Table Of Contents

Sonia Mutreja

Koyel Ghosh
Revolutionizing Construction: Unleashing the Power of Robotics for Faster, Safer, and Smarter Building

Throughout history, the way people build things has always been connected to how societies grow and change. Construction has always played a big role in how humans develop. Primitive attempts at shelter, exemplified by the stone circle at Olduvai Gorge dating back 1.8 million years, highlight the early ingenuity in construction.
Advancements during the Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift, introducing mass production techniques and novel materials like cast iron and steel. This era witnessed the rise of more durable and intricate structures, with iconic examples being the Crystal Palace and the Eiffel Tower, showcasing the early utilization of prefabrication methods. The late 19th century Bessemer process further revolutionized construction by making steel production more economical, paving the way for the construction of skyscrapers like the Home Insurance Building in Chicago, considered the world's first skyscraper.
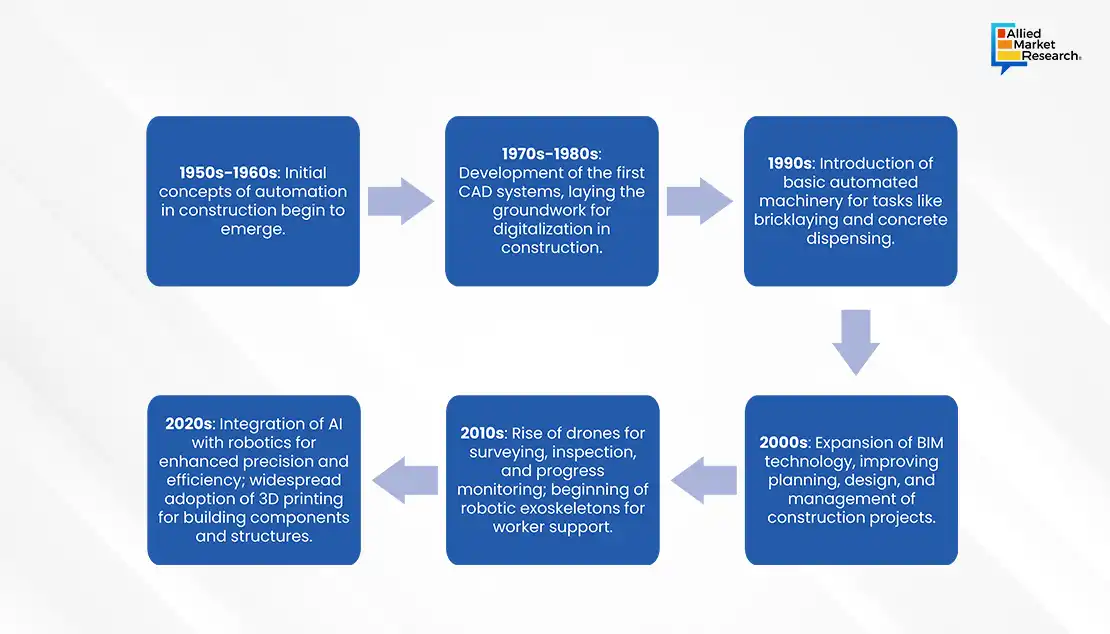
Construction history also reflects an ongoing pursuit of durable materials, transitioning from perishable items to stone, clay, and eventually synthetic materials like plastics and concrete. This journey towards sustainability and the quest for taller and wider structures has been aided by the development of stronger materials and a deeper understanding of their properties.
Today's construction methods are the result of countless innovations and adjustments over many centuries. Moving forward, the industry is ready for more changes ahead, emphasizing sustainability, digital transformation, and the integration of new technologies to meet the evolving needs of society. The integration of robotics into this historical narrative signifies a crucial turning point, promising unprecedented advancements in efficiency, safety, and intelligence in the construction process.
Technology Adoption in the Construction Sector
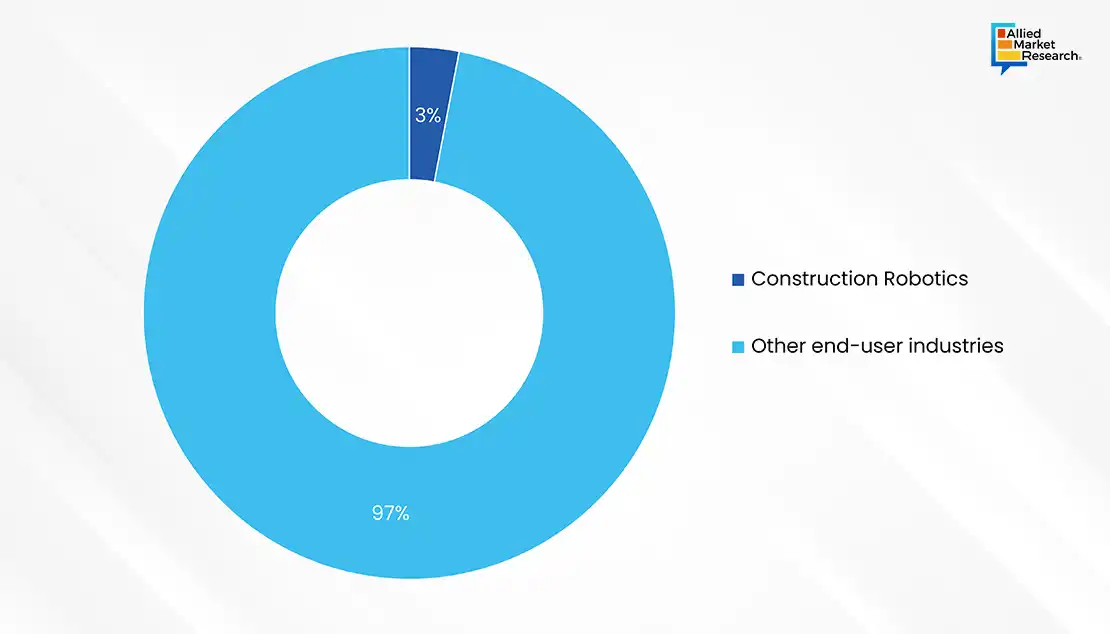
The construction industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the adoption of technology across its various sectors. This shift is not only enhancing efficiency and productivity but also reshaping the industry's future. The advent of the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the industry's digital shift, forcing companies to adopt technologies for remote collaboration, digital site meetings, and electronic order processing. The industry, which has been slow to adopt digital tools, is now quickly embracing collaboration technologies. However, this change is also causing some contractors to struggle, as they deal with fewer projects and tougher competition for bids. For instance, the global construction robotics market was valued at $3,490.1 million in 2023 which is approximately just 3% of the global robotics market.
The construction sector is also witnessing the emergence of marketplaces for materials, equipment, and labor procurement. These digital marketplaces are streamlining the supply chain, improving project transparency, and enhancing productivity and profitability. Just like how retail has changed over time, the construction industry is evolving too. The use of prefabricated components is becoming more popular, and this trend is expected to keep growing. In the construction industry, different companies embrace technology at different levels. Some are quick to adopt tools like Building Information Modeling, drones, and mobile platforms. On the other hand, some companies are slower, especially when it comes to advanced technologies like cognitive machine learning, robotics, and artificial intelligence. This disparity highlights both the potential for significant productivity gains and the challenges of overcoming barriers to technology adoption??.
The construction industry is on the verge of a digital revolution, using technology to tackle issues like productivity, safety, labor shortages, and collaboration. Companies are now working to incorporate new technologies, embrace digital platforms, and utilize data analytics and machine learning to boost efficiency and foster growth in the construction sector.
How Robotics is Making a Difference
Robotics is increasingly becoming a pivotal part of the construction industry, offering solutions to long-standing challenges such as labor shortages, safety hazards, and productivity issues. One of the groundbreaking innovations in this field is the development of robots like TyBOT, which automates the repetitive and physically demanding task of tying rebar. This robot can tie intersections much faster than human workers, significantly enhancing productivity and reducing physical strain on workers. The adoption of TyBOT points towards a future where robotics not only complement but enhance human efforts on construction sites??. Recently in September 2023, Samsung C&T Corp., a South Korean construction and engineering company, invested 15 billion won ($11.2 million) in Robotics Construction Technologies (Robocon), becoming its largest shareholder. Samsung C&T aims to leverage Robocon's automated rebar processing robot, Aron, for synergy in construction projects. The investment, structured as a limited partnership through Samsung Venture Investment Corp., aligns with Samsung C&T's focus on internal construction robot development, showcasing its commitment to innovative solutions in the construction industry. Last month, Samsung C&T, Robocon, and Hyundai Engineering & Construction signed a memorandum of understanding for technical cooperation, showcasing a collaborative effort to expand the construction sector's technological ecosystem.
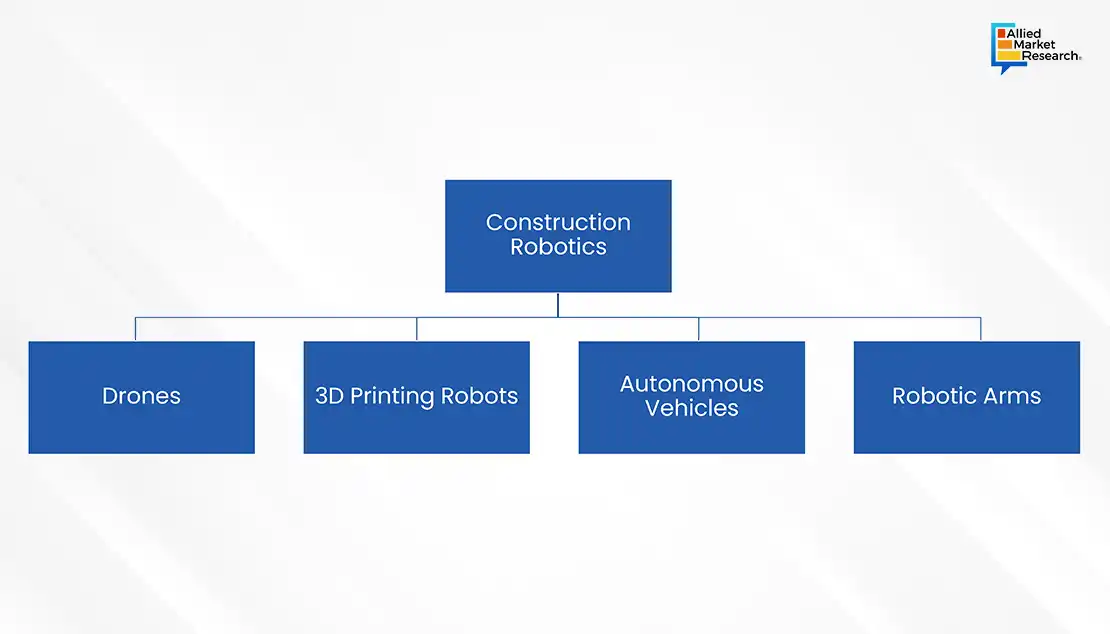
Moreover, the construction industry is seeing the introduction of versatile robots capable of performing a variety of tasks, from 3D printing of buildings to automated material handling and assembly. For instance, cartesian robots are now being used for 3D printing in construction, enabling the efficient and rapid production of homes and other structures. This new method of building has the potential to completely transform the industry. Collaborative robots, or cobots, represent another significant advancement, designed to work alongside humans to perform tasks that are either too laborious or delicate for human workers alone. Humans and robots working together are anticipated to address labor shortages in the industry. Robots can handle routine, low-skilled tasks, freeing up human workers to concentrate on more intricate responsibilities. Furthermore, drones are revolutionizing the construction sites by offering real-time updates, conducting aerial inspections, and enhancing site security with less need for human intervention. This technological adoption highlights a shift towards more efficient, safe, and cost-effective project management and execution??. For example, in February 2024, US technology company Trimble announced a strategic partnership with DroneDeploy, a cloud-based software solution for drones, to enhance drone mapping capabilities. Trimble's Applanix POSPac Cloud, a post-processed kinematic (PPK) GNSS positioning service, is now seamlessly integrated with DroneDeploy's reality-capture platform through collaboration. This integration is anticipated to provide centimetre-level accuracy, streamlining workflows for DroneDeploy users in construction, topography, and temporal analysis sectors. The partnership aims to deliver high-precision drone maps effortlessly, enabling users to gain insights into projects with increased confidence and efficiency.
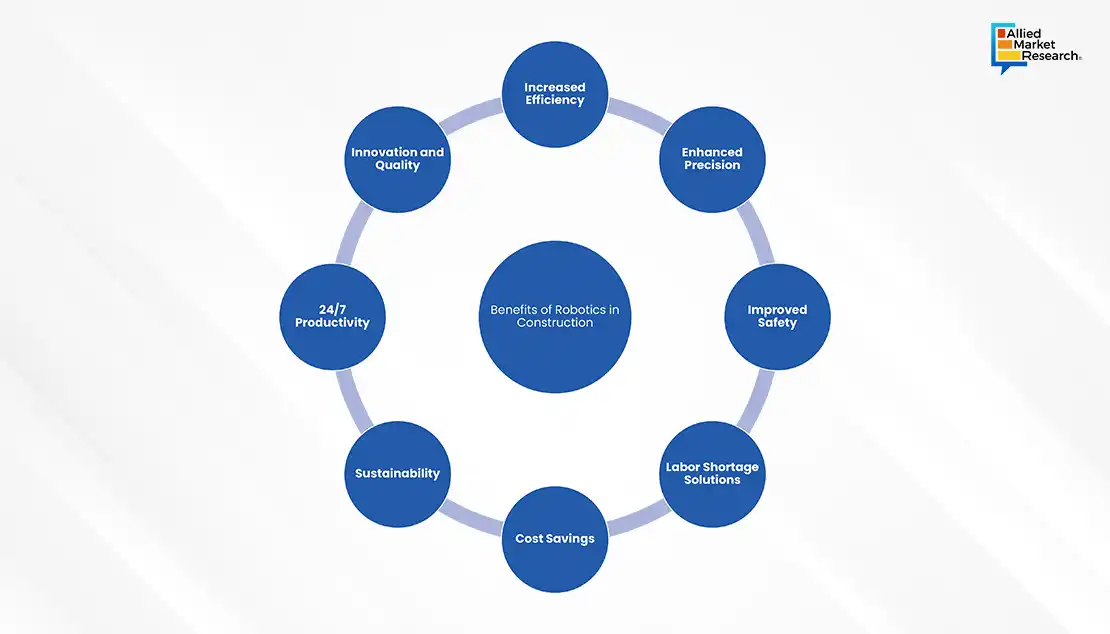
The integration of robotics into construction is not about replacing human workers but rather about augmenting their capabilities, ensuring safety, and improving overall project efficiency. The construction industry is evolving with innovations that promise a future where humans and robots work together to redefine how projects are done. This collaboration aims for faster, safer, and higher-quality construction practices.
Case Study Highlighting the Use of Robotics
Overview: The growing demand for cost-effective prefabricated homes has necessitated streamlined manufacturing processes. Builder Rehkemper & Son, grappling with labor shortages and cumbersome materials, engaged SCADAware, a Kawasaki integrator, to automate the prefabricated wall assembly. The goal was to enhance competitiveness and minimize reliance on human labor.
Challenges: Rehkemper's manual process involved attaching oriented strand board (OSB) sheathing to prefabricated walls, a task complicated by the unwieldy nature of OSB and the imprecise characteristics of wood. Precision in nailing the OSB panels to the hidden wooden studs and beams was crucial.
Solution: SCADAware crafted a unique system with four Kawasaki BX250L robots mounted on Güdel TrackMotion Floor-3 rails. These robots adeptly handled the intricate task of affixing OSB panels to wall frames and creating openings for windows and doors. Custom software guided the robots based on the electronic wall design, ensuring accurate placement of nails and cuts. A motorized table and servo-controlled fingers were deployed to align and straighten wooden studs, compensating for warping.
Two pairs of robots moved along the Güdel tracks, covering the entire table length. The robots exhibited flexibility, seamlessly switching tooling to carve openings while others removed cut sheathing. The reliability and flexibility of Kawasaki robots, recognized for their patented hollow-arm structure, high payload capacity, and advanced motion control technology, proved ideal for this labor-intensive process.
Results: The automated system implementation yielded noteworthy outcomes:
- Efficiency Boost: Throughput increased by a minimum of 25%, with potential for further optimization.
- Labor Cost Reduction: The system addressed the labor shortage, offering a reliable and consistent solution.
- Competitive Edge: Rehkemper & Son now competes more effectively, providing quicker assembly at a lower cost.
- Increased Linear Footage: The system enhanced daily linear footage production by 25%, with anticipated efficiency reaching 35-40%.
- Reduced Reliance on Human Labor: Automation resulted in less downtime, heightened precision, and lowered injury risks.
Conclusion: The collaboration between Rehkemper & Son, SCADAware, Kawasaki, and Güdel yielded a groundbreaking automated assembly system for prefabricated homes. The integration of advanced robotics and precision technology not only addressed challenges posed by cumbersome materials but also significantly improved efficiency, reduced labor costs, and heightened competitiveness in the prefabricated housing industry. This case study's success underlines how automation can transform the construction industry, serving as an example for other manufacturers looking for creative solutions to similar problems.
Future Perspective about the Market
The construction industry is witnessing significant changes, especially with the widespread adoption of robotics and artificial intelligence. This transformation aims to deal with labor shortages and boost efficiency. Key advancements include using AI for workforce training, deploying robots for various construction tasks, and exploring the possibilities of 3D printing. These advancements also intend to optimize processes, improve safety, and potentially revolutionize the industry by introducing new building materials and methods, including mass timber and prefabrication.
Allied Market Research explores the dynamic field of robotics in construction, offering detailed analyses of technological innovations, market trends, and policy frameworks shaping the industry. Our comprehensive reports aim to empower stakeholders with insights into robotics' role in enhancing construction efficiency, safety, and sustainability. This knowledge aids businesses in leveraging robotics technology, seizing growth opportunities, and driving the sector toward smarter, safer, and faster building solutions.

