Table Of Contents
- Current Adoption
- Cellular IoT Market in the Last Decade
- Surge in IoT Connections
- A Guide to Innovative Cellular IoT Solutions
- Advancements in 5G Technology
- Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M Adoption
- Edge Computing Integration
- Industry-specific Applications
- The Future of Virtual Humans: Opportunities and Challenges
- Restraints on the Road Ahead
- Opportunities in a Dynamic Landscape
- Navigating the Future Landscape
- Future Trends in the Cellular IoT Market
- Gateway to the Future

Sonia Mutreja

Pooja Parvatkar
Cellular IoT: Connecting the World

Businesses have taken a huge leap in terms of technological advancements with the advent of Internet of Things (IoT). As industries have become IoT-enabled, daily operations have become more seamless and connected. Thus, according to Techeconomy, a publication of OPI-MEDIA NETWORKS LIMITED, the total number of cellular IoT connections is estimated to reach around 3 billion by 2023. The article on cellular IoT market will analyze the key trends that drive this industry and how the introduction of 5G technology will shape the future.
Cellular IoT capabilities have been overhauled due to improvements in cellular technology especially 5G network, which exhibits ultra-low latency rates for data transmission rates over high volumes of data along with a wide range of device connections, thus opening new frontiers for real-time industrial automation, smart city solutions, as well as connected vehicle applications. Moreover, narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M technologies are enhancing cellular connectivity for low-power data rate IoT devices, which extend network coverage, improve battery life, and reduce cost, thereby making them suitable for applications such as smart metering and asset tracking.
The industry leaders such as Qualcomm, Huawei, and Ericsson are playing a pivotal role in improving the capabilities of cellular IoT devices. For example, on October 26, 2022, Qualcomm unveiled its state-of-the-art cellular IoT solution at MWC Barcelona 2022. This strategy underlines Qualcomm's commitment to expand the business and accelerate digital transformation across industries.
Current Adoption
Cellular IoT devices are deployed across various industries such as smart cities, agriculture, healthcare, industrial automation, and retail to ease real-time data collection; enable remote monitoring; and facilitate seamless connectivity to improve performance, improve processes, and drive innovation in these sectors. For example, in smart cities, these devices enable intelligent traffic management, waste management, environmental monitoring, and other services through real-time data collection. In agriculture, farmers are using IoT sensors to monitor soil moisture, crop health, and weather with cellular connectivity, enabling farmers to make informed decisions about when to fertilize fields to get optimum yield. Furthermore, healthcare is one of the largest IoT-enabled industries and is a quick adopter of IoT devices such as wearable health devices, patient monitoring systems, and telemedicine systems, which improve patient outcomes. In industries that rely on cellular IoT, factories and warehouses leverage IoT sensors for predictive maintenance, asset monitoring, and supply chain optimization.
The cellular IoT module market experienced a staggering 15-fold growth between 2010 and 2022, reaching an estimated shipment of 2.5 billion modules by the end of 2022, marking an unprecedented expansion in the IoT industry. Throughout this period, significant shifts occurred in both the technological and competitive landscapes, exemplified by a decrease from 82% to 55% in global cellular IoT module shipments by the top five module companies, signifying a profound transformation in market dynamics.
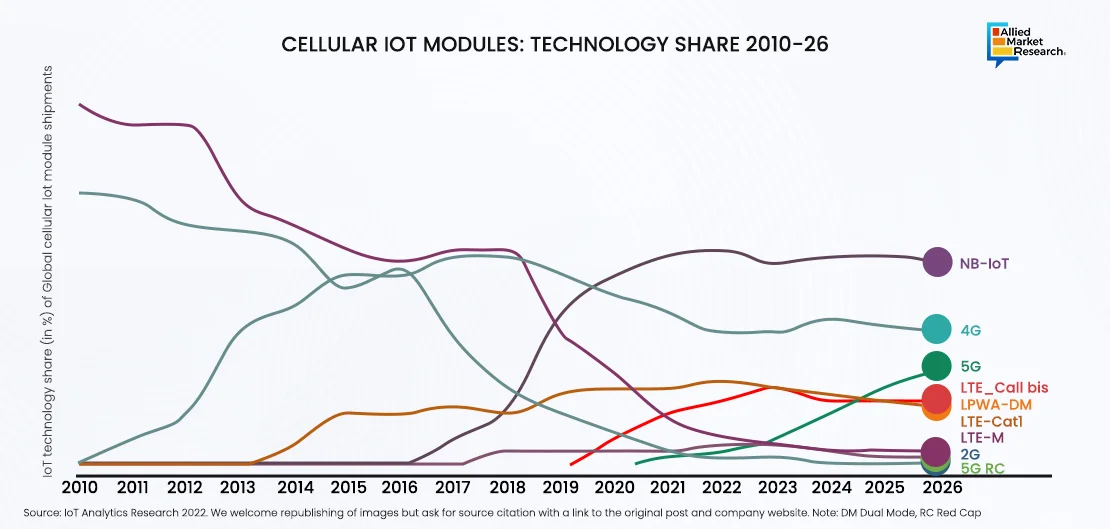
Cellular IoT Market in the Last Decade
The global cellular IoT market is estimated to reach $30 billion by 2032 from $4 billion in 2021. This is attributed to the fact that the technology has been gaining ground since the last decade, driven by advances in cellular technology and widespread adoption of IoT devices. Moreover, surge in demand for connected devices and increase in use of the technology across industries considerably contribute toward the growth of the global market.
The flexibility and connectivity of the technology have made it an asset in a variety of industries, including industrial automation, logistics, and utilities. Its ability to aid in real-time data transmission, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance improves business functions and increase productivity.
As businesses and consumers embrace connected devices and IoT solutions, the demand for technology is expected to increase in the coming years. This growth is expected to be driven by continuous improvements in cellular networks, proliferation of IoT devices, and development of new use cases with increased connectivity across industries.
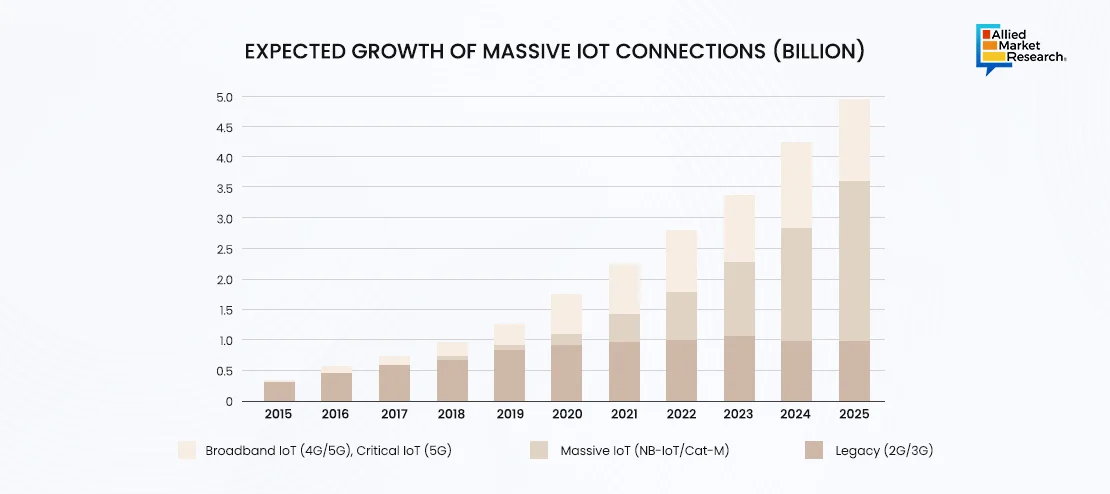
Surge in IoT Connections
From 2015 to 2025, massive IoT connections have witnessed rapid growth due to advancements in connectivity technologies and increase in penetration of IoT-enabled devices, which have led to an unprecedented expansion in the deployment of low-power sensors and devices for diverse applications such as smart cities and industrial automation. On the contrary, broadband IoT has shown steady but significant growth during the same period, fueled by the increasing demand for high-speed connectivity for applications like video surveillance and real-time analytics, facilitated by the deployment of 5G networks and the emergence of edge computing. Legacy IoT technologies have witnessed more modest growth rates compared to massive and broadband IoT, facing challenges related to interoperability and scalability, yet remaining integral in sectors where reliability and compatibility with existing infrastructure are crucial.
A Guide to Innovative Cellular IoT Solutions
The wireless industry is developing innovative solutions to meet the needs of the all-connected world.

Advancements in 5G Technology
The development of 5G technology has brought about a revolution in the landscape of cellular IoT solutions. High speed, reduced latency, and increased capacity enabled by 5G networks enable seamless connection between devices such as sensors and industrial equipment. This facilitates remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, or independent operations across different sectors that depend on real-time data exchange. As 5G is deployed worldwide, there are bound to be endless possibilities for invention in IoT.
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M Adoption
The demand for NB-IoT and LTE-M—two of the most prominent low-power wide-area networking (LPWAN) technologies—is growing within the market. These technologies are tailored to battery-operated gadgets that only require minimal data transfer by extending battery life, expanding network coverage area, as well as decreasing connectivity expenses. In the context of smart meters, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring where effectiveness and longevity are crucial, NB-IoT and LTE-M have become invaluable tools. As industries realize the advantages associated with LPWAN technologies, their rate of acceptance is expected to increase significantly, augmenting the development of the industry. Furthermore, AT&T, an American multinational telecommunications holding company, is planning to expand LTE-M network. AT&T's LTE-M network expansion accelerates the deployment of cellular IoT solutions across various industries.
Edge Computing Integration
The use of edge computing in the context of cellular IoT is changing how data is processed and analyzed. Moreover, edge computing lowers the dependency on centralized cloud resources, which results in faster response times, better security for data, and reduced network traffic. This transition toward edge computing is essential for applications that require real-time insights and decision-making like industrial automation, smart cities, or connected vehicles. As a result of this evolution of edge computing capabilities, the technology will become more agile, energy-efficient, and robust to meet the needs of today’s globally interconnected world. on December 5, 2023, AWS launched its new AWS Wavelength designed to integrate with 5G networks, which enables developers to deploy ultra-low-latency applications, unlocking new possibilities for cellular IoT use cases in areas like autonomous vehicles and smart manufacturing.
Industry-specific Applications
Cellular IoT is driving innovation across different sectors, with customized software applications specifically designed to target problems and challenges. In smart towns, cellular IoT links main infrastructures such as traffic lights, waste disposal facilities, and environmental sensors for data-driven decision-making and optimization of resources. It further supports machinery care in the industrial space by monitoring performance and optimizing production lines for predictive maintenance, thus enhancing efficiency while reducing costs. It enables real-time tracking of shipments and route optimization in connected logistics in addition to inventory control, thereby contributing to supply chain visibility and reliability. Also involved are cellular IoT-based systems that monitor soil conditions, improve irrigation schedules, increase crop yields, allow farmers to make data-driven choices about farming, and maximize productivity. It is in this respect that the technology is driving digitization across all these industries, creating possibilities for growth, efficiency, and sustainability.
The Future of Virtual Humans: Opportunities and Challenges
The growth of the global cellular IoT industry is rapidly driven by the adoption of 5G technology, which offers higher internet speed and lower latency as compared to previous generations. This development allows for easy integration of more kinds of IoT devices, thus resulting in real-time data transfer and strong demand for the technology. Furthermore, the rising need for connected machines across different sectors, including smart cities, industrial automation, and farming is giving impetus to market expansion. With organizations looking forward to streamlining their operations while improving efficiency as well as decision-making processes, the deployment of cellular IoT solutions is increasing substantially. In addition, the advent of LPWAN technologies such as NB-IoT and LTE-M are expanding IoT coverage, especially for battery-operated low data rate devices.

Restraints on the Road Ahead
Although the market witnesses notable growth, security issues regarding IoT devices as well as networks stand as the key deterrent factors of the market. The risk of cyber threats and breaches is growing in tandem with the increasing number of connected devices, which has raised concerns about data privacy and integrity. Moreover, seamless connectivity and integration are being hampered by interoperability issues between various cellular IoT systems. Furthermore, when it comes to deployment, lack of standardized protocols or compatibility among devices produced by different vendors makes it difficult to scale up efforts about deployments. High deployment costs associated with infrastructure upgrades, device procurement, as well as ongoing maintenance present financial challenges for organizations that want to implement the technology. Thus, all these factors are collectively responsible for limited scalability and slow adoption rates of the technology in certain industries.
Opportunities in a Dynamic Landscape
Despite various challenges, there exists fertile ground for innovation, growth, and market penetration of cellular IoT. Edge computing advancements offer significant advantages for enhancing the functionalities of the technology. Investments in research and development are shaping the future direction of IoT technologies, thereby contributing toward more efficient and cost-effective solutions being developed. Moreover, opening new horizons for market penetration and revenue growth through extending cellular IoT into emerging markets is another opportunity that is available to business organizations. In addition, areas like smart cities, healthcare, and agriculture will experience huge demand for IoT solutions as developing regions embrace digital transformation initiatives and infrastructure development projects. Industry players can tap into these markets to unlock new business opportunities, drive innovation, and position themselves effectively in the long run within the realm of the industry.
Navigating the Future Landscape
Despite the challenges that may arise, the cellular IoT market holds significant promise for companies that embrace innovation, collaboration, and adaptability. By proactively addressing security concerns, overcoming interoperability challenges, and prioritizing scalability, businesses can position themselves for success and differentiation in the rapidly evolving market landscape. As technology continues to advance, the technology will play an integral role in shaping the way industries operate and communicate, unlocking new opportunities for growth and transformation.

Future Trends in the Cellular IoT Market
The forthcoming industry will experience game-changing trends that will reshape the sector:
- Advanced Connectivity Solutions: The advent of 5G technology and progress in LPWANs will provide enhanced connectivity options to cellular IoT solutions, thereby allowing real-time data exchange and enabling greater application possibilities across different sectors.
- Edge Computing Integration: By integrating edge computing capabilities, cellular IoT deployments can achieve quicker response times and better processing efficiency of data with decreased latency leading to the adoption of mission-critical IoT applications.
- Industry-specific Solutions: There will be increased demand for sector-specific cellular IoT solutions designed specifically to solve the unique problems faced by smart cities, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing, thereby promoting innovation besides market development.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: Embedding artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into cellular IoT devices and platforms would enable predictive analytics, proactive maintenance, and intelligent decision-making, resulting in improved operational efficiency as well as cost-saving opportunities.
- Data Security and Privacy: With the proliferation of connected devices and data exchange, ensuring robust security measures and data privacy protocols will be paramount, driving investment in cybersecurity solutions and regulatory compliance frameworks.
- Sustainable IoT Solutions: The focus on sustainability and environmental conservation will drive the development of energy-efficient, eco-friendly cellular IoT solutions, fostering responsible deployment practices and minimizing environmental impact.
- Data Security and Privacy: With increase in the number of interconnected gadgets and data communication, there will be a need to ensure strict security measures and protocols for keeping data private. Consequently, this will require substantial investments in cyber security systems as well as regulatory compliance frameworks.
- Sustainable IoT Solutions: Emphasizing sustainability and environmental preservation is expected to stimulate the creation of energy-efficient, environment-friendly cellular IoT solutions that support responsible deployment practices while minimizing environmental effects.
- These transformative trends are set to turn around the market as it prepares for an era when everything will be connected, including intelligent systems, resulting in excellent digital experiences, promoting innovation, as well as meeting changing market requirements.
Gateway to the Future
In conclusion, the cellular IoT market is evolving rapidly due to technological improvements and rising need for connectivity in different sectors. There are considerable opportunities for creativity and prosperity despite some difficulties like safety concerns and a state of compatibility. By assimilating emerging technologies such as 5G, edge computing, and AI together with continuous investments in research and development, cellular IoT is ready to take on a new shape.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

