Table Of Contents
- Addressing User Needs and Potential Use Cases
- Development Stage
- 3D Printing Development Timeline
- Landscape and Current Market of 3D Printing
- State and Maturity
- Key Innovators and Developers
- Recent Breakthroughs
- Technical Limitations and Challenges
- Integration with Existing Technologies
- Adoption of 3D Printing
- Driving Factors and Barriers
- Early Adopters and Future Expansion
- Future Outlook for 3D Printing in Construction Industry
- Future Capabilities and Applications
- Development Roadmaps and Mainstream Adoption
- Risks and Concerns
- Innovations to Lead the Market to Full Potential

Sonia Mutreja

Pooja Parvatkar
3D Printing Revolutionizing the Construction Industry: Building the Future

3D printing, a transformative technology, is revolutionizing the construction industry by offering innovative solutions to traditional building challenges. This technology, also known as additive manufacturing, operates on the principle of layering materials to create three-dimensional structures based on digital models. At its core, 3D printing in construction involves the use of specialized printers that can extrude building materials, most commonly concrete, as well as polymers, metal, and composite materials, to construct buildings and various structural components directly from computer-aided design (CAD) data.
Addressing User Needs and Potential Use Cases
The technology directly addresses pressing global needs for faster, more cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable construction methods. It holds the promise of significantly reducing material waste, lowering construction costs, and cutting down on project timelines. For instance, companies such as ICON are pioneering the use of 3D printing to create affordable housing solutions, addressing the global housing crisis by building homes for those in dire need, including entire villages designed for the most vulnerable populations. This is particularly compelling given the estimation that over 1.6 billion people currently lack adequate housing, with projections suggesting demand for shelter could include up to three billion people by 2050.
Development Stage
The 3D printing in construction market is emerging from a phase of experimentation into more widespread application, showcasing rapid evolution from small-scale prototypes to fully habitable structures.
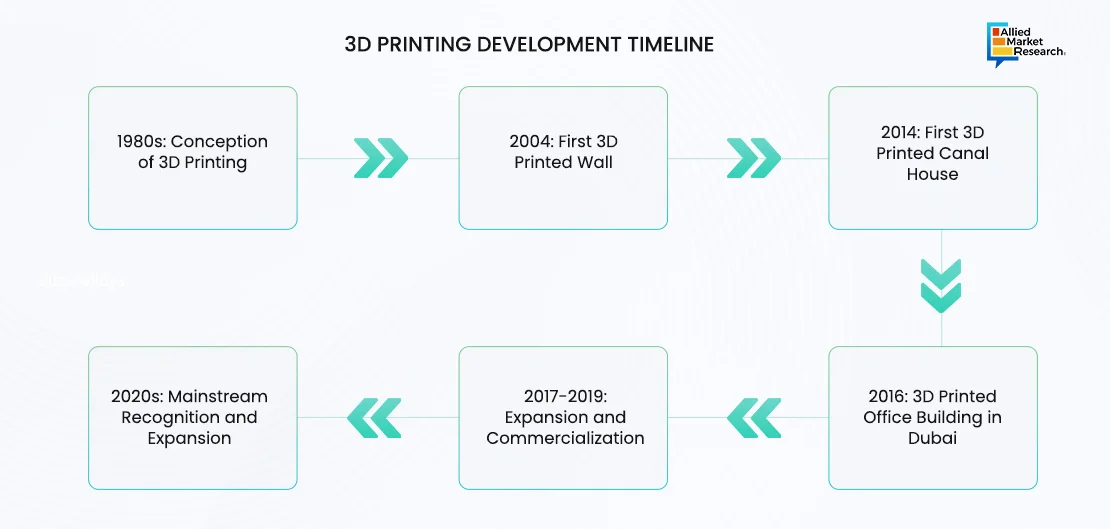
3D Printing Development Timeline
The technology’s journey began with basic applications in the 1980s and has now reached a point where entire buildings and complex structural elements can be printed. Recent projects include the construction of affordable housing, intricate bridges, and even proposals for extraterrestrial habitats. For instance, 14Trees, a Holcim and British International Investment (BII) joint venture driving innovative, sustainable and affordable construction solutions, completed the printing of 10 housing units in Kenya in February 2023, noted to be one of the largest 3D-printed affordable housing projects.
Landscape and Current Market of 3D Printing
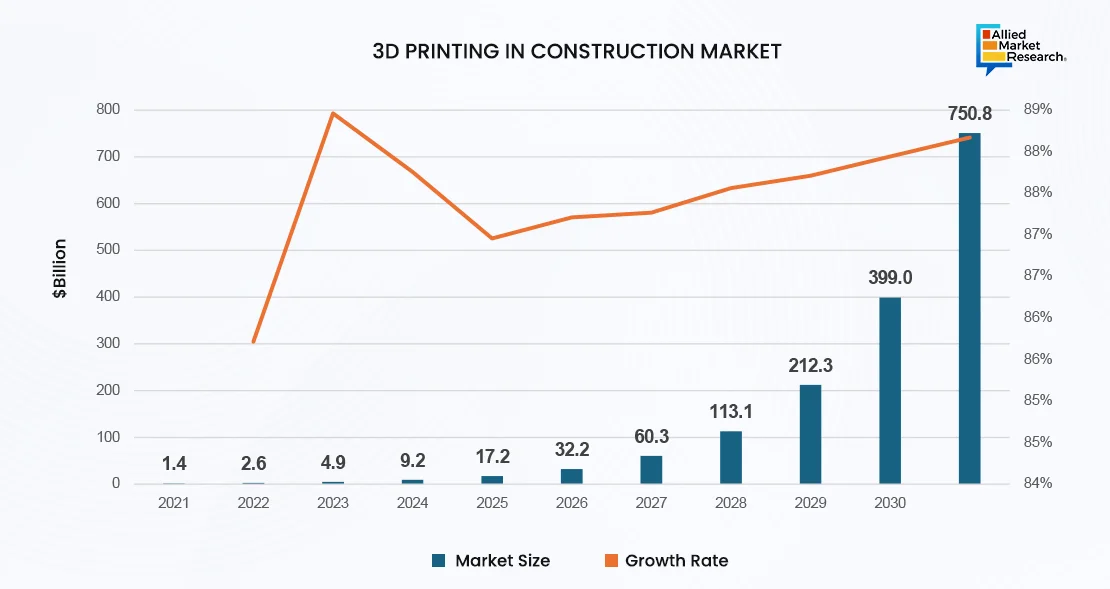
The 3D printing construction market size was valued at $1.4 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $750.8 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 87.3% from 2022 to 2031, with a notable expansion in materials used, including concrete, which dominates due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.
Innovative companies and projects globally demonstrate the technology's versatility, from ICON's initiatives in affordable housing using their Vulcan printer to print homes and community buildings, to Apis Cor's ambitions of 3D printing structures on Earth and beyond, and Winsun's achievements in China, where they claim to have constructed the tallest 3D-printed building.
These advancements highlight a significant shift towards more sustainable, efficient, and customizable construction practices.
However, the adoption of 3D printing in construction also faces challenges, including high equipment costs, need for specialized labor, and regulatory hurdles. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 3D printing, such as increased construction speed, waste reduction, and design freedom, offer a promising future for this technology in the construction industry.
3D printing in the construction industry has evolved significantly, moving from conceptual and experimental stages to more practical and impactful applications. This shift is marked by advancements in technology, the diversity of materials used, and increase in involvement of key innovators and companies.
State and Maturity
3D printing technology in construction has matured from initial experiments to the construction of habitable structures and complex architectural projects. Technology has proven capable of producing a wide range of structures, from small-scale models to fully functional buildings, indicating a significant leap in its development and application.
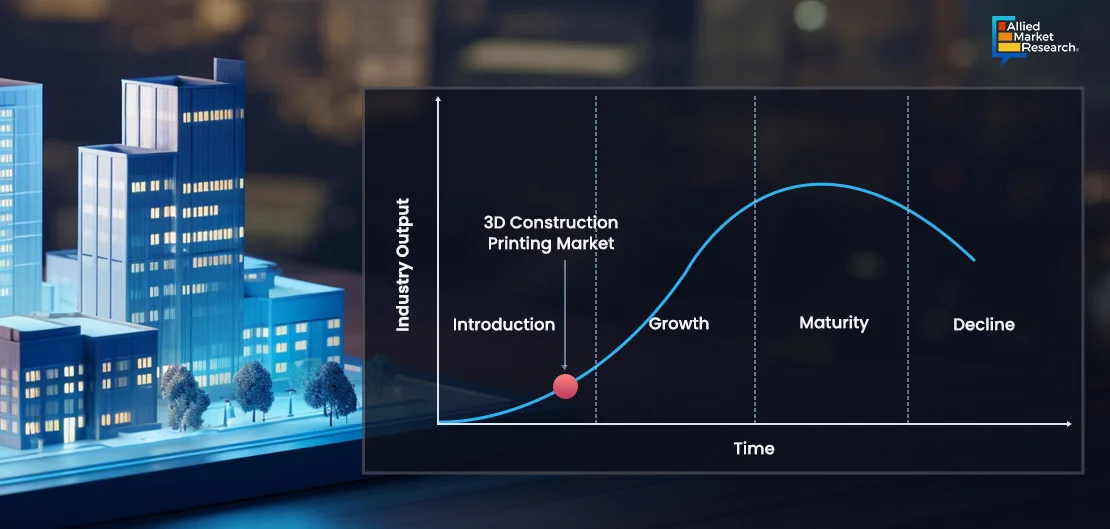
The current state of 3D printing showcases a technology that is not only viable but increasingly becoming an integral part of the construction industry's future??. Currently, in 2024 the technology is at the end stage of the Introduction phase and soon will enter the growth phase in the next 3-5 years.
Key Innovators and Developers
Innovators and companies such as ICON, Apis Cor, WinSun, and Contour Crafting are at the forefront of this transformation. For instance, ICON has made efforts in printing entire communities for the homeless, demonstrating the technology's potential to address significant societal challenges such as the global housing crisis. Similarly, WinSun has achieved milestones in constructing large-scale structures, including apartment buildings, showcasing the scalability of 3D printing technologies in construction.
Recent Breakthroughs
Recent technological breakthroughs have expanded the possibilities of 3D printing in construction. Innovations include the development of new materials such as ICON's Lavacrete, which offers durability and resilience needed for construction, and advancements in printer designs that allow for the creation of larger structures more efficiently and at a lower cost. These breakthroughs have made construction of buildings time-efficient and less costly as compared to traditional methods, thus opening new avenues for affordable housing and rapid deployment of infrastructure.
Technical Limitations and Challenges
Despite notable advancements in 3D printing within the construction industry, persistent challenges impede widespread adoption. The financial barrier remains substantial, as the cost of 3D printing equipment poses a significant challenge, particularly for extensive construction projects. Additionally, the scalability of the technology for large-scale endeavors remains a key hurdle, limiting its feasibility in practical applications. These technical limitations, coupled with the intricate demands for construction projects, present formidable obstacles to the seamless integration of 3D printing technology in the industry. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic focus on cost reduction and scalability solutions to unlock the full potential of 3D printing in construction.
In addition, there are concerns about the long-term material performance, a need for tailored building codes tailored to 3D printed structures, and the seamless union of 3D printing with conventional construction techniques to attain optimal outcomes. Material longevity poses an ongoing concern, demanding meticulous exploration and improvement to ensure sustained structural integrity. The absence of standardized building codes tailored for 3D printed structures adds complexity, requiring the establishment of comprehensive guidelines. Moreover, achieving synergy between 3D printing and traditional construction methods remains a critical objective for the industry, necessitating strategic integration approaches for enhanced efficacy. These challenges not only impede technological advancement but also create uncertainties, influencing market dynamics by constraining widespread adoption and impacting investor confidence.

Integration with Existing Technologies
3D printing technology in construction integrates with and complements existing technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and computer-aided design (CAD) software. These integrations are crucial for the precise execution of construction projects, allowing for detailed planning, simulation, and execution of complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional methods.
In conclusion, the 3D printing in the construction industry is marked by rapid advancements, significant challenges, and a clear path toward broader adoption. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to redefine construction processes, making them efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable. The commitment of key innovators and the ongoing development of new materials and methods are critical to overcoming existing limitations and fully realizing the potential of 3D printing in construction.
Adoption of 3D Printing
The adoption of 3D printing technology in the construction industry, although still in its nascent stages, is witnessing a steady increase, driven by its potential to revolutionize building processes. This adoption phase is characterized by diverse applications across different contexts, from residential buildings to infrastructure projects, underpinned by various factors driving interest and momentum.

Driving Factors and Barriers
Interest and momentum behind 3D printing in construction are largely driven by its potential to reduce costs, decrease construction times, minimize waste, and offer unprecedented design flexibility. The technology's capacity to address the global housing crisis by providing affordable and quickly deployable housing solutions is also a significant factor contributing to its adoption.
However, several barriers could hinder widespread adoption. These include the high cost of 3D printing equipment, the need for specialized labor, regulatory challenges, and concerns about the long-term durability and performance of 3D printed structures.
Early Adopters and Future Expansion
Early adopters of 3D printing technology in construction include specialized construction firms, innovative startups, and non-profit organizations focused on affordable housing. Industries that are expected to further embrace this technology include residential construction, infrastructure development, and disaster relief housing, where speed, cost-efficiency, and flexibility are paramount.
As the technology matures and overcomes current barriers, its adoption is expected to expand in many traditional construction firms and projects. This expansion is anticipated to be facilitated by advancements in printer technology, material science, and regulatory frameworks that accommodate the unique aspects of 3D-printed constructions.
In conclusion, while 3D printing in construction is still emerging, its adoption is set to grow as the technology continues to evolve. Owing to factors such as reduced costs, faster construction times, and environmental benefits, the adoption of 3D printing in the construction industry is expected to rise. Overcoming current challenges will be key to unlocking its full potential and achieving broader adoption across the industry.
Future Outlook for 3D Printing in Construction Industry
The future outlook for 3D printing in the construction industry is marked by its potential to bring innovation to building designs, construction processes, and materials. The future of this technology is envisioned to expand capabilities, applications, and adoption, influenced by ongoing research, development, and the exploration of new frontiers.
Future Capabilities and Applications
The potential future capabilities of 3D printing in construction are vast. Innovations are bound to lead to the development of sophisticated, multi-material printers that are capable of integrating electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems within structures as they are printed, streamlining the construction process and reducing the need for traditional labor-intensive installation techniques. Moreover, the technology's application potentially can extend beyond Earth, with projects such as NASA's initiatives to use 3D printing for building habitats on Mars and the Moon, underscoring the technology's versatility and potential for extraterrestrial architecture??.
Development Roadmaps and Mainstream Adoption
Experts forecast a continued evolution of 3D printing technology, with development roadmaps focusing on enhancing printer efficiency, material diversity, and architectural possibilities. Mainstream adoption is expected to be facilitated by improvements in printer speed, cost reduction, and the demonstration of long-term durability and compliance with international building codes. As the technology proves its value through successful projects, any lack of conviction is likely to diminish, paving the way for more widespread use in the construction industry.
Risks and Concerns
The 3D printing in construction market includes risks and concerns. such as long-term reliability of 3D printed structures, the environmental impacts of new materials, and potential disruptions to the traditional construction workforce. Strategies to mitigate these risks include rigorous testing and certification processes, research in eco-friendly printing materials, and training programs to train workers for new roles in 3D printing in the construction sector.
Innovations to Lead the Market to Full Potential
To realize the full potential of 3D printing in construction, several technical, business, and social innovations are necessary. These include development of new materials that offer enhanced properties such as greater strength and environmental resistance, creation of standardized guidelines and regulations specific to 3D printed structures, and cultivation of a skilled workforce capable of operating advanced 3D printing equipment. In addition, public perception is expected to play a crucial role in the adoption of 3D-printed buildings, requiring efforts to demonstrate their safety, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
In conclusion, the future of 3D printing in construction is bright, with significant advancements that are expected to redefine how buildings are designed and constructed. By addressing current limitations and focusing on innovation, the industry can unlock the full potential of 3D printing technology, leading to a new era of construction that is efficient, sustainable, and creative. For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

