The global space propulsion system market was valued at $8.9 billion in 2021, and is projected to reach $32.8 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 14.3% from 2022 to 2031.
The space propulsion system market is segmented into Type, Class of Orbit and End User.
The most critical factor in the design and operation of aviation or spacecraft missions is the propulsive force. The propulsion system provides the necessary propulsive force or power to push an airplane, rocket, or other object moving in air or space forward. Space propulsion system comprises fuel tanks, valves, propellant assembly, pressure regulator, thrusters, manifold subsystems, and regulators. Owing to the presence of a wide range of spacecraft and satellites, several different propulsion technologies are used by different space agencies globally. Spacecraft propulsion and satellite propulsion are accomplished through the use of a rocket engine or integrated propulsion systems.
The space propulsion system market is experiencing immense growth, which is driven by the increase in demand for low earth orbit (LEO) based services, surge in space exploration missions, rise in demand for satellite data, and increase in R&D activities related to space propulsion technologies. However, concerns over space debris, heightened emissions due to the rising number of space launches, and implementation of stringent regulations pertaining to space propulsion systems hamper the growth of the space propulsion system market. On the contrary, surge in demand for advanced electric propulsion systems, propulsion systems manufactured through 3D printing, and ongoing developments in nanomaterial-based space propulsion systems are the major factors that are expected to provide lucrative opportunity for the expansion of the global space propulsion system industry during the forecast period.
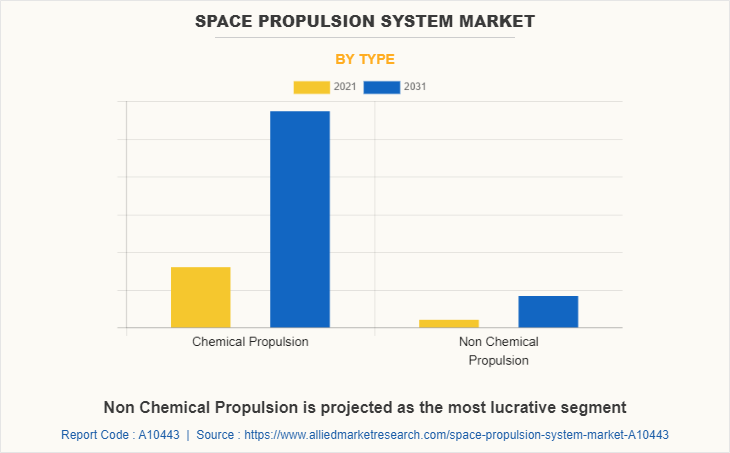
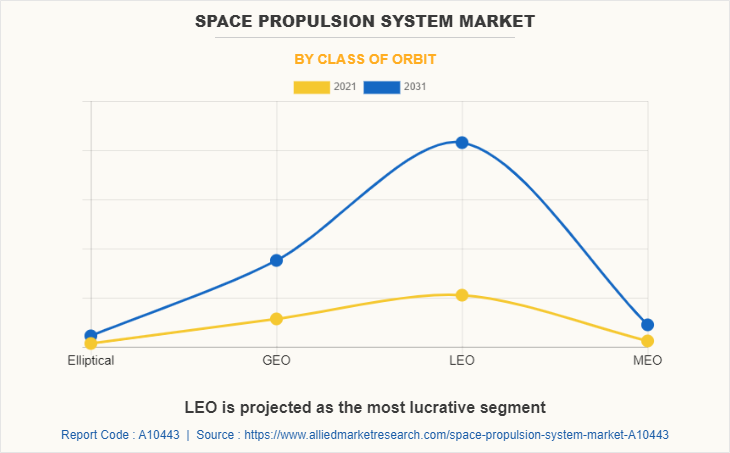
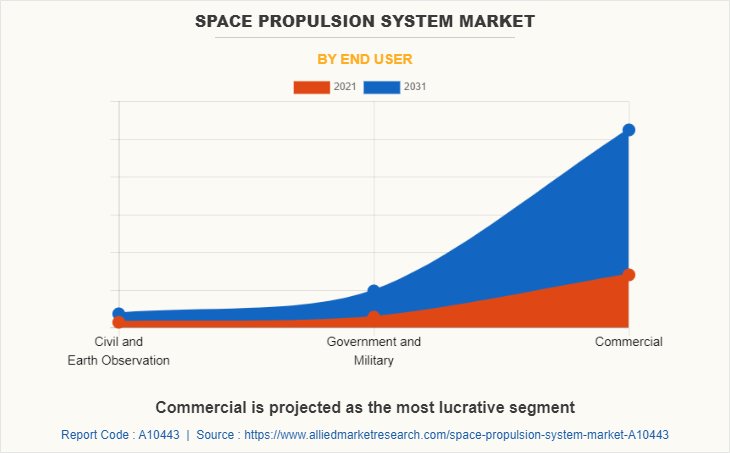
The global space propulsion system market is segmented into type, class of orbit, end user, and region. By type, the market is bifurcated into chemical propulsion and non-chemical propulsion. Depending on class of orbit, it is segregated into elliptical, geostationary earth orbit (GEO), low earth orbit (LEO), and medium earth orbit (MEO). On the basis of end user, it is fragmented into civil & earth observation, government & military, and commercial. Region wise, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
The key players profiled in this space propulsion system market report include Accion Systems, ArianeGroup, IHI Corporation, Moog Inc., Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., Northrop Grumman Corporation, OHB SE, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Thales Group, and Vacco Industries.
Increase in demand for low earth orbit-based services
The demand for internet connections via fixed and mobile broadband networks is increasing dramatically. Despite network expansions and enhancements, only around half of the world's households have access to fixed broadband services. With the development of LEO constellations, satellite broadband services are projected to increase broadband penetration. Owing to constellations of several hundred LEO spacecraft, a global broadband internet might be accessible from everywhere on the planet. In addition, local service providers will be able to expand their networks in terms of service range and geographic reach, allowing local services to be supplied over a global network. Such a rise in the demand for LEO-based spacecraft is expected to create demand for spacecraft propulsion systems.
Furthermore, satellites are primarily mass-produced to meet customer demand for high-speed internet connectivity almost anywhere, including aircraft, cruise ships, and remote spots throughout the world. SpaceX, OneWeb, and Boing are among the companies proposing and building LEO satellite networks to provide global high-speed internet connectivity. LEO satellites are widely used for communications, military reconnaissance, spying, and other imaging applications. For instance, in July 2021, Inmarsat announced to launch around 150 satellites into LEO to enhance its existing telecommunications capabilities. Increased bandwidth provided by Inmarsat's LEO satellites might be useful for congested sea routes or crowded aviation corridors. This growing number of LEO satellites creates demand for propulsion systems, which is anticipated to drive the growth of the global space propulsion system market.
Rise in space exploration missions
Private companies are increasingly involved in space exploration, and the number of collaborations between government and private space agencies as well as agreements and outsources, including sourcing of different electrical parts & ancillary equipment, modern propulsion systems, robotic gadgets, and software development, have increased in the recent years. Amazon and SpaceX have revealed plans to colonize the moon and Mars, accordingly. For instance, in February 2022, CEO of SpaceX, Elon Musk announced SpaceX’s megarocket Starship that will one day take people and cargo to the moon, Mars, and other destinations in space. Such developments in space exploration for space tourism are expected to enhance spacecraft manufacturing capabilities and create demand for advanced space propulsion systems during the forecast period.
Moreover, space exploration has resulted in the research and construction of more dependable and efficient propulsion systems and spacecraft, lowering the possibility of system failure and increasing mission success rates. This factor pushed organizations and market players to develop new efficient propulsion systems for space missions. For instance, in February 2021, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) announced that it is exploring the possibility of developing a new propulsion technology to fuel spacecraft for its future deep space missions. In addition, in January 2021, ISRO issued an invitation for “expression of interest” for design and modeling; simulation and analysis; testing and qualification of 100W Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTEG) without radio isotope, an alpha source thermoelectric propulsion technology. In addition, in April 2020, the University of Central Florida researcher developed an advanced new rocket-propulsion system known as a rotating detonation rocket engine, which will allow upper stage rockets for space missions to become lighter, travel farther, and burn more cleanly. Such developments in space propulsion systems are due to increase in space exploration missions, which is expected to drive the growth of the space propulsion system market during the forecast period.
Concerns over space debris
Space debris, often known as space junk, is made up of wasted launch vehicles or spacecraft pieces that float around in space thousands of kilometers above the earth, posing a risk of colliding with satellites or a space station. In addition, debris can be created by an implosion in space or by countries testing missiles to destroy their existing satellites. Apart from Russia, China, the U.S., and India have all destroyed satellites, resulting in space debris. As space junk orbits the earth at such high speeds roughly 15,700 miles per hour (25,265 kph) in LEO, a collision with a satellite or spacecraft may inflict substantial damage. Moreover, in May 2021, more than 27,000 pieces of orbital debris were tracked by the Department of Defense’s global Space Surveillance Network (SSN) sensors, and as of August 2021, the European Space Agency (ESA) reports that approximately 29,210 pieces of debris are tracked on a regular basis by Space Surveillance Networks. Such a growing population of space debris poses a risk to all space vehicles, including spacecraft carrying humans, international space station, and satellites. These factors create concerns related to reducing space debris through decrease in the number of satellites and space vehicles, which are expected to negatively impact the space propulsion system market growth.
Demand for advanced electric propulsion systems
Electric propulsion is a type of space propulsion that uses electrical power to accelerate a propellant through various electrical and/or magnetic means. Electric propulsion systems employ energy from external sources such as nuclear reactors or solar power to ionize or positively charge gas fuels such as xenon. Subsequently, ions are accelerated and propelled out of the thruster. These systems can be less expensive, carry more, and consume up to 90% less fuel than traditional chemical propulsion techniques. In addition, electric propulsion, contrary to chemical systems, requires very little bulk to accelerate a spaceship. As the propellant is discharged up to 20 times quicker than in a traditional chemical thruster, the total system is many times more mass-efficient. Thus, when compared to conventional chemical thrusters, the utilization of electrical power improves the propulsion performances of electronic propulsion thrusters. Although electric propulsion systems are currently employed in satellites and robotic missions, NASA is focusing on developing more powerful versions for human exploration of the solar system. For instance, in April 2021, NASA shared a $15 million fund with the Georgia Institute of Technology and 11 partner universities, and 17 researchers for the Joint Advanced Propulsion Institute (JANUS), a new Space Technology Research Institutes (STRI) to develop strategies and methodologies to surmount limitations in ground testing of high-power electric propulsion systems. In addition, developments and tests of new electric propulsion systems are anticipated to boost the growth of the market during the forecast period. For instance, in March 2022, SpaceLogistics, a satellite-servicing firm owned by Northrop Grumman, successfully fired the electric propulsion system it is developing for the Mission Extension Pods it plans to launch in 2024. Such demand and developments in electric propulsion systems are expected to offer remunerative opportunities for the expansion of the global space propulsion system market during the forecast period.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the space propulsion system market analysis from 2021 to 2031 to identify the prevailing space propulsion system market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the space propulsion system market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global space propulsion system market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Space Propulsion System Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| By Type |
|
| By Class of Orbit |
|
| By End User |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Accion Systems, Ariane Group, OHB SE, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Vacco Industries, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Thales Group, IHI Corporation, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd, Moog Inc |
Analyst Review
The space propulsion system market is expected to exhibit high growth potential attributed to rapid technological advancements in space propulsion systems and increase in space exploration missions. In addition, many countries have begun to take steps toward space missions such as the moon and Mars exploration missions. Such applications may necessitate the usage of advanced spacecraft propulsion systems.
Moreover, the space propulsion system market is expected to witness significant growth due to the collaboration of the market players for the development of space systems. For instance, in March 2022, Northrop Grumman Corporation entered into a collaboration with Lockheed Martin Corporation to perform the final full-scale ground test of the abort motor for NASA’s Orion spacecraft Launch Abort System (LAS) at Northrop Grumman’s Promontory test facility. In addition, in April 2021, OHB System AG—a subsidiary of the European space and technology group, OHB SE—entered into collaboration with Thales Alenia Space for the European System Providing Refueling, Infrastructure, and Telecommunications (ESPRIT) module for the new Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway. Under this collaboration, OHB SE developed a system for refueling the electrical propulsion system of the Lunar Gateway with xenon.
The CXOs further added that numerous developments have been carried out by key players, which are anticipated to create remunerative opportunities for expansion of the market during the forecast period. For instance, in July 2021, Sierra Nevada Corporation developed and completed testing of its hypergolic, or storable, liquid rocket propulsion system for orbit transfer, maneuvering, and guidance control.
Estimated size of the market stood at $8.9 billion in 2021, which is expected to value $32.8 billion by 2031, witnessing a CAGR of 14.3%
Commercial is the leading application of Space Propulsion System Market.
North America is the largest regional market for Space Propulsion System market.
Rise in usage of non-chemical propulsion technologies; reduction in costs of space propulsion systems.
Leading companies that hold a significant market share in Space Propulsion System are Northrop Grumman Corporation, IHI Corporation, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd., Moog Inc., and Ariane Group
Loading Table Of Content...



