Exploring the Potential: Understanding Virtual Currency

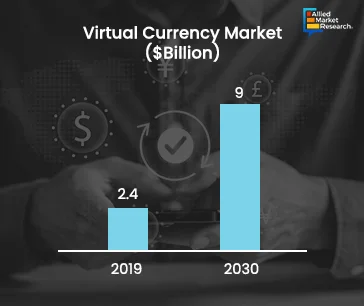
Virtual currencies, a significant financial innovation, have rapidly evolved to influence various aspects of the global economy. Originating as niche technological experiments, virtual currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have flourished into a diverse ecosystem of digital assets. These currencies leverage blockchain technology to ensure decentralized control and enhance security, contrasting sharply with traditional, centralized financial systems. This has caused the virtual currency market to grow from $2.4 billion in 2022 to $9 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of over 14%.
A prime example of the practical application of virtual currencies is in the realm of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). Over 130 countries are exploring the development of CBDCs, with nations like The Bahamas, Jamaica, and Nigeria having already launched their digital currencies. The European Central Bank, too, is making strides with the digital euro, aiming to enhance financial inclusion and streamline payment systems??. For instance, in October 2023, the European Central Bank (ECB) announced the commencement of a two-year "preparation phase" starting November 1 for the digital euro project. During this period, the ECB aims to finalize regulations and choose private-sector collaborators. This phase will involve testing and experimentation, but a final decision on launching the digital euro has not been made. The digital euro would allow the use of central bank money in digital format, complementing traditional banknotes and coins.
The momentum behind these digital currencies isn't confined to governmental initiatives. The private sector, too, plays a crucial role. For instance, companies are exploring the use of virtual currencies for cross-border transactions, which could significantly reduce transaction times and costs. For example, Singapore's collaboration in October 2023 on Project Mandala is a case in point, aiming to embed regulatory compliance in cross-border transactions through decentralized finance (DeFi) technologies??.

Additionally, innovative approaches in other regions, such as Zimbabwe's introduction of a gold-backed digital currency in October 2023, highlight the diverse strategies being employed to stabilize national economies and provide more secure financial instruments.
The landscape of virtual currencies is dynamic and multifaceted, presenting a mixture of opportunities and challenges. As this sector continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of finance globally.
Technological Foundations and Innovations in Virtual Currencies
The evolution of blockchain technology highlights the growth and efficiency of these currencies, transforming numerous industries through enhanced security, transparency, and functionality.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Enhanced Security: The adoption of advanced cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs have been pivotal. These protocols allow for the verification of transactions without revealing any underlying data, thus ensuring privacy and security within blockchain networks. This technology is particularly beneficial in sectors like healthcare, where the secure exchange of sensitive information is crucial.
Interoperability Between Blockchains: Recent developments in blockchain technology have significantly improved interoperability, allowing for seamless communication between different blockchain networks. This is achieved through protocols that enable the transfer of liquidity and smart contracts across diverse systems, enhancing the utility and efficiency of digital assets across various platforms. For instance, in May 2024, The Interchain Amplifier developed by Interop Labs is advancing blockchain interoperability by connecting Bitcoin, Polkadot, and Hedera networks. This smart-contract-based toolkit facilitates permissionless connections between these platforms, aimed at enhancing security and broadening use cases across the blockchain ecosystem. The initiative is currently in the development phase, with pilot participants including Stacks and Moonriver, exploring applications ranging from finance to gaming.

Tokenization of Assets: The process of asset tokenization, converting physical and digital assets into digital tokens, has been on the rise. This method provides liquidity and makes high-value assets more accessible to a broader range of investors. Notable applications include real estate and art, where blockchain facilitates transparent and efficient transactions.

Smart Contracts and Automation: Blockchain technology facilitates the use of smart contracts, which automatically execute agreements based on predefined rules. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, decreasing costs and increasing transaction speed. This technology is not only applicable in finance but also in areas like supply chain management, where it ensures the authenticity and traceability of products.
Expansion of Blockchain Applications: The versatility of blockchain is evident as it extends beyond traditional finance. Governments and industries are increasingly exploring blockchain for data management and digital identities, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize public administration and commercial activities.
These technological advancements are setting a strong foundation for the future of virtual currencies, promising more innovative applications and broader adoption across different sectors.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Domain of Virtual Currency The virtual currency market, while offering substantial economic opportunities, presents numerous challenges that necessitate careful navigation. This complex landscape demands robust regulatory frameworks to mitigate risks while capitalizing on the potential benefits.
Regulatory Challenges: One of the primary challenges in the virtual currency market is the need for comprehensive regulatory frameworks to manage the risks associated with these digital assets. The regulatory landscape is fragmented and rapidly evolving, with different jurisdictions having varying approaches to crypto assets and virtual currencies. For example, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has exerted jurisdiction over investments made in virtual currencies as securities, indicating that traditional securities laws apply to these new forms of investments. For instance, in June 2023, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Coinbase, the largest U.S. cryptocurrency platform, for operating without proper disclosures and for trading at least 13 crypto assets that it contends should have been registered as securities. These assets include tokens like Solana, Cardano, and Polygon. The lawsuit, filed in Manhattan federal court, seeks financial penalties and compliance with U.S. securities laws. Similarly, South Africa in October 2022 officially classified crypto assets as financial products, bringing them under closer regulatory oversight by the country's Financial Sector Conduct Authority. This classification, effective immediately, regards crypto assets as digital representations of value that can be traded, transferred, or stored electronically for various purposes including payment and investment. This regulatory move aims to increase control amidst the global tightening of cryptocurrency regulations following market volatility and company failures.
Financial Crime Risks: Virtual currencies also pose significant financial crime risks. They enable rapid international transactions with a degree of anonymity, which can be exploited for money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities. For instance, virtual currencies have been used for a variety of criminal activities, from funding illegal enterprises to evading financial regulations. Also, their utilization in ransomware attacks and other cybercrimes has prompted significant scrutiny and regulatory response. However, they do offer potential benefits such as quicker and cost-efficient transaction settlements, which could enhance the efficiency of financial systems globally.
Opportunities for Innovation: Despite these challenges, virtual currencies present remarkable opportunities for innovation in financial services. They facilitate faster transaction processing and potentially lower transaction costs, contributing to more dynamic financial markets. Moreover, virtual currencies can increase financial inclusion by providing services to those with limited access to traditional banking facilities.
Technological Advancements: The development and integration of advanced blockchain technologies, such as smart contracts and DeFi platforms, offer ways to overcome some of the inherent challenges in the virtual currency market. These technologies can provide more secure, transparent, and efficient transaction mechanisms compared to traditional financial systems.
Collaboration and Global Coordination: To fully utilize virtual currencies while managing risks, cooperation among governments, the virtual currency industry, and traditional financial sectors is highly important. This includes international cooperation to create harmonized regulatory standards and innovative solutions to prevent financial crimes and enhance transaction security.
Case Study: The Sand Dollar - Pioneering Financial Inclusion in The Bahamas
Introduction
The Sand Dollar project in the Bahamas represents a pioneering move toward leveraging digital currency to enhance financial inclusion, especially in remote areas. The Sand Dollar, launched by the Central Bank of the Bahamas in October 2020, aimed to improve financial access in remote areas with fewer people and spread-out locations.
Objectives and Implementation
The primary goal of the Sand Dollar was to make financial services more accessible and reduce the costs associated with physical cash management across the islands. This digital currency was distributed through an e-wallet system and managed by Authorized Financial Institutions (AFIs), facilitating transactions that are both secure and efficient. The Sand Dollar allows for various transaction limits based on user verification levels, accommodating different user needs while maintaining security and regulatory compliance.
Challenges
Despite the innovative approach, the Sand Dollar faced challenges related to adoption and impact. Initial research suggested that financial exclusion was less of an issue than anticipated, with a high percentage of the population already engaged in the banking system via traditional means. Nonetheless, the high costs and logistical challenges of transporting physical currency to remote islands presented a significant barrier to financial inclusion, which the Sand Dollar aimed to mitigate.
Outcomes
Two years post-launch, the adoption rate of the Sand Dollar was modest, indicating the need for more robust community engagement and education strategies to boost acceptance and usage. The low initial adoption rates highlight the challenges of transitioning from traditional financial systems to a digital-first approach, especially in regions with established banking practices and potential resistance to new technologies.
Future Prospects
Despite the challenges, the potential of the Sand Dollar to foster greater financial inclusion remains significant. The Central Bank of the Bahamas is working hard to make people more aware, improve infrastructure, and update regulations, which could make this initiative more successful and widespread. The Sand Dollar project serves as a valuable model for other nations considering similar initiatives to address financial inclusion, particularly in regions facing geographical and logistical obstacles.
Strategic Insights
This case study underscores the importance of understanding the local context in the deployment of digital currencies aimed at enhancing financial inclusion. It also highlights the need for ongoing public education and engagement to ensure the successful adoption and utilization of innovative financial technologies. For countries exploring similar initiatives, the experiences of the Sand Dollar provide important insights into the potential challenges and strategies necessary to maximize the benefits of digital currencies in enhancing access to financial services.
Summing up
Yet, there should be active public involvement, clear regulations, and tailored technological systems. Learning from global experiences will also be important in building a strong digital finance future.
Allied Market Research provides an in-depth analysis of the burgeoning virtual currency market, focusing on technological advancements, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks. Our detailed reports equip stakeholders with essential insights into the pivotal role of these currencies in enhancing financial transactions, security, and environmental sustainability. Businesses can utilize these insights to tap into new opportunities, drive innovations, and foster smarter, sustainable financial solutions that improve the market's efficiency. For a comprehensive examination of growth drivers and investment opportunities in the industry, feel free to contact our experts!



