The Future of Travel: Unveiling the Global Impact and Strategic Insights of E-Passports

E-passports represent a significant evolution in travel documentation, combining traditional passport features with advanced digital security technologies. Introduced to enhance border security and streamline immigration processes, e-passports are equipped with an embedded electronic chip. This chip securely stores the biographical data and biometric information, such as fingerprints and digital photographs of the passport holder.
The inception of e-passports began as early as 2005, with more than 140 countries now issuing these secure travel documents to aid in the fight against identity theft and fraudulent activities??. E-passports use Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) technology to protect the integrity of the data stored on the chip. This system involves digital certificates and encryption to verify identities and secure data, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized users to access or alter the information?.
The design of e-passports prioritizes security, which includes a variety of measures like holograms, ultraviolet printing, and tamper-evident materials. These features are carefully designed to deter forgery and help in verifying the authenticity of the passport under inspection. The inclusion of biometric data further fortifies security, ensuring that the passport holder presenting the document is the legitimate owner.
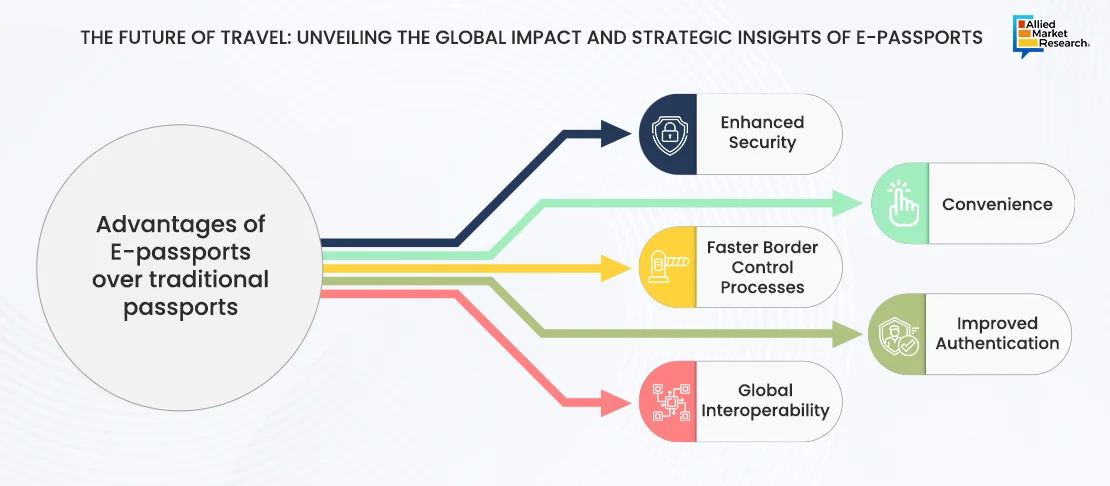
Globally, the adoption of e-passports is encouraged by standards set by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), which promotes interoperability and security among international travel documents. This standardization facilitates global acceptance of e-passports, enabling smoother and more secure international travel?.
Countries like India have taken significant steps toward the modernization of their passport systems. In February 2022, the Indian government announced its plans to introduce chip-based e-passports. These passports will incorporate advanced security features like contactless smart card technology and RFID chips. This initiative aims to bolster security measures and improve convenience for travelers.E-passports are not just a tool for security but also convenience. They support automated border control systems, such as e-gates, which use biometric verification to speed up the immigration process, thereby reducing queues and improving the overall travel experience??.
As technology evolves, so does the capability of e-passports. Future enhancements may include additional biometric verifications like iris scans, potentially increasing the reliability and security of international travel documents even further. This ongoing development underscores the critical role e-passports play in the modernization of global travel and border security.
Adoption Trends of E-Passports
The global adoption of e-passports has been significantly increasing, driven by the need for enhanced security and more efficient border control processes. In 2023, a notable surge in the usage of biometric passports, a synonym for e-passports, was observed globally. These passports incorporate advanced biometric technology, including features like facial recognition, fingerprint scans, and sometimes iris scans, embedded in an RFID chip to prevent identity theft and fraud??.
Europe leads in the adoption and integration of e-passports, spurred by early initiatives and extensive application of technology. European countries were among the first to adopt e-passports, embedding advanced security features and biometric data. The European Union requires all member states to issue biometric passports, ensuring secure and efficient cross-border travel.
In the Asia-Pacific region, countries like Australia, Japan, and South Korea have embraced biometric passports as part of their border security enhancement strategies. The adoption in this region reflects a broader trend toward strengthening national security and improving operational efficiencies at borders through technology?.
The Middle East, including nations like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, has also adopted e-passports to boost security measures. These countries utilize state-of-the-art border control technologies with biometric passports to ensure the safety of both citizens and visitors?.
Simultaneously, the US has implemented biometric features in its e-passports as part of its strategy to enhance border security and combat identity fraud. The Department of Homeland Security has progressively integrated biometric screening at various entry points, which not only enhances security but also expedites the travel process.
On the technological and market development front, companies are continuously innovating to enhance the security and user-friendliness of e-passports. Innovations include the development of new biometric recognition technologies, advanced encryption techniques, and anti-tampering measures. For instance, in December 2022, Infineon Technologies AG introduced cutting-edge e-passport security designed for the quantum computing age. This innovation enables effortless border crossings by seamlessly transferring data between the secure e-passport and airport scanners to swiftly verify passenger identities, all without the need for physical contact. Similarly, in November 2022, Idemia unveiled its latest innovation: the 'Abroadia' demo passport, featuring state-of-the-art security enhancements. These passports offer a seamless authentication experience, enabling individuals to securely verify their identity using a smartphone, effectively transitioning their physical identity into a digital one. This advancement empowers travelers to conveniently check-in for flights from home and expedite their journey through security checkpoints.
Security Enhancements and Challenges in E-Passports
The evolution of e-passports has introduced significant security enhancements, making international travel more secure and efficient. These documents incorporate an electronic chip that stores the traveler's biographic information and biometric identifiers such as digital photographs, which are crucial for verifying the traveler's identity. The United States, for instance, mandates that e-passports issued under the Visa Waiver Program include these security features to prevent unauthorized data skimming and ensure the document's integrity?.
E-passports employ various advanced technologies, including Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and biometrics, which significantly bolster border security measures. These technologies facilitate the secure and rapid verification of travelers' identities at points of entry, streamlining immigration procedures and reducing the potential for human error.

Despite the broad adoption, the implementation of e-passports comes with challenges, including high costs and privacy concerns. The sophisticated technology required for e-passports leads to higher production costs, which can be a barrier to widespread adoption in less economically developed countries?.
Another major concern is privacy; there is a risk that sensitive personal data could be intercepted or misused. This concern necessitates continuous improvements in cryptographic methods and the secure handling of biometric data to safeguard against potential breaches.
Moreover, tampering and counterfeiting threats persist for the physical components of e-passports, including the passport booklet. Security printing techniques are therefore critical in maintaining the integrity of these documents. High-security printing methods, including the use of special inks and papers that are difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, play a vital role in protecting these elements?.
The security of e-passports is further enhanced through international cooperation, with countries and regulatory bodies working together to standardize technologies and enhance security protocols. Such collaboration is essential for adapting to evolving threats and ensuring the effectiveness of e-passports as a tool against fraud and illegal entry?.
Even though e-passports represent a significant leap forward in travel security, they require ongoing innovation and vigilance to address challenges such as data privacy, potential system vulnerabilities, and the ever-present risk of counterfeiting.
It's essential to prioritize these efforts to maintain the balance between the advantages of e-passports and the challenges they pose, particularly as they play a more central role in global travel security.
As we progress, the integration of emerging technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, is expected to further enhance the security and efficiency of e-passports. This ongoing evolution highlights the significant role that e-passports are set to play in the future of global travel and border security?.
Case Study: HID Designs Kingdom of Bahrain’s New e-passport Solution
Overview
The Kingdom of Bahrain, an island country in the Arabian Gulf, is known for its rich culture and as a financial and tourist hub. To modernize its passport system, Bahrain partnered with HID to develop an innovative e-passport solution. This case study explores the challenges faced, the solutions implemented, and the outcomes of this modernization effort.
Challenge

Bahrain needed to upgrade its machine-readable passport system to an e-passport system to enhance travel security and efficiency for its citizens. The challenge was to develop a comprehensive solution covering enrollment, adjudication, personalization, and issuance of identity documents.
Solution
Bahrain collaborated with HID's award-winning design team, known for their work in various countries including Estonia and Ireland, to create a robust e-passport solution. This involved an extensive workshop with Bahrain officials to design a passport that reflects the nation's culture.
The new e-passport features:
Distinct Visa Pages: Incorporating ten unique designs representing Bahraini culture, including elements like sea life and Formula One racing.
Advanced Security Features: These passports include features like HID Mirage, which uses negative laser engraving for enhanced security, and HID Safelink, which provides resistance against data page tampering.
Biometric and Biographical Security:Encrypted data stored on a chip, including a color portrait of the holder, ensuring high security and global compliance.
Technology Integration
HID Integrale Software: Manages the data from enrollment through to issuance, ensuring secure handling of personal data.
SOMA Chip Operating System: Used for storing biometric data securely on the chip.
Result :The introduction of the e-passports has streamlined visa applications and improved the immigration process for Bahraini travelers. The use of eGates based on these new passports has made international travel more efficient. Furthermore, Bahrain’s inclusion in the ICAO Public Key Directory has enhanced the global acceptance of its electronic passport, allowing for faster border control processes and potentially reducing visa requirements for its citizens.
Impact :The successful deployment of Bahrain’s e-passport system exemplifies how technology can enhance national security while preserving and promoting cultural heritage. This case highlights the effectiveness of integrating advanced security features in travel documents and the benefits of international cooperation in standardizing travel security measures.
Summing up
E-passports, embedded with biometric data and advanced security features, are reshaping international travel. These documents enhance border security, streamline immigration processes, and ensure global interoperability by adhering to international standards. As technology evolves, e-passports are set to integrate further innovations like blockchain and AI, promising to make global travel more secure and efficient while fostering international cooperation.
Allied Market Research delves deeply into the flourishing sector of e-passports, offering detailed analyses of technological innovations, market trends, and the regulatory environments shaping the industry. Our comprehensive reports are tailored to provide stakeholders with crucial insights into the essential role of these passports in enhancing travel security, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Businesses can leverage these insights to capitalize on emerging opportunities, spearhead innovations, and promote smarter, more sustainable travel solutions that enhance the sector's effectiveness.
For a detailed exploration of the growth drivers and investment opportunities in the e-passport industry, feel free to contact our experts!



