Table Of Contents
- Integration of Real-time Analytics
- Equity Management Software Instrumental in Driving Success
- Private Equity Exhibits Potential for Higher Returns
- Regulatory Compliance Associated with Equity Management Software
- The Future of Equity Management Software Industry
- Challenges Ahead
- Future Trends to Revolutionize Equity Management Software
- The Bottom Line

Onkar Sumant

Pooja Parvatkar
Equity Management Software: A Potent Tool for Equity-driven Businesses

Integration of Real-time Analytics
The equity management software industry is constantly evolving due to rise in need for real-time analytics solutions. Real-time analytics helps businesses to manage equity by monitoring and analyzing equity plans, grants, and transactions instantaneously. This facilitates better decision-making and management of equity-related activities. As a result, businesses are able to check their stock holdings' current worth accurately. Organizations may use real-time analytics to make educated decisions about equity-based incentives and employee compensation by receiving rapid information on the value of stock options and equity grants. Companies promptly detect any inconsistencies, mistakes, or compliance problems by keeping an eye on equity-related operations in real time and implementing prompt corrective measures. This aids businesses in maintaining the integrity and authenticity of their equity data while averting unfavorable outcomes such as fines for noncompliance or harm to their reputation.
Equity Management Software Instrumental in Driving Success
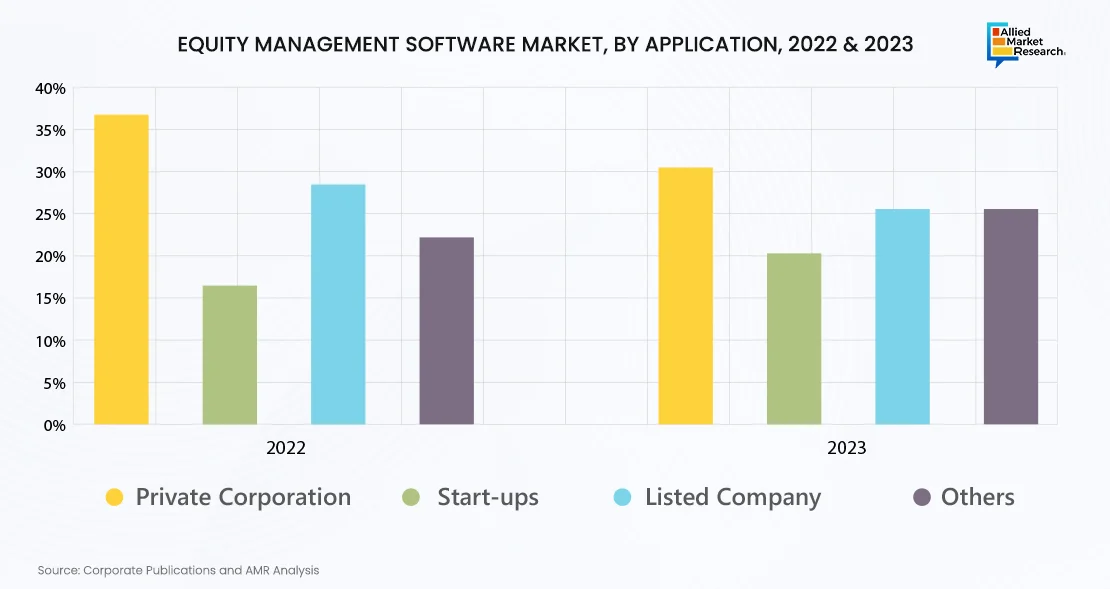
The software finds its major application in private corporations, start-ups, listed companies, and others. It incorporates a range of graphs different types of entities to visualize ownership structures, compensation plans, financial performance, and stakeholder engagement in ways that are tailored to each entity's goals, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder preferences.
Private Equity Exhibits Potential for Higher Returns
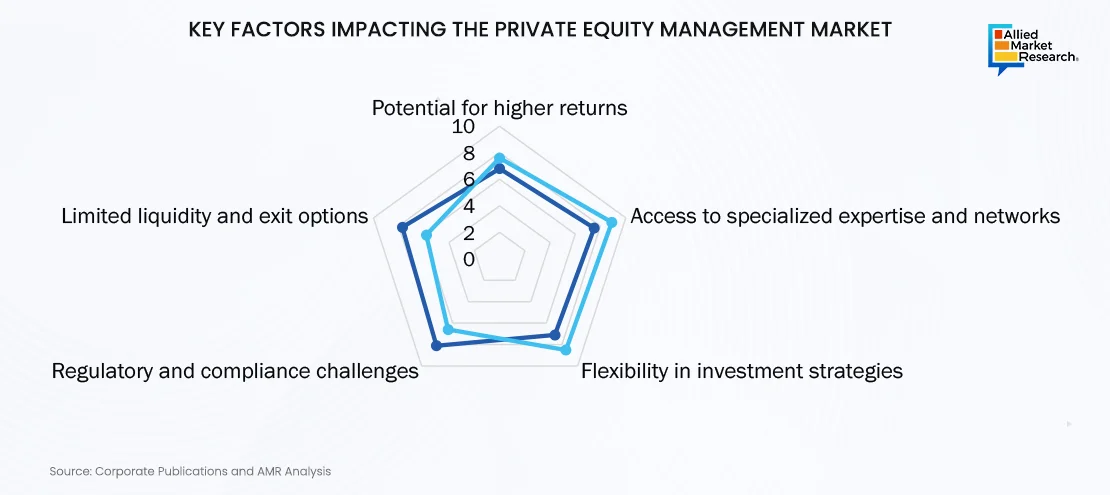
Private equity has the potential for higher returns stemming from active involvement in company management, facilitating operational enhancements and strategic changes that promote company value. It often works closely with the management of the acquired companies to implement strategic changes, enhance performance, and maximize returns for both the investors and the company. This investment approach involves a longer term horizon than publicly traded stocks and can encompass various industries and business stages, from start-ups to mature companies seeking growth or turnaround. In addition, the access to specialized expertise and vast networks enables private equity firms to guide portfolio companies toward growth, innovation, and efficiency. The flexibility of the market allows for diverse investment strategies across industries and company stages, optimizing risk while tapping into various opportunities. However, private equity firms face a myriad of regulatory challenges in the realm of the software, predominantly stemming from compliance with securities laws, tax regulations, and reporting requirements. These firms must meticulously adhere to security laws governing the issuance and transfer of equity securities, such as Regulation D and Rule 144, which regulate private placements and the resale of restricted securities, respectively. Moreover, private equity funds are subject to stringent regulations concerning fund structuring and reporting, including compliance with the Investment Company Act of 1940 and the Securities Act of 1933, governing the registration and offering of investment funds. Ensuring investor reporting and transparency is crucial, necessitating accurate and timely disclosures of financial statements and performance metrics. Furthermore, potential for higher returns, access to specialized expertise and networks, and flexibility in investment strategies boost the growth of the global private equity industry. However, regulatory and compliance challenges hamper the market growth. On the contrary, limited liquidity and exit options is expected to offer remunerative opportunities for expansion of the private equity market during the forecast period.
Regulatory Compliance Associated with Equity Management Software
In North America, the market is influenced by an intersection of industry-specific guidelines, including data protection legislation and financial compliance requirements. Transparency, equity, and investor protection are all protected by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which is in charge of overseeing equities management procedures in the U.S. Users and vendors of equities management software must adhere to SEC laws, including the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Advisers Act. Financial data privacy regulations, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), also place strict restrictions on how sensitive financial data is handled and protected.
Furthermore, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) offers regulatory supervision and direction on a range of securities and market regulation topics, such as investor protection, trading venues, and data reporting. To guarantee compliance with EU laws and standards, equity management software solutions are developed and implemented under the direction and guidelines of ESMA. Furthermore, processing, storing, and transferring personal data inside the EU and EEA are subject to stringent regulations under data privacy laws, such as the General Data privacy Regulation (GDPR). To guarantee compliance and safeguard investors' and customers' privacy, suppliers must abide by GDPR principles, which include data minimization, purpose limitation, and the rights of data subjects.
Regional regulatory organizations, national financial authorities, and international norms all have an impact on the regulatory framework that governs the Asia-Pacific equity management software industry. Every country in Asia-Pacific has its own laws pertaining to financial services and equity management procedures. For instance, in Japan, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) is responsible for supervising the securities sector and enforcing laws such as the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act (FIEA), which regulates investment advice services and securities trading.
In addition, regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) in the UAE and the Capital Market Authority (CMA) in Saudi Arabia oversee equity markets and enforce laws to ensure transparency, investor protection, and market integrity in Middle Eastern nations such as the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. Regulatory agencies that manage equity management activities in Africa include the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) in South Africa and the Capital Markets Authority (CMA) in Kenya. They also ensure adherence to laws and regulations concerning financial reporting, investment management, and securities trading.

The Future of Equity Management Software Industry
In the dynamic world, businesses increasingly recognize the importance of efficient equity administration. With rise in remote work culture and globalization of businesses, the demand for digital solutions that streamline equity management processes is expected to grow significantly. The industry is likely to witness continued innovation, with software platforms incorporating advanced features such as artificial intelligence for predictive analytics, blockchain for enhanced security and transparency, and integrations with financial and HR systems. As regulations pertaining to equity compensation become more complex, software solutions will play a vital role in ensuring compliance and mitigating risks. Furthermore, the industry is expected to expand its scope to cater to a diverse range of business sizes, from start-ups to large enterprises, with tailored solutions to meet their unique needs. As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations become increasingly important, the software may also evolve to incorporate features that track and report on sustainability and social impact metrics. For instance, Altvia partnered with Passthrough to launch OnboardingBridge, the first solution to fully integrate a CRM with an investor onboarding solution, so that general partners can provide a best-in-class investor experience.
Challenges Ahead
As regulations governing equity compensation evolve and become more intricate, software solutions must continually update and adapt to ensure accurate tracking and reporting. Additionally, data security and privacy concerns pose a constant challenge, especially considering the sensitive nature of equity-related information. The industry must prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential breaches and unauthorized access. Moreover, as businesses continue to globalize, the industry will face challenges in facilitating cross-border transactions and managing diverse regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions. Ensuring data security and privacy will remain a paramount concern, given the growing sophistication of cyber threats and the increasing importance of safeguarding sensitive financial information. Software providers will need to prioritize robust security measures and compliance with data protection regulations to instill trust and confidence among users. Moreover, the continued digitization of financial processes and the emergence of new technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, will present both opportunities and challenges for the industry. Successfully addressing these challenges will require ongoing innovation, collaboration with regulatory bodies, and commitment to meet the evolving needs of users in an ever-changing business landscape.
Future Trends to Revolutionize Equity Management Software
- Blockchain Technology: The integration of blockchain is likely to revolutionize the industry by enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency in tracking ownership and transactions. Blockchain can provide a decentralized and immutable ledger, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring trustworthy and accurate records of equity ownership.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Predictive Analytics: AI-powered features, such as predictive analytics, will play a crucial role in forecasting trends, valuations, and optimizing equity compensation plans. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data to provide insights that aid decision-making, ensuring companies make informed choices regarding equity allocations.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures: With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, the future of the market will prioritize advanced cybersecurity measures. This includes robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and other security protocols to safeguard sensitive equity-related data.
- Integration with Financial and HR Systems: Seamless integration with other critical business systems, such as financial and HR software, will become a key trend. This integration ensures a cohesive and comprehensive approach to equity management, streamlining workflows and reducing the potential for errors or discrepancies in data.
- Mobile Accessibility: Increase in emphasis on mobile accessibility is likely to be witnessed in the coming years. With companies embracing remote work culture and increasing need for on-the-go access to information, mobile-friendly applications will enable stakeholders to manage equity-related tasks efficiently from anywhere.
- Sustainability and ESG Integration: As ESG considerations gain prominence, the software will incorporate features that track and report on sustainability metrics. This aligns with the broader trend of integrating ESG factors into corporate decision-making and reporting.
- User-friendly Interfaces and Education: To overcome user adoption challenges, software providers will focus on offering intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. In addition, comprehensive education and training resources will empower stakeholders to navigate and utilize the software effectively, ensuring widespread acceptance within organizations.
- Tailored Solutions for Diverse Business Sizes: The industry is likely to witness the development of more tailored solutions catering to the specific needs of businesses of varying sizes. Start-ups may benefit from simpler, cost-effective platforms, while larger enterprises may require more sophisticated and scalable solutions.
The Bottom Line
The future of equity management software holds exciting prospects, driven by transformative trends that promise to reshape how businesses administer and optimize their equity-related processes. The integration of blockchain technology for enhanced security, AI for predictive analytics, and seamless connectivity with financial and HR systems are set to revolutionize the industry. These advancements address current challenges such as regulatory complexity, data security concerns, and the need for tailored solutions across diverse business sizes. Moreover, the focus on mobile accessibility, user-friendly interfaces, and comprehensive education initiatives aims to overcome adoption hurdles and ensure that stakeholders can harness the full potential. As sustainability and ESG considerations gain prominence, the industry's evolution toward incorporating these metrics reflects a broader shift toward responsible and transparent corporate practices.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

