Table Of Contents
- Embracing Sustainability Amidst Global Demand and Climate Imperatives
- Understanding Emission Sources and Sustainability Challenges
- Achieving the Semiconductor Industry's 1.5°C Target by 2030
- Near Term Actions
- Mid Term Actions
- Long Term Actions
- What Are the Leading Semiconductor Manufacturers up to?
- Conclusion

Sonia Mutreja

Koyel Ghosh
Environmental Sustainability in Semiconductors Manufacturing
"The surging demand for semiconductors is leading to an increase in industry emissions. While semiconductor fabs are vocalizing their sustainability commitments, further actions are indispensable to realize the goal of achieving net-zero emissions."
Embracing Sustainability Amidst Global Demand and Climate Imperatives
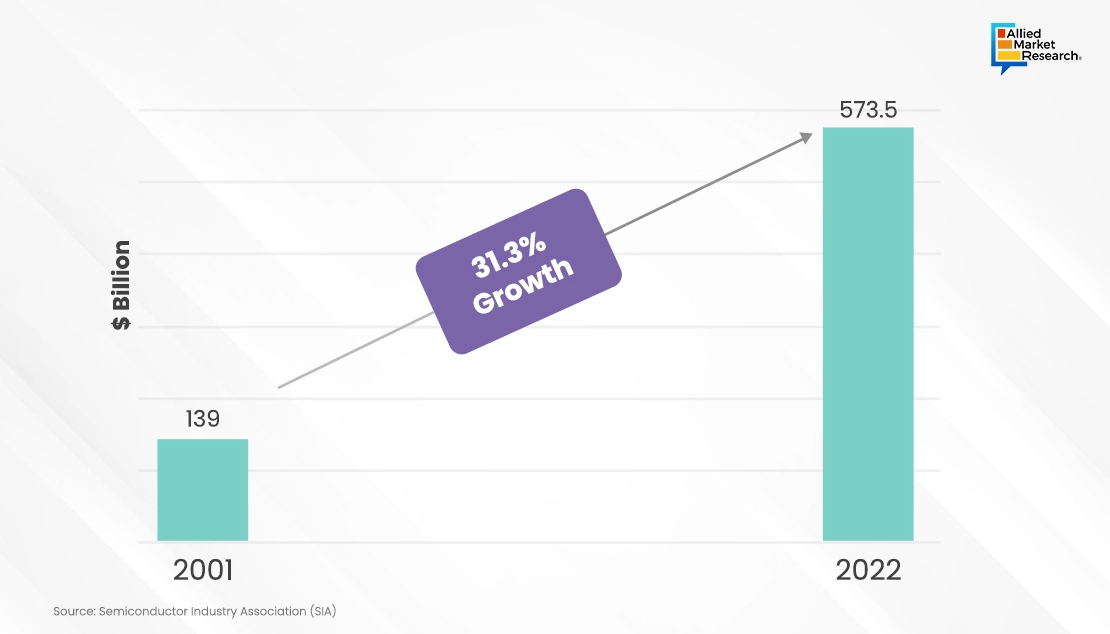
Taking a broader perspective beyond short-term fluctuations in demand and examining the long-term trajectory spanning the past two decades, the semiconductor industry has demonstrated consistent expansion. Over the last twenty years, the semiconductor industry has steadily grown, looking beyond temporary ups and downs in demand. According to the Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA), annual sales of semiconductors surged from $139 billion in 2001 to $573.5 billion in 2022, marking a notable 313% growth.
The ever-increasing global demand for semiconductors, coupled with efforts by manufacturers to expand their capacities, highlights the heightened importance of sustainability across corporate, investor, and government spheres. Amid the urgent global obligation to combat climate change, semiconductor companies are confronted with a multitude of considerations as they assess both their present and future operational strategies. This shift requires industries to reassess practices, focusing on sustainable growth and reducing environmental impact through innovation and collaboration. With increasing demand for environmental responsibility, customers are asking suppliers, including semiconductor firms, to cut greenhouse gas emissions and aim for net-zero carbon footprints across their supply chains. Responding to this demand isn't just about retaining business; it's about aligning with the urgent global mission to combat climate change and leaving a positive environmental legacy.
Understanding Emission Sources and Sustainability Challenges
Predominantly, industrial operations are responsible for global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, contributing substantially to the overall environmental footprint. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) serves as a crucial metric for quantifying the impact of various GHGs on global warming. A few years ago, overall industrial production activities contributed over 40% of the world's CO2e emissions stemming from fuel combustion, while commercial logistics account for more than 10% of this total. However, according to IEA, IPCC, Climatewatch, and BCG, overall CO2e emissions were reduced by 5% to 10% due to the impact of COVID-19. But post-pandemic, manufacturing operations resumed, and the semiconductor industry in emerging markets is likely to witness an increase in the number of new semiconductor companies in the coming years. These findings showcase the adverse impact of industrial and logistical processes on the environment, emphasizing the urgent need for sustainable practices and emissions reduction strategies within these sectors.
In the semiconductor industry, emissions originate from various sources, with fabs being a primary contributor due to the utilization of process gases with high global warming potential (GWP) during critical activities such as wafer etching and chamber cleaning. Additionally, emissions stem from high-GWP heat-transfer fluids, posing challenges when used in chillers and potentially leaking into the atmosphere. According to Mckinsey, such emissions from semiconductor fabs account for 35% of the total emissions in the semiconductor industry. Moreover, emissions arise from purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling equipment, with production tools and utilities being the primary contributors, accounting for 45% of overall emissions, as per McKinsey. Furthermore, the industry grapples with indirect emissions across its value chain, including upstream emissions generated by suppliers, whereas downstream emissions are associated with the usage of products equipped with semiconductors, which accounts for the remaining 20% of emissions. Addressing these multifaceted emission issues requires a holistic approach, emphasizing innovation, collaboration, and a steadfast commitment to sustainable practices throughout the semiconductor ecosystem.
Achieving the Semiconductor Industry's 1.5°C Target by 2030
As the semiconductor industry is achieving net-zero emissions by 2030, a concerted and strategic approach is imperative. This calls for maximizing the implementation of existing sustainability strategies while concurrently spearheading the development and adoption of innovative and greener technologies. By embracing this dual approach, the industry can effectively navigate toward its environmental goals while fostering continuous advancement and leadership in sustainable practices. Industrial emissions must be reduced by 45% by 2030 to meet the ambitious 1.5°C target set in climate agreements.
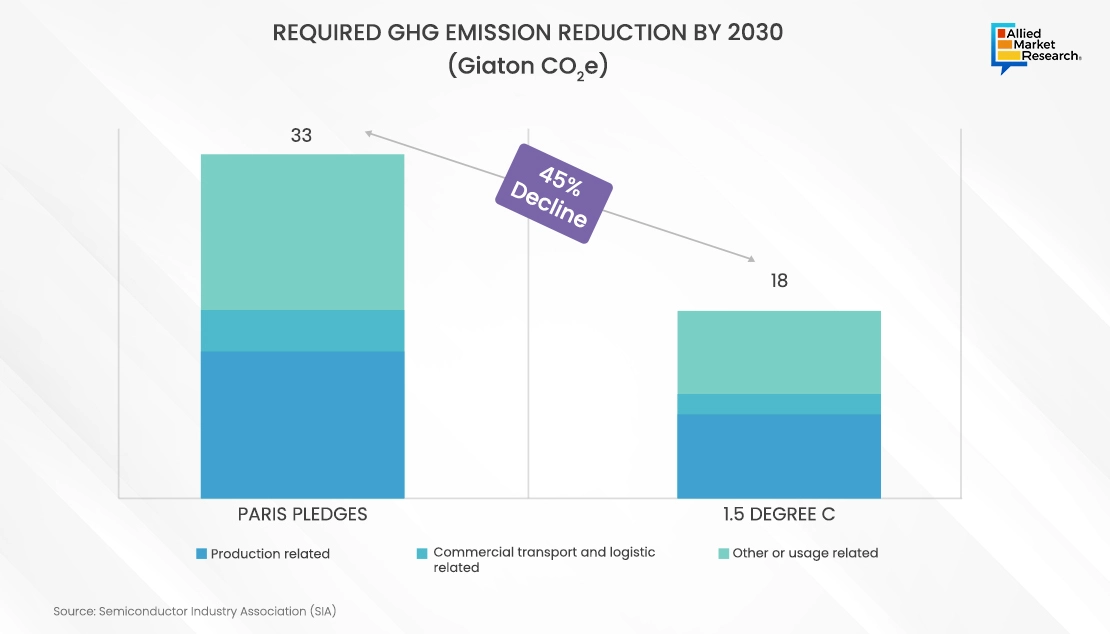
There remains a substantial task ahead to improve the industry's ecological footprint. These considerations lead to actionable steps in the near, medium, and long term.
Near Term Actions
Reduction in Process Gas and Heat Transfer Fluid Consumption
- Semiconductor manufacturers must focus on installing advanced gas abatement systems to possibly reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and optimize usage of alternate gases. This can involve replacing nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) and tetrafluoromethane (CF4) with fluorine (F2) gas, which boasts zero global warming potential.
- Semiconductor fabs must prioritize measures to minimize chiller leakage. Also, to reduce GHG emissions heat transfer fluids must be replaced with low GWP options.
Strategic Imperatives for Sustainable Supply Chains
Companies need to define ambitious and measurable sustainability goals while also seeking to enhance raw material procurement efficiency. It is crucial to eliminate conflict minerals and other materials procurement from questionable sources from the entire supply chain.
Mid Term Actions
Water Conservation and Cleaner Energy Alternatives
Manufacturing organizations in the semiconductor industry should prioritize strategies to reduce water consumption and invest in cleaner alternative power sources for their facilities. Further, companies must shift from their current fuel supply to cleaner alternatives, such as hydrogen or biomass.
Minimizing Waste
Prominent semiconductor firms must implement a range of strategies aimed at reducing waste generated during operations. These initiatives encompass community-level programs, such as driving environmental awareness campaigns in their operational areas and optimizing recycling initiatives within their facilities.
Long Term Actions
Minimizing Transportation Footprint and Use of Hazardous Chemicals:
- In the long run, the industry must effectively manage the impact of transportation and logistics activities on the environment by optimizing its shipping and distribution practices.
- In semiconductor manufacturing, many chemicals are used in the production process, and the ability of fabs to shift towards less toxic alternatives in the foreseeable future will have a considerable impact on the environment.
What Are the Leading Semiconductor Manufacturers up to?
The primary objective of leading companies is to develop groundbreaking technology that positively impacts the lives of individuals globally. Pursuing the reduction of environmental impact, enhancing energy efficiency, and minimizing the carbon footprint of products and platforms are essential strategies for achieving this overarching goal.
Intel, one of the leading manufacturers in the semiconductor industry, has set below goals to be achieved between 2030 and 2040.
The company is demonstrating commendable strides towards these objectives. By the end of 2022, its prominent achievements comprised:

- Successfully attained 100% renewable electricity in the U.S., European Union, Israel, and Malaysia, with Costa Rica nearing the same milestone, resulting in a global total of 93%. Over the past five years, Intel procured 33.6 billion kWh of renewable electricity, sufficient to supply the energy needs of over 3.2 million households in the United States for one year.
- The company effectively preserved an estimated 9.6 billion gallons of water within its operations and facilitated the restoration of 3.0 billion gallons through watershed revitalization initiatives. Additionally, the company attained a net positive water balance in the United States and India.
To establish preeminence in sustainable semiconductor manufacturing, fabs must establish ambitious environmental objectives.
Conclusion
The semiconductor industry plays a pivotal role in driving numerous initiatives aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change. By powering information technology, semiconductors can boost energy efficiency and support clean energy solutions, thus promoting sustainable development. Yet, the industry needs ongoing innovation to produce chips in an environmentally responsible way. Companies embracing sustainability can expect huge benefits, as the growing number of stakeholders prioritize moving society toward a sustainable future.
As a market research company, we, at Allied Market Research, aim to equip vendors with essential knowledge on environmental sustainability practices in the semiconductor industry. By embracing sustainable strategies, they can not only contribute to global environmental goals but also enhance their corporate standing, meet evolving customer expectations, and potentially access new market opportunities. We provide a thorough understanding of incorporating measures such as reducing emissions, optimizing resource usage, and adopting cleaner technologies to help them position themselves as leaders in sustainable semiconductor manufacturing. Our comprehensive insights empower our clients to explore the evolving landscape, make informed decisions, and thrive in an environmentally conscious industry.

