Table Of Contents

Roshan Deshmukh

Pooja Parvatkar
Future of Consumer Durable Products: Shift in Trends from Disposable to Durable

In today's fast-paced consumer landscape, a significant shift is underway from disposable products to durable goods. This transition not only reflects changing consumer preferences but also signifies a broader societal shift towards sustainability and longevity. Increase in awareness about environmental issues has prompted consumers to seek durable goods that offer longevity and value. This trend reflects a growing recognition of the ecological impact of disposable products and a desire to minimize waste through responsible purchasing decisions.
As consumers prioritize quality over quantity, they are increasingly willing to invest in products that offer superior performance and durability. Durable goods often provide better value for money in the long run, leading to a rise in demand for these products. This shift is evident in multiple sectors, ranging from electronics to furniture, as manufacturers are adapting by emphasizing durability, skillful craftsmanship, and the ability to repair the product. By opting for durable goods, consumers have the opportunity to reduce the impact on the environment and save money in the future, promoting a more sustainable and conscientious approach to consumption.
Advancements and Adoption of Consumer Durables
The transition from disposable to consumer durable products is driving innovation and creativity in the manufacturing sector. Companies are exploring new materials, design concepts, and production techniques to create products that are both durable and environmentally friendly. This trend is reshaping the way products are designed, marketed, and consumed, with an emphasis on longevity, functionality, and sustainability. The shift towards consumer durables represents a fundamental change in consumer behavior and industry practices, with profound implications for the future of consumption and environmental stewardship.
Many companies are proactively responding to consumer demand for sustainable and durable products by integrating corporate responsibility into their business strategies. This includes initiatives such as adopting sustainable sourcing practices, reducing waste throughout the supply chain, and investing in product innovation that prioritizes durability and longevity. By aligning their values with those of environmentally conscious consumers, companies can drive positive change and differentiate themselves in the market.
Trends in Consumer Durable Industry
A growing number of people are demanding products that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly due to increased awareness about issues of the environment, for instance, pollution and depletion of resources. With increase in demand for sustainable products, manufacturers are focusing on materials and production process to limit the negative effects on environment and design of durable goods that last for a long time.

However, another factor driving the demand for consumer durables is a shift in mindset, where consumers increasingly prioritize value over convenience. In addition, customers have realized that cheap disposable goods that require constant replacement can only be detrimental to their budgets when they seek long-term cost efficiency by investing in higher quality and longer-lasting substitutes. This results from wanting to save money in the future while cutting down on consumption generally, thus giving rise to greater stress on those products, which guarantee durability as well as dependability.
Consumer Goods Industry Landscape
The consumer goods industry landscape is characterized by a diverse array of companies spanning manufacturing, distribution, and retail, offering a wide range of products designed for long-term use by consumers. Major players include multinational corporations such as Samsung, LG, Apple, and Whirlpool, renowned for their innovation and reliability across product categories such as home appliances, consumer electronics, furniture, kitchenware, among others. Durable consumer goods include a wide range of products, including appliances, electronics, furniture, and more.
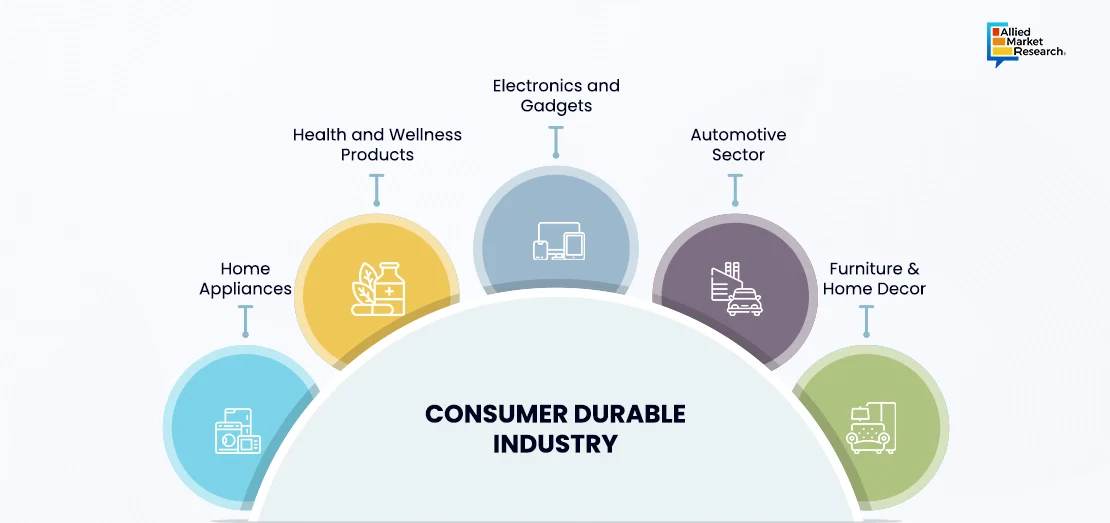
Top 5 Use Cases of Consumer Durable Industry
Use cases highlight the diverse range of products within the consumer durable industry and their significance in meeting various consumer needs and aspirations. Whether it is enhancing comfort at home, staying connected through technology, commuting efficiently, creating inviting living spaces, or prioritizing health and wellness, consumer durables play a crucial role in enriching lives and enhancing quality of life.
Current Technical Limitations and Challenges
While the shift towards durable consumer products is promising, several technical limitations still need to be addressed to fully realize this transition. These limitations include:
Product Longevity : Durable consumer goods are signified to last longer, there is still room for improvement in terms of extending product lifespan. Ensuring that components are robust enough to withstand frequent use without degradation is crucial.
Repairability and Upgradability : Consumer goods are designed in a way that makes repairs difficult or costly. Improving repairability and upgradability can enhance product longevity and reduce electronic waste. However, achieving this without compromising performance or safety is a challenge.
Material Selection and Sustainability :One of the primary challenges is selecting materials that balance durability, performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. There's a growing emphasis on using eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes to reduce environmental impact of the consumer goods materials.
Energy Efficiency :With increasing concerns about energy consumption and environmental sustainability, there's a growing demand for more energy-efficient appliances and electronics. Achieving higher energy efficiency without sacrificing performance and increasing costs requires innovative engineering solutions to minimize energy consumption.
Environmental Factors and Durability Testing :Durable consumer goods are often subjected to various environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and mechanical stress. Ensuring products can withstand these conditions through rigorous durability testing is essential but technically challenging.
Potential Future Capabilities and Applications
Looking into the future, consumer durable goods are likely to undergo significant advancements, driven by technological innovation and changing consumer needs. Here are some potential future capabilities and applications
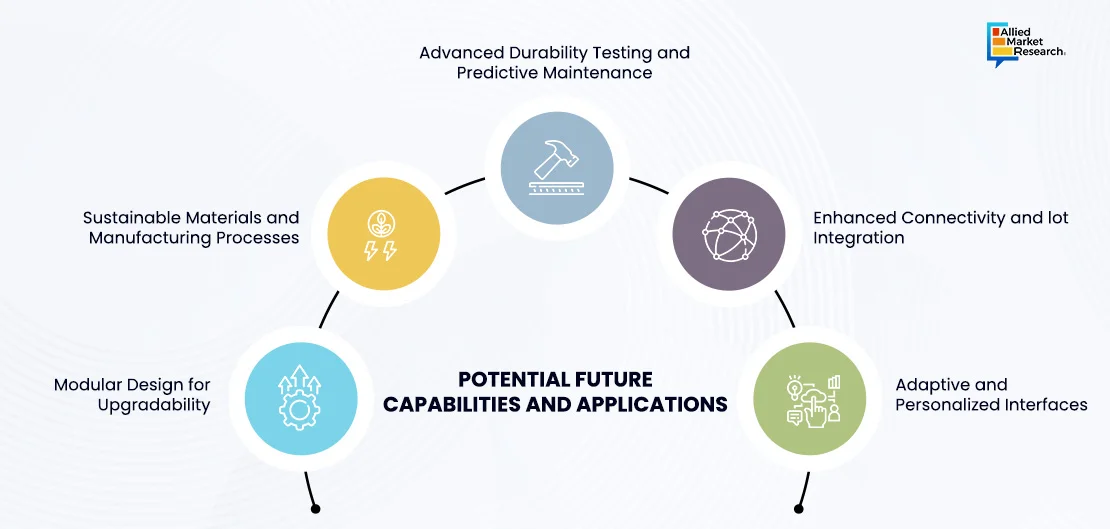
Modular Design for Upgradability: Future consumer goods may feature modular designs that allow users to easily upgrade and replace components, extending the lifespan of products such as smartphones, for example, could enable users to swap outdated components such as processors and cameras for newer ones without replacing the entire device.
Enhanced Connectivity and IoT Integration: Durable consumer goods will likely become more interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling seamless communication and automation. Smart appliances could anticipate user needs, optimize energy usage, and provide personalized experiences based on data insights.
Adaptive and Personalized Interfaces:Consumer goods may feature adaptive interfaces that learn from user behavior and preferences to provide personalized experiences. For example, smart home devices could adjust settings based on individual preferences, environmental conditions, enhancing comfort and convenience.
Advanced Durability Testing and Predictive Maintenance :Innovations in durability testing and predictive maintenance algorithms could enable manufacturers to anticipate and prevent potential failures before they occur. Real-time monitoring and analytics could help identify early signs of degradation, allowing for timely interventions to prolong product lifespan.
Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing Processes :With growing environmental concerns, future consumer goods are likely to utilize sustainable materials and manufacturing processes to minimize environmental impact. This could involve the use of recycled materials, bio-based alternatives, and eco-friendly production methods.
The Future of Consumer Durables
In conclusion, the trajectory of consumer durable products is undeniably shifting towards sustainability and durability, marking a departure from the disposable culture of the past. As consumers increasingly prioritize quality, longevity, and environmental responsibility, manufacturers are compelled to innovate and adapt. By emphasizing product longevity, enhancing repairability and upgradability, selecting sustainable materials, improving energy efficiency, and conducting rigorous durability testing, the industry is poised to meet the evolving demands of conscientious consumers. This transition not only benefits the environment by reducing waste and resource consumption but also offers consumers products that deliver greater value, performance, and peace of mind. Embracing these trends offers a promising future where consumer durables contribute to a more sustainable and responsible approach to consumption, ensuring a better world for future generations.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

