Table Of Contents

Roshan Deshmukh

Koyel Ghosh
The Current and Future State of the Sharing Economy

The sharing economy, often referred to as the economy of collaboration or peer economy, is a type of capitalism, in which people or companies provide access to goods, services, or assets to other people via online markets or digital platforms. In place of buying things altogether, it enables peer-to-peer transactions by utilizing technology to make renting, sharing, and exchanging products and services possible. Ride-sharing services such as Uber and Lyft, home-sharing services such as Airbnb, peer-to-peer financing channels, co-working facilities, and even freelancing platforms where people give their talents and services to others are typical instances of sharing economy platforms. The sharing economy fosters a feeling of community and social trust among members while also promoting efficiency of resources, environmental responsibility, and cost savings.
There are five main types of categories in the Sharing Economy Market, which can be summarized as:
- Sharing Accommodation
- Short-term Rental
- Long-term Rental
- Shared Transportation
- Ride-Hailing
- Carpooling
- Micromobility
- Peer-to-peer Car Rental
- Sharing Finance
- Peer-to-peer Lending
- Crowdfunding
- Micro Finance
- Payment Processing
- Sharing Good and Services
- Skill-sharing
- Tool and Equipment Rental
- Clothing & Fashion Rental
- Food & Grocery Sharing
- Co-working Spaces
Importance of ride-hailing ecosystem
Ride-hailing, also referred to as ridesharing or app-based transport, is a service that allows customers to book trips from a network of drivers using a smartphone app. This business often works on a peer-to-peer basis, connecting clients with local drivers who utilize their automobiles for transportation. According to AMR, the ride-hailing segment holds the major market share in the sharing economy market.
The present ride-hailing industry landscape is characterized by intense competition between big competitors such as Uber and Lyft, as well as regional players such as Grab and Didi Chuxing. These platforms have changed urban mobility by providing quick, on-demand trips at affordable rates. Factors influencing the market include increased urbanization, which raises demand for mobility alternatives, particularly in densely populated regions where buying a car is impracticable.
Furthermore, the growth of the gig economy has increased the available pool of drivers, allowing ride-hailing businesses to fulfill rising demand more effectively. In addition, technological improvements, notably the increasing use of smartphones and navigational devices with GPS, have made booking and routing operations more user-friendly, improving the entire customer experience. Furthermore, the focus on sustainability and ecological issues has resulted in the introduction of electric and hybrid cars into the ride-hailing services, this helps the transportation sector to shift towards greener initiatives to safeguard the environment. On the other hand, regulatory problems, such as concerns about labor rights, security regulations, and lack of price transparency for booking rides, continue to hinder the growth of the market.
Ride-hailing has become an integral part of urban mobility in North America, with high acceptance rates in major cities such as New York, San Francisco, and Toronto. The availability of cell phones, a substantial population density, and a vibrant gig economy all contribute to its appeal. Similarly, ride-hailing has grown rapidly in Europe, particularly in major cities such as London, Paris, and Berlin, in which it integrates existing public transportation networks and tackles last-mile connection issues. – The concept has grown dramatically in the Asia-Pacific area too, owing to a growing middle-class population, increased urbanization, and the widespread use of smartphones. Companies like Grab in Southeastern Asia and Didi Chuxing in the People's Republic of China dominate the sector, providing a diverse variety of services such as delivery of food and finance.
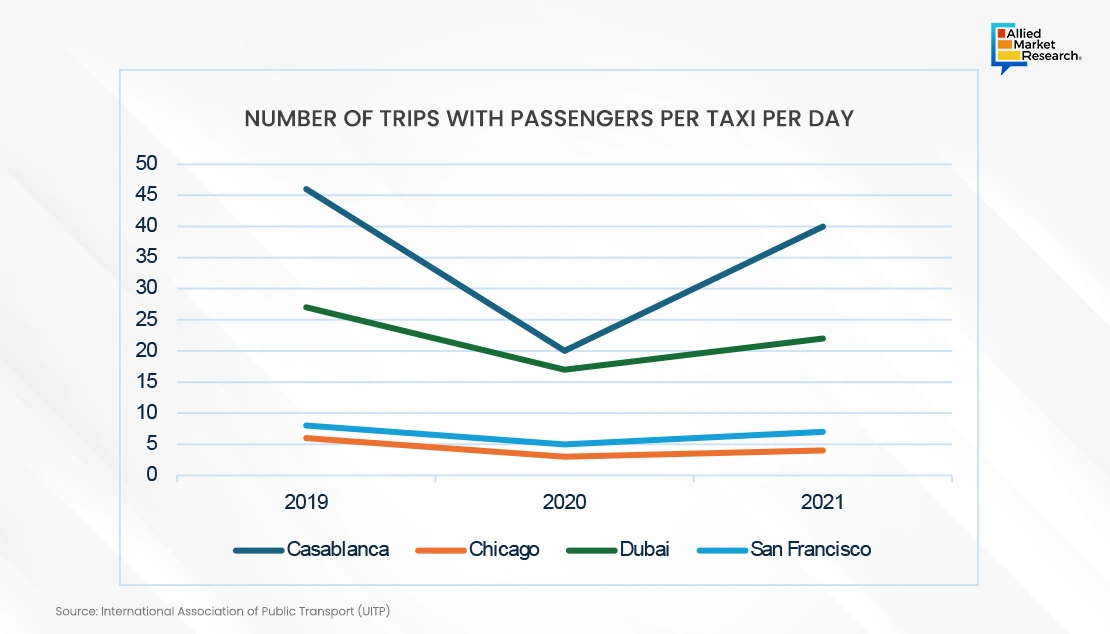
Role and importance of the Internet
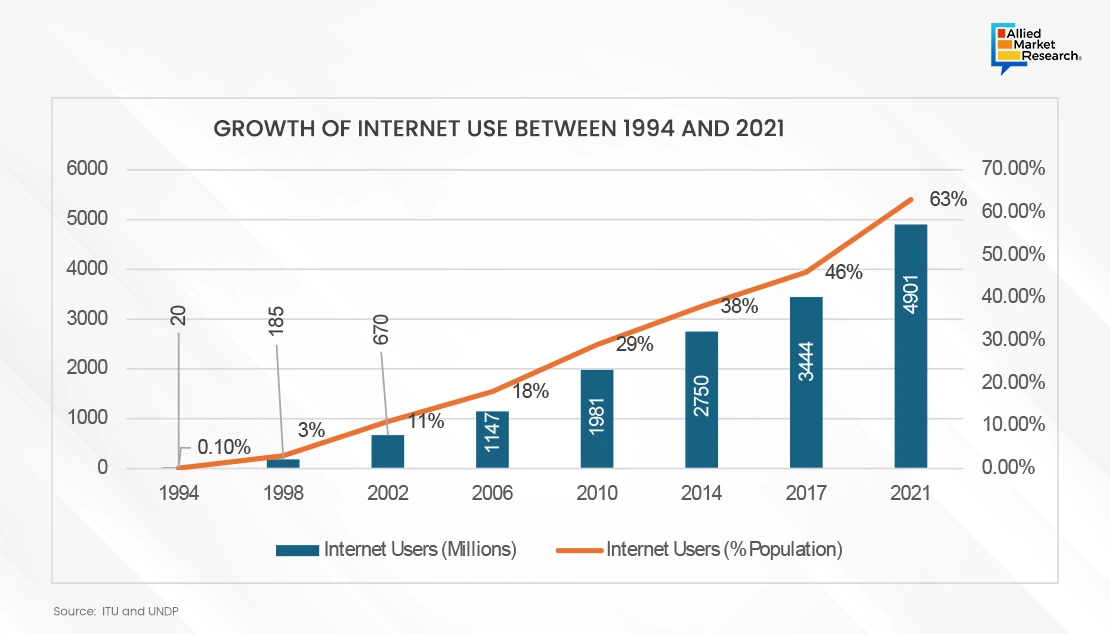
The internet is important for promoting and defining the sharing economy industry, since it serves as the foundation for peer-to-peer interactions, transactions, and participant confidence. For starters, it offers digital platforms and markets where people may directly engage and deal with one another, reducing the need for conventional middlemen and allowing for more effective resource allocation. Whether it's sharing accommodations on platforms like Airbnb, giving rides on applications like Uber, or leasing out personal possessions on platforms like Airbnb, the internet acts as a virtual marketplace where these transactions may take place easily. Additionally, the internet provides improved transparency and recognition infrastructure, allowing users to obtain ratings, evaluations, and feedback from past transactions, therefore establishing trust and mitigating the dangers inherent in peer-to-peer transactions. Furthermore, the Internet facilitates real-time interaction and collaboration among users, allowing for fast booking, processing of payments, and service delivery. Furthermore, the internet enables data-driven insights and personalized suggestions by employing algorithms and user data to match supply and demand more efficiently while also improving user experiences.
The potential of the sharing economy is being recognized in different sectors and by different countries which has increased the surge in acquisitions and expansion initiatives by companies within the sharing economy industry signals a promising outlook for the sector. Companies from diverse industries are consciously acquiring or collaborating with sharing economy firms to diversify their services, increase their customer base reach, and generate new revenue streams. These investments not only show faith in the sharing economy's long-term viability but also illustrate a proactive attitude to adjusting to changing consumer tastes and market dynamics. Additionally, the increasing trend implies a global need for shared transportation, lodging, and services, which is being pushed by urbanization, technology improvements, and shifts in lifestyles. Sharing economy entrepreneurs may accelerate development, scale operations, and better negotiate regulatory difficulties by using existing organizations' resources, experience, and networks.
List of Acquisitions and Partnerships in Different Sectors (2021-2023)
Transportation:
- Avis Group, a traditional car rental company, acquired Zipcar peer-to-peer car-sharing company in 2023.
- In 2021, Hyundai invested $400 million in Motional, a joint venture of Hyundai and Aptiv Group. The investment was for the R&D of autonomous vehicle development for future ride-sharing services.
Hospitality:

- In 2021, Accor Hotels invested in Oasis Collections, to increase co-living facilities and offer affordable living spaces.
Food Delivery:
- In 2023, Deliveroo a food delivery company partnered with Gopuff a digital delivery service company, to offer grocery delivery services in U.S. and Europe
- In 2021, Just Eat, a food delivery company, acquired Grubhub, a food ordering platform.
Artificial Intelligence as a key element in the sharing economy ecosystem
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays an important role in both the present and future landscapes of the sharing economy market, revolutionizing resource allocation, transaction facilitation, and user experience personalization. AI technologies are currently being incorporated into sharing economy platforms to increase efficiency and customer engagement. AI-powered algorithms analyze massive volumes of data to optimize pricing tactics, match supply and demand, and forecast customer preferences, ultimately increasing the utilization of resources and income for service providers.
Additionally, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide real-time help and personalized suggestions to consumers, improving the entire customer experience and instilling trust and loyalty. For instance, Airbnb's trip platform uses AI for personalized recommendations, Uber uses machine learning to predict car maintenance, and Turo uses AI to optimize pricing for car rentals.
The importance of AI in the sharing economy industry is expected to grow at a significant rate. Machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision advances will encourage the introduction of more advanced AI applications, such as automated forecasting, autonomous decision-making, and self-driving cars, which have the potential to change the traditional pattern of how products and services are distributed and consumed. AI-driven platforms can bring in fresh business models and revenue streams like dynamic pricing, targeted marketing, and on-demand services. This can lead to more innovation and growth in the sharing economy. However, as AI continues to alter the sharing economy market, it will create key ethical and regulatory concerns, such as data privacy, algorithmic prejudice, and job displacement, all of which can contribute to hindering market growth.
Future scenario for sharing economy industry
Looking into the future, the sharing economy market is expected to witness some major changes which would include the introduction of innovation, growth into new areas, and greater technological integration.
A key aspect of the sharing economy's future scenario is the growth of collaborative platforms that serve an extensive variety of requirements other than traditional transportation and lodging. The sharing economy, which includes shared workplaces, equipment, peer-to-peer loans, and skill-sharing networks, is expected to encompass various businesses. This will offer consumers more options, cost savings, and better access to resources. Moreover, technological breakthroughs such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things will play a significant role in increasing efficiency, trust, and transparency in sharing economy transactions.
Smart contracts and decentralized platforms will speed up the trade of goods and services, while AI-powered algorithms will personalize suggestions and optimize resource allocation. Furthermore, sustainability will become a prominent feature in the future sharing economy, eco-friendly practices, circular business models, and shared asset ownership to reduce waste and environmental damage. Regulatory frameworks will change further to handle growing difficulties and maintain a fair and impartial environment for both existing players and new entrants to the sharing economy ecosystem.
At Allied Market Research, our commitment is to provide vendors with a comprehensive understanding of the sharing economy. By offering you insights into this evolving practice, we aim to guide you in exploring its potential to the fullest extent. Adopting the sharing economy can bring new opportunities to your business, encouraging innovation, efficiency, and better engagement with customers. We are here to support you on this transformative journey, providing the knowledge and strategies necessary to seamlessly incorporate the sharing economy into your business model.

