 4.0, and each of these represents notable milestones in the progress of manufacturing. The mechanization of production by water and steam power during Industry 1.0 enabled the basis for mass production and industrialization. Also called assembly line electrification, industry 2.0 fundamentally transformed production efficiency and scale through this means.
With computers and automation systems, the digital revolution was heralded by Industry 3.0, which made it possible to introduce such devices that are capable of being programmed and controlled automatically using precise instructions that are expressed numerically in the form of words or symbols. After that came industry 4.0, tagged as a fourth industrial revolution that highlighted the need to incorporate internet of things (IoT) and cyber-physical systems data analytics into smart manufacturing predictive maintenance. It represents a paradigm shift toward human-centric manufacturing where humans work together with machines to bring about higher levels of productivity, flexibility, and innovation manufacturing processes.
Industry 5.0 Innovations Driving Human-Centric Manufacturing Excellence
Industry 5.0 has embraced human-centric manufacturing, collaborative robotics, digital twins, edge computing, and additive manufacturing to drive productivity, flexibility, and innovation in manufacturing processes:

- Human-Centric Manufacturing: The idea of human-centric manufacturing is at the core of Industry 5.0, which embraces humans working together with smart machines. By giving their employees advanced tools and technologies, firms realize their potential in full and create a context for continuous improvement and innovation.
- Collaborative Robotics (Cobots): Collaborative robots, or Cobots, play a significant role in Industry 5.0 by cooperating with humans to carry out complex tasks efficiently and accurately. These Cobots are fitted with high-tech sensors and AI algorithms that enable them to adapt to changing conditions while safely working with people, thereby increasing productivity and flexibility on the shop floor.
- Digital Twins and Simulation: Digital twins, virtual copies of real-world objects, have transformed the ways products are designed, produced, and maintained. Manufacturers create digital twins for production processes or equipment to simulate different situations; boost performance; detect potential problems before they happen; reduce downtime losses; and improve overall productivity.
- The Basics of Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics: By allowing manufacturers to process and analyze data closer to the source; edge computing technologies have made decision-making faster and security stronger. The incorporation of real-time analytics and machine learning algorithms at the edge provides actionable insights into sensor data collection, quality control, & energy management, optimizes production processes, and facilitates continuous improvement.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing or 3D printing has changed the way products are prototyped, customized, or produced. With progress in material science as well as printing technology, manufacturers now create intricate geometries, reduce waste material volumes, and shorten lead times, thus opening up new opportunities for innovation and ideal supply chain performance, respectively. For instance, on April 2, 2024, Volkmann USA introduced its vHub 250 metal powder storage system at the RAPID + TCT event. The vHub 250 features an in-line holding container that is installed upstream of a 3D printer as a powder supply and downstream to collect and hold excess metal powder from a build box after printing. The collected metal powder is sieved and stored or returned to the printer for reprocessing.
Future Industry 5.0 Applications
Industry 5.0 is poised to transform manufacturing across a wide range of industries and was valued at $129.1 billion in 2022. Further, it has witnessed a significant surge in various industrial applications. For instance, on March 14, 2024, Siemens Health announced a partnership with a leading medical research institute to develop a new AI-powered system for personalized cancer treatment. This system leverages Industry 5.0 principles by combining human expertise with machine learning to analyze patient data and recommend personalized treatment plans. Some of the key applications of Industry 5.0 include:
- Smart Factories: Industry 5.0 is responsible for the creation of intelligent and connected factories, which are agile and responsive to customer needs. Manufacturers achieve better efficiency, quality, and flexibility in production processes by integrating AI algorithms, IoT sensors, and robotics.
- Personalized Manufacturing: Industry 5.0 allows manufacturers to embrace mass customization by producing products that are tailored to individual customer preferences. Companies provide unique products with shorter lead times and higher levels of customer satisfaction by utilizing digital design tools, additive manufacturing techniques, and real-time data analytics.
- Remote Maintenance and Diagnostics: Industry 5.0 through the use of IoT-enabled sensors and augmented reality tools enables remote maintenance and diagnostics for industrial equipment. Downtime is minimized, maintenance costs are reduced, and asset utilization is optimized through real-time monitoring of equipment performance while remotely identifying problems in it.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Industry 5.0 enables end-to-end visibility and optimization of supply chains through the integration of IoT devices, blockchain technology, and predictive analytics. By tracking the movement of raw materials, components, and finished goods in real-time, manufacturers improve inventory management, mitigate risks, and enhance collaboration with suppliers & partners.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Industry 5.0 presents unprecedented opportunities for innovation and growth, it also poses several challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential. Some of the key challenges in the industry 5.0 market include:

- Cybersecurity Risks: With increased connectivity and data exchange, manufacturers are exposed to cybersecurity threats such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, and intellectual property theft. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and regulatory compliance frameworks is essential to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining trust in digital ecosystems.
- Skills Shortages: For Industry 5.0 to work, there must be a workforce with skills to exploit advanced technologies and adjust to fast-changing production environments. To close the skills gap and equip employees for success in the digital age, manufacturers need to invest in training and upskilling programs.
- Interoperability and Standards: Achieving seamless integration and interoperability between disparate systems and devices remains a significant challenge in Industry 5.0. Establishing common standards and protocols for data exchange, communication, and interoperability is crucial to enabling collaboration across different platforms and ecosystems.
However, despite these challenges, Industry 5.0 offers huge opportunities for manufacturers that enhance innovation, increase efficiency, as well as add value to the digital economy.

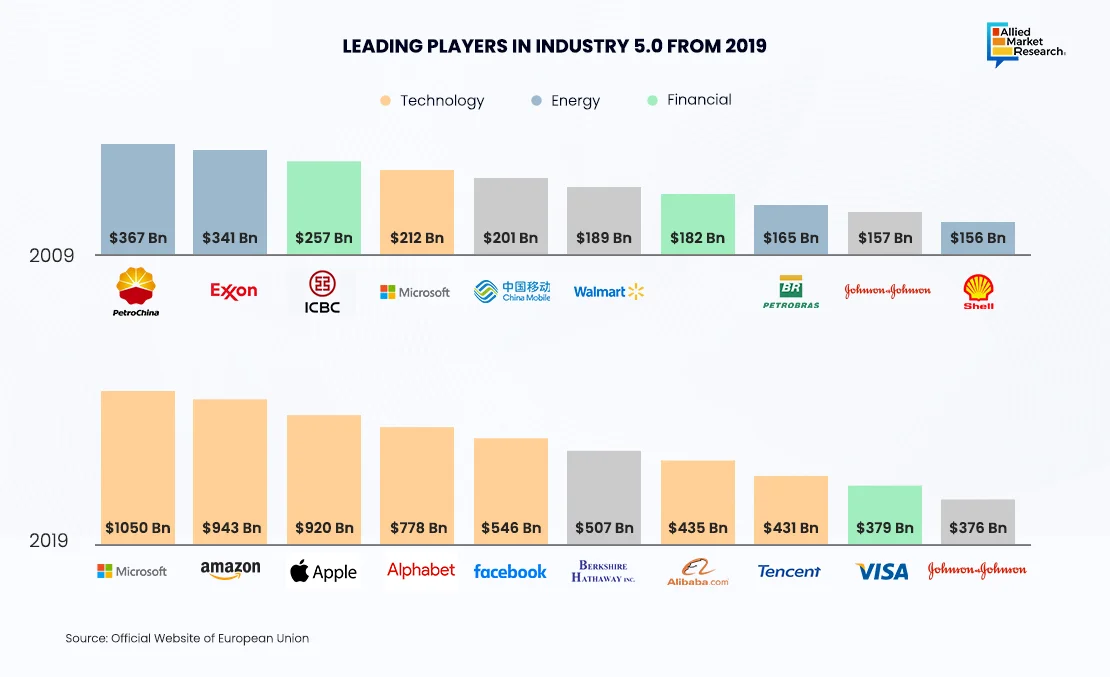
Top Trends and Industry Leaders
Industry 5.0 is characterized by automation, AI, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, which are the major reasons why Microsoft and Amazon stand out from the rest in this industry. These companies have customized their products to meet their customers’ needs. For instance, Microsoft Azure offers a wide range of AI tools and IoT solutions so that every product is modified according to specific requirements. In contrast, the strength of Amazon lies in its cloud-based offerings that assist in process automation and drive efficiency.
Industry 5.0 is an enhancement of Industry 4.0 concepts with more focus on collaboration between machines and humans, contributing to sustainability and innovation. Such modern technologies such as IoT and AI are not meant to replace people, however, rather develop their capabilities. Consequently, this makes it possible for industry 5.0 to be flexible in production, creative in manufacturing, and competent at troubleshooting & problem solving skills. In addition, industry 5.0 focuses on ethicality and sustainability through green manufacturing and circular economy principles integrated into it. It therefore implies that industry 5.0 represents a paradigm shift toward an inclusive and responsible industrial future where technology is used to empower human beings by making them better versions of themselves. Industry 5.0 aims to produce ecosystems that are socially aware, flexible, and withstand onslaught of time, thus ensuring sustainable development.
Future Trends in the Industry 5.0 Market: Anticipated Transformations
The industry is expected to experience game-changing trends that are expected to reshape the market:
Augmented Reality (AR) in Manufacturing: In the real sense, this is a technology that changes the manufacturing process of Industry 5.0 as such it overlays digital information onto physical subjects. This will enable employees to access important data and instructions or visual aids within their range of vision at work; something which improves production as well as efficiency and precision on the production line.
Predictive Maintenance with IoT Sensors: Industry 5.0 companies give priority to preemptive maintenance techniques that are facilitated through IoT sensors for continuous monitoring of machine health and performance data. With up-to-date knowledge, manufacturers predict possible failures, position maintenance interventions accordingly, and reduce downtime to optimize asset employment thereby lowering operational costs.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology offers unprecedented levels of transparency and traceability in supply chains, making it a key trend in Industry 5.0. By conducting transactions and validating them across a decentralized network, reliability and accuracy between product origins, manufacturing processes plus logistics are kept intact thereby creating a trustful and responsible framework throughout the supply chain community.
Customized Mass Production: Industry 5.0 makes possible the customization of items on a large scale through such advanced manufacturing technologies as 3D printing and robotics. Manufacturers create goods that are tailor-made to the preferences and needs of individual customers by utilizing AI algorithms and client information collected over time, giving rise to unique personalized experiences for consumers without compromising mass production efficiencies.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Technologies: HMI technologies such as gesture recognition, voice commands, and haptic feedback, are transforming the way humans interact with machines in Industry 5.0. The intuitive nature of these interfaces improves communication, collaboration, and control on the factory floor, which in turn enables employees to operate machinery and systems more efficiently and safely.
Distributed Manufacturing Networks: In a bid to promote the decentralization of manufacturing operations, industry 5.0 is in support of distributed manufacturing networks. By employing digital technologies and interconnected systems, manufacturers collaborate with their partners and suppliers across the globe toward producing goods closer to consumption centers so that lead times are reduced, transportation costs lowered, and environmental impact minimized.
Circular Economy Initiatives: Industry 5.0 supports the concept of circular economy where products or materials are reused, recycled, or repurposed to reduce waste and minimize environmental footprints based on sustainability objectives. Through adoption of closed-loop systems and innovative recycling technologies, waste streams are transformed into valuable assets by producers, which is projected to help them preserve natural resources and foster stewardship of nature.

Transformations in the Manufacturing Processes
In summary, Industry 5.0 has brought a shift in the manufacturing processes. From human-centered to machine-based; this vision is characterized by human-machine collaboration, digital transformation, and innovation. As industries grapple with the intricacies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), Industry 5.0 has given them a new transformative goal for outmost production. By adopting modern technologies, nurturing an innovative climate, as well as tackling major challenges confronting them, manufacturers tap into new opportunities for expansion, competitiveness, and sustainability in global markets. Industry 5.0 is expected to redefine how goods are designed, manufactured, and consumed ushering us into another era of smart adaptive production systems.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

